Star - Astrophysics
... around the forming star,potentially detectable as an infra-red source. We may also observe bipolar molecular outflows from young stellar objects (YSOs). Denser knots in these outflows are called Herbig-Haro objects. Once the surrounding gas and dust is burned off we see a T Tauri star. [Fig. 59:Infr ...
... around the forming star,potentially detectable as an infra-red source. We may also observe bipolar molecular outflows from young stellar objects (YSOs). Denser knots in these outflows are called Herbig-Haro objects. Once the surrounding gas and dust is burned off we see a T Tauri star. [Fig. 59:Infr ...
To the Stars - LBlackwell
... are great enough, nuclear fusion begins and a star is born. A star typically exists for millions or even billions of years, until the gradual build up of heavy elements in the star's centre causes the core to collapse. When the core collapses, the star explodes. This is called a supernova. The rema ...
... are great enough, nuclear fusion begins and a star is born. A star typically exists for millions or even billions of years, until the gradual build up of heavy elements in the star's centre causes the core to collapse. When the core collapses, the star explodes. This is called a supernova. The rema ...
Set 1
... exponential decay from an initial burst, viz: (t) exp (-t / ) where is some time constant. If the IMF (M) is invariant, obtain an expression for the observed number of stars of a given mass at time t in terms of its main sequence lifetime. Comment briefly on the differences you would expect ...
... exponential decay from an initial burst, viz: (t) exp (-t / ) where is some time constant. If the IMF (M) is invariant, obtain an expression for the observed number of stars of a given mass at time t in terms of its main sequence lifetime. Comment briefly on the differences you would expect ...
History of the Universe and Solar System
... traveling longer than they actually have. Thus the estimates of 14-18 BY, with 14 BY being the current choice of most physicists/astronomers. Observations of pulsating Cepheid variable stars in remote galaxies allowed Hubble astronomers to conclude the universe is roughly 13.7 billion years old. ...
... traveling longer than they actually have. Thus the estimates of 14-18 BY, with 14 BY being the current choice of most physicists/astronomers. Observations of pulsating Cepheid variable stars in remote galaxies allowed Hubble astronomers to conclude the universe is roughly 13.7 billion years old. ...
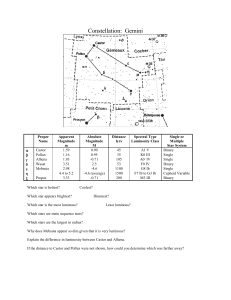
Gemini
... several yellow and orange giants of spectral type late G to early K). Its hottest main sequence star is given as of spectral class B3 (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), and its Trumpler classification as III,3,r by all sources. It is approaching us at 5 km/sec. Even the naked eye finds this cluster easily near ...
... several yellow and orange giants of spectral type late G to early K). Its hottest main sequence star is given as of spectral class B3 (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), and its Trumpler classification as III,3,r by all sources. It is approaching us at 5 km/sec. Even the naked eye finds this cluster easily near ...
Fulltext PDF
... James Jeans proposed gravitational collapse as the mechanism for formation of stars. The conditions for this to take place was that the GMC is cold and dense. As the core gains mass, material accretes on to it, forming a disc. When the temperature of the core rises to 106 K, nuclear fusion begins an ...
... James Jeans proposed gravitational collapse as the mechanism for formation of stars. The conditions for this to take place was that the GMC is cold and dense. As the core gains mass, material accretes on to it, forming a disc. When the temperature of the core rises to 106 K, nuclear fusion begins an ...
Space The Life of a Star
... and it is colored white. Once it cools down further, the star becomes a black dwarf. Now, the star is finished with its life cycle. High-mass stars explode after their red giant stage. If the star is massive enough, it will eventually become a black hole. Other high-mass red giants may become neutro ...
... and it is colored white. Once it cools down further, the star becomes a black dwarf. Now, the star is finished with its life cycle. High-mass stars explode after their red giant stage. If the star is massive enough, it will eventually become a black hole. Other high-mass red giants may become neutro ...
Stellar Evolution Guiding Questions Stars Evolve
... • In low-mass star, the compressed core is not an ideal gas, instead it is in an electron-degeneracy state • Electron-degeneracy: the electrons are so closely packed that they can not be further compressed. The core of a lowmass star becomes eventually being supported by degenerate-electron pressure ...
... • In low-mass star, the compressed core is not an ideal gas, instead it is in an electron-degeneracy state • Electron-degeneracy: the electrons are so closely packed that they can not be further compressed. The core of a lowmass star becomes eventually being supported by degenerate-electron pressure ...
Chapter 19 I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B
... A. Sun is our closest star B. Everything revolves around the Sun C. Planets and distant stars are visible in the night sky D. Earth is part of Solar System E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition ...
