* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
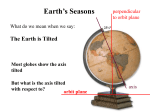
Astronomy Earth and Space Big Bang Theory theory that the universe formed in an instant, billions of yrs. ago, in an enormous explosion Edwin Hubble •Hubble discovered that galaxies are moving away from us and each other. •He discovered the relationship between distance to a galaxy and its speed. Hubble’s Law The farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us. Hubble’s Revolution Video http://www.discovery.com/tv-shows/other-shows/videos/how-the-universe-works-hubbles-revolution/ The galaxies in the universe are like the raisins in rising bread dough. How does rising raisin bread dough resemble the expanding universe? Proof of Hubble’s Law •Cosmic Background Radiation – faint radiation glow that comes from all directions in space •This is leftover thermal radiation from the Big Bang. Once the universe was formed, individual bodies formed in space and began to move in relation to each other… Kepler’s Law 1. Planets are orbiting the Sun in the path of an ellipse. LAW OF ELLIPSES Kepler’s Law 2. Planets move faster when they are closer to the sun and slower when they are farther away. Kepler’s Law 3. The farther away a planet is the longer it takes to go around the sun. Rotation vs Revolution How many days does it take for the Earth to spin on its axis Rotation (spin) = 24 hrs How many days does it take for the Earth to orbit the sun? Revolution (orbit) = 365 days Astronomy Booklet Work Time! • 30 minutes The Electromagnetic Spectrum •The entire range of wavelengths or frequencies of electromagnetic radiation extending from Gamma Rays to the longest Radio Waves. •Includes Visible Light. What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum? What can we use visible light for?? •We use the visible light spectrum to help us determine what direction things are moving in SPACE! RED SHIFT •When an object is moving AWAY, the light is shifted to the RED end of the spectrum. •The wavelength gets longer. BLUE SHIFT •When an object is moving CLOSER, the light is shifted to the BLUE end of the spectrum. •The wavelength gets shorter. Red Shift and Blue Shift Types of Heat Transfer • Conduction – Direct contact between two materials • Ex. Stove and pot • Convection – Interaction of molecules • Usually fluids or gases • Radiation – movement of heat waves. • This is how we get heat from the sun. Why do we have seasons? •The Earth is tilted on its axis at a 23.5o angle. •The Earth’s poles are either tilted AWAY from the sun or TOWARD the sun. Why do we have seasons? •When the sun’s energy is spread over a larger area, the heat must be dispersed. •When the sun’s energy heat is more concentrated, that area will become hotter. Important Dates to know SOLSTICE •Winter Solstice – December 21st. Shortest day of the year •Summer Solstice – June 21st Longest day of the year EQUINOX • Fall (Autumnal) Equinox – September 21st. Equal amounts of day and night • Spring (Vernal) Equinox – March 21st. Equal amounts of day and night Winter Solstice December 21st Vernal Equinox March 21st Winter Solstice December 21st Vernal Equinox March 21st Summer Solstice June 21st Winter Solstice December 21st Vernal Equinox March 21st Summer Solstice June 21st Winter Solstice December 21st Autumnal Equinox September 21st Phases of the Moon •Waxing = getting bigger •Waning = getting smaller •Crescent = < half lit •Gibbous = > half lit •1/4 (First/Third) = half lit P H A S E S O F T H E M O O N Spectroscope Lab Due by the end of the period!! Tides – Spring Tide A Spring Tide occurs when the moon is either full or new. The gravitational pull of the moon and sun are combined to make high tide even higher and low tide even lower. Tides – Neap Tide A Neap Tide occurs when the moon is in its quarter phases. The moon, Earth, and sun for a right angle. There is a smaller difference between high tide and low tide. Graph of Spring Tide vs. Neap Tide Eclipses – Lunar Eclipse When a Full Moon is being blocked by the Earth. Eclipses – Solar Eclipse When a New Moon is being blocked by the sun.