Hungry Young Stars: A New Explanation for the FU Ori Outbursts
... • We provide an explanation for the origin of FU Ori bursts. • A young star devours embryos that form in the disk, resulting in colossal bursts of luminosity. This process repeats as long as nebular material rains onto the disk. • The new feature in our model is the self-consistent formation and evo ...
... • We provide an explanation for the origin of FU Ori bursts. • A young star devours embryos that form in the disk, resulting in colossal bursts of luminosity. This process repeats as long as nebular material rains onto the disk. • The new feature in our model is the self-consistent formation and evo ...
UGS303, Extraterrestrial Life: REVIEW FOR FIRST TEST
... energy in your explanation, as well as the different types of forces. ...
... energy in your explanation, as well as the different types of forces. ...
Stellar Notes
... On our test we will be diagraming the life cycle of a star, explaining the EM spectrum and how astronomers ID stars. ...
... On our test we will be diagraming the life cycle of a star, explaining the EM spectrum and how astronomers ID stars. ...
ASTR 1120H – Spring Semester 2010 Exam 2 – Answers The
... have been ionized by UV radiation from nearby hot stars. The hydrogen nuclei (i.e., protons) and electrons recombine in excited energy states and when the electron cascades back down toward the ground state, the transition from n = 3 to n = 2 releases Hα photons (i.e., red light). Hot stars are requ ...
... have been ionized by UV radiation from nearby hot stars. The hydrogen nuclei (i.e., protons) and electrons recombine in excited energy states and when the electron cascades back down toward the ground state, the transition from n = 3 to n = 2 releases Hα photons (i.e., red light). Hot stars are requ ...
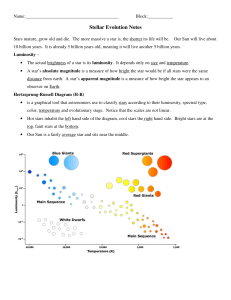
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
... A galaxy is a group of hundreds of billions of stars that are relatively close to each other. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, contains over 100 billion stars. The universe has more than 100 billion galaxies with each galaxy containing an average of 100 billion stars. ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 •
... Extinction and Reddening We can quantify the amount of light absorbed by a cloud. ...
... Extinction and Reddening We can quantify the amount of light absorbed by a cloud. ...
Nebulae - Innovative Teachers BG
... Planetary Nebulae Planetary nebulae in their Photography by Emil Ivanov physical nature are different from nebulae discussed above and being essentially gas-dust clouds. Planetary nebula is an evolution phase of stars with masses 7-8 solar masses and greater. When a star forward in its evolution, l ...
... Planetary Nebulae Planetary nebulae in their Photography by Emil Ivanov physical nature are different from nebulae discussed above and being essentially gas-dust clouds. Planetary nebula is an evolution phase of stars with masses 7-8 solar masses and greater. When a star forward in its evolution, l ...
AST101_lect_13
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) ...
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) ...
Review 1 Solutions
... 1. The night sky is mostly dark because we can only see stars within about 13.8 billion light years of us. T 2. The “rotation curves” that plot stars’ orbital speeds versus their distance from their galaxy’s center initially surprised astronomers by suggesting that large amounts of invisible matter ...
... 1. The night sky is mostly dark because we can only see stars within about 13.8 billion light years of us. T 2. The “rotation curves” that plot stars’ orbital speeds versus their distance from their galaxy’s center initially surprised astronomers by suggesting that large amounts of invisible matter ...
AST101 Lecture 13 The Lives of the Stars
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) ...
... • Stars generate luminosity through fusion of H into He • The lifetime of a star is proportional to the amount of fuel it has (mass) divided by the rate at which it expends the fuel (luminosity) ...
Document
... Helium and into other elements, this creates a release of energy and therefore increased radiation pressure that is called thermal expansion. As the core runs out of energy, the star begins to expand and near the end of it’s life will either collapse into a dwarf due to gravity, or will supernova du ...