... A. Sun is our closest star B. Everything revolves around the Sun C. Planets and distant stars are visible in the night sky D. Earth is part of Solar System E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to the Earth. 2. True definition ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... drive faster fusion rates and created higher luminosities. The higher luminosities “burn” mass faster and the star will then “burn” through its core reserves of hydrogen faster. Low mass stars have slower fusion rates because the fusion rate is slower due to the lower central pressure of these low m ...
... drive faster fusion rates and created higher luminosities. The higher luminosities “burn” mass faster and the star will then “burn” through its core reserves of hydrogen faster. Low mass stars have slower fusion rates because the fusion rate is slower due to the lower central pressure of these low m ...
Astronomy 21 – Test 2 – Answers
... silhouettes does not earn points). (a) Dust will get heated by proto-stars that are inside those dark clouds. The temperatures of the dust may rise to a few hundred degrees Kelvin. Warm dust grains then emit the same radiation as any solid or dense bodies do – they emit black body radiation that pea ...
... silhouettes does not earn points). (a) Dust will get heated by proto-stars that are inside those dark clouds. The temperatures of the dust may rise to a few hundred degrees Kelvin. Warm dust grains then emit the same radiation as any solid or dense bodies do – they emit black body radiation that pea ...
The Temperatures of Stars
... began improving on the system that Fleming had developed while also recording more stellar spectra and classifying them by eye. Cannon discovered a new sequence that simplified the lettering to O B A F G K M. This is the system ...
... began improving on the system that Fleming had developed while also recording more stellar spectra and classifying them by eye. Cannon discovered a new sequence that simplified the lettering to O B A F G K M. This is the system ...
Stars
... Milky Way but no one knows the exact answer. Scientists predict that there are between 200 and 400 billion stars in our Milky Way. That’s a lot of stars! ...
... Milky Way but no one knows the exact answer. Scientists predict that there are between 200 and 400 billion stars in our Milky Way. That’s a lot of stars! ...
PART 3 Galaxies
... – Younger, blue, “Population I” stars were found mostly in the disks and spiral arms. Typically less than a few billion years old; Follow circular orbits in the galactic plane – Older, red, “Population II” stars were found mostly in the halo and ...
... – Younger, blue, “Population I” stars were found mostly in the disks and spiral arms. Typically less than a few billion years old; Follow circular orbits in the galactic plane – Older, red, “Population II” stars were found mostly in the halo and ...
Document
... (Early Molecular Galaxies, EMGs) • Dense molecular Gas as traced by HCN emission is a star formation rate indicator. The mass of dense molecular gas is the key to understanding the star formation rate • HCN observations at low and high z. • A new Star Formation Law HCN Observations: Solomon, Downes ...
... (Early Molecular Galaxies, EMGs) • Dense molecular Gas as traced by HCN emission is a star formation rate indicator. The mass of dense molecular gas is the key to understanding the star formation rate • HCN observations at low and high z. • A new Star Formation Law HCN Observations: Solomon, Downes ...
The Sun is a mass of Incandescent Gas
... The Sun and other stars are really only roughly in equilibrium. The Sun is extremely dynamic, and has storms larger than the Earth. ...
... The Sun and other stars are really only roughly in equilibrium. The Sun is extremely dynamic, and has storms larger than the Earth. ...
Four Homework Assignments
... radius (R), assuming Kramers opacity, and using the ideal gas law, derive a very approximate R(M ) for main-sequence stars from ∼1.5 M to 4.0 M . [Hint: You will need to know whether hydrogen burning is proceeding by the PP chain or the CNO cycle.] Retain the µ dependence of your result. What powe ...
... radius (R), assuming Kramers opacity, and using the ideal gas law, derive a very approximate R(M ) for main-sequence stars from ∼1.5 M to 4.0 M . [Hint: You will need to know whether hydrogen burning is proceeding by the PP chain or the CNO cycle.] Retain the µ dependence of your result. What powe ...
2.5.4 astronomical distances Parallax and Distances to Stars
... is NOT a definition of time. It is the distance that light can travel through a vacuum in 1 year. If you work it out it is – 9.461 x 1015m When you consider the ridiculous distance involved in astronomy, it makes sense to have large units! ...
... is NOT a definition of time. It is the distance that light can travel through a vacuum in 1 year. If you work it out it is – 9.461 x 1015m When you consider the ridiculous distance involved in astronomy, it makes sense to have large units! ...
The Night Sky
... Sunflower galaxy- A galaxy in a spiral form discovered in 1779 Whirlpool galaxy- A whirlpool like galaxy. thought to be about 14 million lght years ...
... Sunflower galaxy- A galaxy in a spiral form discovered in 1779 Whirlpool galaxy- A whirlpool like galaxy. thought to be about 14 million lght years ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Small, rapidly rotating objects Can’t be white dwarfs; must be neutron stars ...
... Small, rapidly rotating objects Can’t be white dwarfs; must be neutron stars ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.