* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motions and Their Effects
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
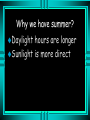
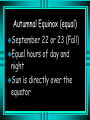
Motions and Their Effects Seasonal Change and Planetary Movement Seasons The tilt of the Earth’s axis is 23.5 degrees This tilt causes seasonal changes Winter Solstice December 21 or 22 North Pole in darkness for 24 hours South Pole has continual daylight Sun is at its lowest point Why do we have winter? Fewer hours of sunlight during the day North pole is tilted away from the sun Light rays are less direct Vernal Equinox (equal) March 20 or 21 (Spring) Sun is directly over the equator Every part of the Earth experiences equal hours of day and night Summer Solstice June 20 or 21 South Pole in Darkness North Pole in Light Sun appears at its highest point Why we have summer? Daylight hours are longer Sunlight is more direct Autumnal Equinox (equal) September 22 or 23 (Fall) Equal hours of day and night Sun is directly over the equator Questions How many months apart are the solstices and the equinoxes? How is the vernal equinox similar to the autumnal equinox? Questions What are the differences between the summer and the winter solstices? Why do we have changes in seasons during the year? Kepler Each planet moves in an elliptical orbit (stretched out circle) Planets speed up their orbit as they approach the Sun and slow down as they move away from it Questions What was Kepler’s contribution to the understanding of planetary movement? TRANSPARENCIES