The Life and Death of Stars
... http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/ add_aqa_pre_2011/atomic/atomstrucrev1.shtml ...
... http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/ add_aqa_pre_2011/atomic/atomstrucrev1.shtml ...
Lecture 10 - Concord University
... Fusing light elements together results in more nuclear binding energy and less mass per nucleon. When the mass disappears, it is converted to energy so light-element fusion produces energy. But, when fusing any element to Fe, you now need to PROVIDE some energy to be converted into mass and Natu ...
... Fusing light elements together results in more nuclear binding energy and less mass per nucleon. When the mass disappears, it is converted to energy so light-element fusion produces energy. But, when fusing any element to Fe, you now need to PROVIDE some energy to be converted into mass and Natu ...
2. Stellar Physics
... Problem of stellar structure is simplified by making several reasonable assumptions, which hold in most (not all) cases. 1) Spherical symmetry An isolated, non-rotating star which does not contain strong magnetic fields will be spherically symmetric, i.e.: All quantities (e.g. density, temperature, ...
... Problem of stellar structure is simplified by making several reasonable assumptions, which hold in most (not all) cases. 1) Spherical symmetry An isolated, non-rotating star which does not contain strong magnetic fields will be spherically symmetric, i.e.: All quantities (e.g. density, temperature, ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... • Begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called nebulae • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusio ...
... • Begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called nebulae • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusio ...
The first stars, as seen by supercomputers
... Figure 1. The gathering place. These six panels show density (top; red is less dense; yellow, denser) and temperature (bottom; red is 10 K; yellow, 1000 K) profiles of gas that falls into dark-matter gravitational potentials. (a) Visible here are spoke-like accretion shocks (blue on top; yellow on b ...
... Figure 1. The gathering place. These six panels show density (top; red is less dense; yellow, denser) and temperature (bottom; red is 10 K; yellow, 1000 K) profiles of gas that falls into dark-matter gravitational potentials. (a) Visible here are spoke-like accretion shocks (blue on top; yellow on b ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... Earth is called the intensity (I) of the star’s radiation This is related to the power output per metre squared L of the star’s surface in this way ...
... Earth is called the intensity (I) of the star’s radiation This is related to the power output per metre squared L of the star’s surface in this way ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... main-sequence star • This leaves a core of nearly pure helium surrounded by a shell through which hydrogen fusion works its way outward in the star • The core shrinks and becomes hotter, while the star’s outer layers expand and cool • The result is a red giant star ...
... main-sequence star • This leaves a core of nearly pure helium surrounded by a shell through which hydrogen fusion works its way outward in the star • The core shrinks and becomes hotter, while the star’s outer layers expand and cool • The result is a red giant star ...
Document
... Must have a mass of 2.7£106M¯. Not a black hole from a single stellar collapse, but must be built up over time. We shall meet these again when we come to look at quasars, but we have to ask “Just how active was the young Milky Way”? ...
... Must have a mass of 2.7£106M¯. Not a black hole from a single stellar collapse, but must be built up over time. We shall meet these again when we come to look at quasars, but we have to ask “Just how active was the young Milky Way”? ...
Universe and Star Formation - White Plains Public Schools
... • A nebula is a cloud of gas and/or dust in space. • There are two major types of nebulae: 1. Bright nebula - concentrations of gas/dust where stars have been or are being formed….. - Emission nebula - Reflection nebula http://www.atlasoftheuniverse.com/nebulae.html 2. Dark nebula – opaque dark clou ...
... • A nebula is a cloud of gas and/or dust in space. • There are two major types of nebulae: 1. Bright nebula - concentrations of gas/dust where stars have been or are being formed….. - Emission nebula - Reflection nebula http://www.atlasoftheuniverse.com/nebulae.html 2. Dark nebula – opaque dark clou ...
Report Sheet
... 5. The primary element in any space nebula is the element _______________________ 6. What other elements are M42 made of? _________________________________________________________ 7. What force begins to shape a nebula into a star? _______________________________________ 8. Name one other nebula tha ...
... 5. The primary element in any space nebula is the element _______________________ 6. What other elements are M42 made of? _________________________________________________________ 7. What force begins to shape a nebula into a star? _______________________________________ 8. Name one other nebula tha ...
Stages - A Summary - University of Dayton
... the red super- giant region; the star could continue the nuclear reaction sequence and fuse the carbon atoms, but its gravity is not high enough to generate the temperatures needed (about 600 million K) for this to happen, so it has essentially reached the end of its nuclear-burning lifetime, and de ...
