The Death of Stars - Mounds Park Academy Blogs
... • This is a picture of Supernova 1987a seen in the Large Magellanic Cloud, Feb. 24, 1987 ...
... • This is a picture of Supernova 1987a seen in the Large Magellanic Cloud, Feb. 24, 1987 ...
Earth in the Universe
... • When is it fastest? • When is it slowest? • Revolution- the time it takes a planet to go all the way around the sun. Explain how a planet’s distance from the sun determines the speed of a ...
... • When is it fastest? • When is it slowest? • Revolution- the time it takes a planet to go all the way around the sun. Explain how a planet’s distance from the sun determines the speed of a ...
Solar System Summary Sheet File
... Gas clouds in space, called nebulae, are mainly made up of Hydrogen gas and some Helium gas and dust particles. Gravitational forces acting between all the particles caused them to pull towards each other and clump together. As the particles are forced to move, due to gravitational forces, the ...
... Gas clouds in space, called nebulae, are mainly made up of Hydrogen gas and some Helium gas and dust particles. Gravitational forces acting between all the particles caused them to pull towards each other and clump together. As the particles are forced to move, due to gravitational forces, the ...
Chapter20
... •After helium burning begins, a star has two sources of energy, hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core and helium fusion in the core •The core of the star becomes rich in carbon and oxygen nuclei, and the star's surface temperature goes up to become a horizontal branch star •Stars with masses gr ...
... •After helium burning begins, a star has two sources of energy, hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core and helium fusion in the core •The core of the star becomes rich in carbon and oxygen nuclei, and the star's surface temperature goes up to become a horizontal branch star •Stars with masses gr ...
Due: January 14, 2014 Name: White dwarfs are “has been
... Describe the energy source that causes a protostar to shine. How does this source differ from the energy source inside a main-sequence star? ...
... Describe the energy source that causes a protostar to shine. How does this source differ from the energy source inside a main-sequence star? ...
Study Guide: Chapters 32-‐34 FROSH CHAPTER 32 1. What is
... 18. A star somewhat larger than our Sun produces more heat as it contracts. This star will then fuse _____ into heavier elements. ...
... 18. A star somewhat larger than our Sun produces more heat as it contracts. This star will then fuse _____ into heavier elements. ...
EM Spectrum Notes 2015-2016
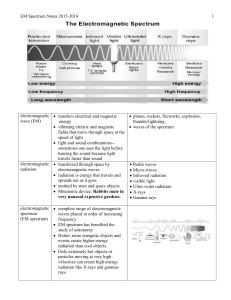
... to gather and focus light To study the size, composition, and movement of stars and galaxies They make distant objects appear closer and brighter. To find black holes and map galactic centers Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze t ...
... to gather and focus light To study the size, composition, and movement of stars and galaxies They make distant objects appear closer and brighter. To find black holes and map galactic centers Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze t ...
Stars Study Guide KEY
... Originally, the universe was tiny, hot, and dense. (Everything was compressed together into a small ball.) Then, an enormous explosion threw matter in all directions. (The matter eventually formed everything that we now see.) 18. What evidence is used to support the theory? (Tell two) Galaxies are s ...
... Originally, the universe was tiny, hot, and dense. (Everything was compressed together into a small ball.) Then, an enormous explosion threw matter in all directions. (The matter eventually formed everything that we now see.) 18. What evidence is used to support the theory? (Tell two) Galaxies are s ...
Outline of the Course - UH Institute for Astronomy
... for example, the protostars. The objects that are the remains of stars that have ‘died’, for example, the neutron stars, or the white dwarfs. A star is ‘dead’ after it had stopped generating energy through nuclear fusion. ...
... for example, the protostars. The objects that are the remains of stars that have ‘died’, for example, the neutron stars, or the white dwarfs. A star is ‘dead’ after it had stopped generating energy through nuclear fusion. ...
Stars - Moodle
... High mass stars • After the main sequence, stars with a mass much greater than the sun can burn and create larger and larger elements • When it gets to iron, it takes too much energy to create other elements so it collapses • This causes a supernova, this is when heavier elements are made ...
... High mass stars • After the main sequence, stars with a mass much greater than the sun can burn and create larger and larger elements • When it gets to iron, it takes too much energy to create other elements so it collapses • This causes a supernova, this is when heavier elements are made ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... One major category is core-collapse supernovae, where a very massive star becomes unstable and explodes. The most mysterious of these are known as Type IIb. Theory and computational simulations suggested that some may be stars that have entered the Wolf-Rayet phase of their final existence. In Wolf- ...
... One major category is core-collapse supernovae, where a very massive star becomes unstable and explodes. The most mysterious of these are known as Type IIb. Theory and computational simulations suggested that some may be stars that have entered the Wolf-Rayet phase of their final existence. In Wolf- ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram – Study Guide
... 13. Planetary nebulae are about the size of __Earth (planets)__ . 14. Neutron stars are about ___12__ miles in diameter. 15. The MOST massive of stars live (the longest or the shortest) lives. 16. Supernovas are produced by the explosion of _super massive__ stars. The remaining star is either a _ne ...
... 13. Planetary nebulae are about the size of __Earth (planets)__ . 14. Neutron stars are about ___12__ miles in diameter. 15. The MOST massive of stars live (the longest or the shortest) lives. 16. Supernovas are produced by the explosion of _super massive__ stars. The remaining star is either a _ne ...
Characteristics of Stars
... 1. On the above diagram, locate and label the main sequence, white dwarfs, red giants, and supergiants. ...
... 1. On the above diagram, locate and label the main sequence, white dwarfs, red giants, and supergiants. ...
Stars & Galaxies
... Edwin Hubble – made discovery that distant stars and galaxies are receding from the Earth in all directions. This implies that the universe is still expanding. Planetsimals are aggregations of gas and dust which may be several hundred kilometers in diameter. Earth is believed to have been formed by ...
... Edwin Hubble – made discovery that distant stars and galaxies are receding from the Earth in all directions. This implies that the universe is still expanding. Planetsimals are aggregations of gas and dust which may be several hundred kilometers in diameter. Earth is believed to have been formed by ...
Variable and Binary Stars
... Common in globular clusters – Spectral type F2-A2, yellow or white giant – Population II (as one would expect in a globular cluster) ...
... Common in globular clusters – Spectral type F2-A2, yellow or white giant – Population II (as one would expect in a globular cluster) ...
Pistol Star - University of Dayton
... • The big bang was initially suggested because it explains why distant galaxies are traveling away from us at great speeds. The theory also predicts the existence of cosmic background radiation (the glow left over from the explosion itself). • The Big Bang Theory received its strongest confirmation ...
... • The big bang was initially suggested because it explains why distant galaxies are traveling away from us at great speeds. The theory also predicts the existence of cosmic background radiation (the glow left over from the explosion itself). • The Big Bang Theory received its strongest confirmation ...
Molecular Line Emission in Star
... The Doppler effect is the relationship between an observed frequency and the radial velocity of the emitting source. Velocities are usually calculated respect to the Local Standard of Rest (LSR), an ideal point in rotation around the Galactic centre as far as the Sun. The relationship between veloci ...
... The Doppler effect is the relationship between an observed frequency and the radial velocity of the emitting source. Velocities are usually calculated respect to the Local Standard of Rest (LSR), an ideal point in rotation around the Galactic centre as far as the Sun. The relationship between veloci ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.