... Helium and into other elements, this creates a release of energy and therefore increased radiation pressure that is called thermal expansion. As the core runs out of energy, the star begins to expand and near the end of it’s life will either collapse into a dwarf due to gravity, or will supernova du ...
Chapter 15 Stars, Galaxies
... 8. d 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a. Protostar b. Supergiant c. Supernova d. Black Hole e. Stars that are the most massive become black holes. Stars that are less massive but still high-mass stars become neutron stars. f. They all start out as a part of nebulas that contract to form protostars. g. Low-mass ...
... 8. d 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a. Protostar b. Supergiant c. Supernova d. Black Hole e. Stars that are the most massive become black holes. Stars that are less massive but still high-mass stars become neutron stars. f. They all start out as a part of nebulas that contract to form protostars. g. Low-mass ...
Our Community`s Place Among the Stars
... the leftover core of a massive star after a supernova Black holes create such a large gravitational pull that not even light can escape ...
... the leftover core of a massive star after a supernova Black holes create such a large gravitational pull that not even light can escape ...
N.2 Formation of Mass
... • Helium forms -- Eventually two protons and two neutrons were attracted to each other via strong force and helium nuclei were formed. • Lithium forms: Three protons & three neutrons come together become lithium ...
... • Helium forms -- Eventually two protons and two neutrons were attracted to each other via strong force and helium nuclei were formed. • Lithium forms: Three protons & three neutrons come together become lithium ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Small, rapidly rotating objects Can’t be white dwarfs; must be neutron stars ...
... Small, rapidly rotating objects Can’t be white dwarfs; must be neutron stars ...
S E N S ` 2 0 0 6
... remain. However, the ice covered dust grains are able to sustain further away from the protostar due to a decreased absorption in thermal energy. Dust particles within the solar nebula will often coalesce into matter conglomerates referred to as planetesimals. The formation of the planetisimals is a ...
... remain. However, the ice covered dust grains are able to sustain further away from the protostar due to a decreased absorption in thermal energy. Dust particles within the solar nebula will often coalesce into matter conglomerates referred to as planetesimals. The formation of the planetisimals is a ...
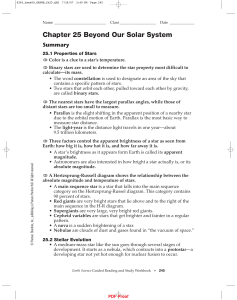
Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System
... dwarf, and finally, a black dwarf. • White dwarfs are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. • Neutron stars, which are smaller and more massive than white dwarfs, are thought to be the remnants of supernova events. • A spinning neutron star that appears to give off pulses of radio waves is ...
... dwarf, and finally, a black dwarf. • White dwarfs are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. • Neutron stars, which are smaller and more massive than white dwarfs, are thought to be the remnants of supernova events. • A spinning neutron star that appears to give off pulses of radio waves is ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... • any object 15 to 75 times the mass of Jupiter • the object would not have been able to sustain fusion like a regular star - called "failed stars" • all are parts of a binary system. (two stars orbit around one another) • possible that brown dwarfs represent a lot of the mass in the universe ...
... • any object 15 to 75 times the mass of Jupiter • the object would not have been able to sustain fusion like a regular star - called "failed stars" • all are parts of a binary system. (two stars orbit around one another) • possible that brown dwarfs represent a lot of the mass in the universe ...
Questions for The Elements: Forged in Stars
... 2. What percent of each of these two elements do they have? 3. What happens to Hydrogen atoms in a star’s core? 4. For about what percent of a star’s life does it do this? 5. What happens when a star runs out of Hydrogen to use as fuel for fusion? 6. If you fuse three Helium atoms together, what ele ...
... 2. What percent of each of these two elements do they have? 3. What happens to Hydrogen atoms in a star’s core? 4. For about what percent of a star’s life does it do this? 5. What happens when a star runs out of Hydrogen to use as fuel for fusion? 6. If you fuse three Helium atoms together, what ele ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.