... the red super- giant region; the star could continue the nuclear reaction sequence and fuse the carbon atoms, but its gravity is not high enough to generate the temperatures needed (about 600 million K) for this to happen, so it has essentially reached the end of its nuclear-burning lifetime, and de ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Andromeda is like a larger version of our own Milky Way galaxy. It’s a flat disk that spans more than a quarter-million light-years. Its brightest stars form spiral arms that make the galaxy look like a pinwheel. Yet the galaxy is so far away that its structure is visible only through telescopes. Th ...
... Andromeda is like a larger version of our own Milky Way galaxy. It’s a flat disk that spans more than a quarter-million light-years. Its brightest stars form spiral arms that make the galaxy look like a pinwheel. Yet the galaxy is so far away that its structure is visible only through telescopes. Th ...
Birth and Death of Stars
... • After the supergiant stage, massive stars contract with a gravitational force much greater than low mass stars. The high pressures and temperatures that result causes nuclear fusion to begin again. This time the core fuses into heavier elements such as oxygen, magnesium, or silicon. Fusion continu ...
... • After the supergiant stage, massive stars contract with a gravitational force much greater than low mass stars. The high pressures and temperatures that result causes nuclear fusion to begin again. This time the core fuses into heavier elements such as oxygen, magnesium, or silicon. Fusion continu ...
galaxy - 106Thursday130-430
... • It is not the ordinary matter of stars, gas , dust, and planets. • The visible matter is surrounded by a halo of this dark matter containing the major portion of the total galaxy mass and extending very far beyond the visible matter. Some indirect means suggest that the dark matter halo may extend ...
... • It is not the ordinary matter of stars, gas , dust, and planets. • The visible matter is surrounded by a halo of this dark matter containing the major portion of the total galaxy mass and extending very far beyond the visible matter. Some indirect means suggest that the dark matter halo may extend ...
Astronomical Ideas Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1. Two stars
... The HR diagram is a clock for the age of star clusters. We can look at the HR diagram to see which are the bluest stars burning on the main sequence. The bluest stars correspond to the most massive stars that are still burning hydrogen on the main sequence. (More massive stars burn faster, hotter an ...
... The HR diagram is a clock for the age of star clusters. We can look at the HR diagram to see which are the bluest stars burning on the main sequence. The bluest stars correspond to the most massive stars that are still burning hydrogen on the main sequence. (More massive stars burn faster, hotter an ...
Stars - Haag
... Astronomers use a tool called a spectrograph, which breaks down light into its different wavelengths. ...
... Astronomers use a tool called a spectrograph, which breaks down light into its different wavelengths. ...
A Poetic Interlude
... The Earth, formed out of the same debris of which the sun was born, existed at the center of a star that exploded many billions of years ago. Isaac Asimov ...
... The Earth, formed out of the same debris of which the sun was born, existed at the center of a star that exploded many billions of years ago. Isaac Asimov ...
Ordinary Stars - Edgewood High School
... As the temperature of a star increases, the peak of its radiation is shifted toward shorter (blue) wavelengths Stefan-Boltzmann Law As the temperature of a star increases, the total energy output increases as the 4th power of the temperature ...
... As the temperature of a star increases, the peak of its radiation is shifted toward shorter (blue) wavelengths Stefan-Boltzmann Law As the temperature of a star increases, the total energy output increases as the 4th power of the temperature ...
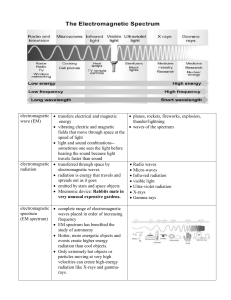
EMS Notes 1617 - Biloxi Public Schools
... To study the size, composition, and movement of stars and galaxies They make distant objects appear closer and brighter. To find black holes and map galactic centers Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze their composition Stars and o ...
... To study the size, composition, and movement of stars and galaxies They make distant objects appear closer and brighter. To find black holes and map galactic centers Some have been used to monitor radio signals given off by earthquakes To map sources and analyze their composition Stars and o ...
galaxy phenomenology
... ‣ most massive gravitational bound objects in the Universe ‣ contain up to thousands of galaxies ‣ most baryons intracluster gas, T~107-108 K gas ‣ smaller collections of bound galaxies are called 'groups' ...
... ‣ most massive gravitational bound objects in the Universe ‣ contain up to thousands of galaxies ‣ most baryons intracluster gas, T~107-108 K gas ‣ smaller collections of bound galaxies are called 'groups' ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.