Nova & SuperNova - Heart of the Valley Astronomers
... – 1 Joule is the energy to lift 1kg about 10cm on the surface of the earth. – 1043 J = energy to lift 1043 kg about 10cm – Mass of the Earth is ~ 5.9742 × 1024 kg ...
... – 1 Joule is the energy to lift 1kg about 10cm on the surface of the earth. – 1043 J = energy to lift 1043 kg about 10cm – Mass of the Earth is ~ 5.9742 × 1024 kg ...
Death of Low Mass Stars 8 Solar Masses or less
... • The resistance of electrons from being squeezed together (electromagnetic repulsion) keeps gravity from compressing it further. Called Electron Degeneracy • The black dwarf will continue to exist at temps close to absolute zero forever…. ...
... • The resistance of electrons from being squeezed together (electromagnetic repulsion) keeps gravity from compressing it further. Called Electron Degeneracy • The black dwarf will continue to exist at temps close to absolute zero forever…. ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... supernova, widely seen on Earth beginning in the year 1006 AD; Earth was about 7200 light-years away. Egyptian astrologer left us a historical description of the supernova - the object was 2-1/2 to three times as large as the disc of Venus, and about one-quarter the brightness of the Moon. ...
... supernova, widely seen on Earth beginning in the year 1006 AD; Earth was about 7200 light-years away. Egyptian astrologer left us a historical description of the supernova - the object was 2-1/2 to three times as large as the disc of Venus, and about one-quarter the brightness of the Moon. ...
ASTRONOMY 1 ... You may use this only this study guide for reference... No electronic devises: I pads, lap tops, phones, etc.
... 4. What is the he proton-proton chain? Why does it need a high temperature? 5. What is a white dwarf? a supergiant star? A main sequence star? What type is our Sun? 6. The sun generates energy by fusion? By fission ? 7. Why are protostars difficult to observe? 8. Why does the main sequence have a li ...
... 4. What is the he proton-proton chain? Why does it need a high temperature? 5. What is a white dwarf? a supergiant star? A main sequence star? What type is our Sun? 6. The sun generates energy by fusion? By fission ? 7. Why are protostars difficult to observe? 8. Why does the main sequence have a li ...
Big Bang, 429
... 4. What is the he proton-proton chain? Why does it need a high temperature? 5. What is a white dwarf? a supergiant star? A main sequence star? What type is our Sun? 6. The sun generates energy by fusion? By fission ? 7. Why are protostars difficult to observe? 8. Why does the main sequence have a li ...
... 4. What is the he proton-proton chain? Why does it need a high temperature? 5. What is a white dwarf? a supergiant star? A main sequence star? What type is our Sun? 6. The sun generates energy by fusion? By fission ? 7. Why are protostars difficult to observe? 8. Why does the main sequence have a li ...
Document
... _____ 9. Why do black lines appear on an absorption spectrum? a. They show where too much light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. b. They show where less light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. c. They are the emission lines of an electrically charged element. d. They show where a star has black ...
... _____ 9. Why do black lines appear on an absorption spectrum? a. They show where too much light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. b. They show where less light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. c. They are the emission lines of an electrically charged element. d. They show where a star has black ...
doc
... So far all we know about stars’ lives is that they are formed within interstellar clouds by contraction under self-gravity, contract until they are hot enough in their cores to burn nuclear fuel, and that the lowest-mass stars live longest. Next we summarize the stages of a star’s life after it begi ...
... So far all we know about stars’ lives is that they are formed within interstellar clouds by contraction under self-gravity, contract until they are hot enough in their cores to burn nuclear fuel, and that the lowest-mass stars live longest. Next we summarize the stages of a star’s life after it begi ...
The big bang left the universe with its first atoms
... made of super-dense matter. Most of their hydrogen and helium are lost to the stellar wind. These stars are so dense that they form a new type of “degenerate” or nuclear matter. ...
... made of super-dense matter. Most of their hydrogen and helium are lost to the stellar wind. These stars are so dense that they form a new type of “degenerate” or nuclear matter. ...
Part B
... • Hypernovae - collapse of stars of greater than 30 solar masses which are spinning rapidly. • The black hole forms before star outer layers contract very much. ...
... • Hypernovae - collapse of stars of greater than 30 solar masses which are spinning rapidly. • The black hole forms before star outer layers contract very much. ...
Where Did All The Elements Come From??
... made of super-dense matter. Most of their hydrogen and helium are lost to the stellar wind. These stars are so dense that they form a new type of “degenerate” or nuclear matter. ...
... made of super-dense matter. Most of their hydrogen and helium are lost to the stellar wind. These stars are so dense that they form a new type of “degenerate” or nuclear matter. ...
Birth of Stars - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... Are new stars still being created, or did creation cease billions of years ago? Where are new stars being created? Are planets a natural result of star formation or is our solar system unique in the universe? How can we observe planets around distant ...
... Are new stars still being created, or did creation cease billions of years ago? Where are new stars being created? Are planets a natural result of star formation or is our solar system unique in the universe? How can we observe planets around distant ...
PC2491 Examples 2
... where Ro is the distance from the galactic centre to the Sun, o is the angular velocity of the Sun and (r) is the angular velocity at radius r. An H1 cloud in the galactic plane at l=30o is observed to have a velocity relative to the local standard of rest of +80 km s-1. Assume the galactic rotati ...
... where Ro is the distance from the galactic centre to the Sun, o is the angular velocity of the Sun and (r) is the angular velocity at radius r. An H1 cloud in the galactic plane at l=30o is observed to have a velocity relative to the local standard of rest of +80 km s-1. Assume the galactic rotati ...
Space - lucu
... • Derived from the Latin word for "clouds". • Nebulae are the basic building blocks of the universe • They contain the elements from which stars and solar systems are built. • Most nebulae are composed of about 90% hydrogen, 10% helium, and 0.1% heavy elements such as carbon, nitrogen, magnesium, po ...
... • Derived from the Latin word for "clouds". • Nebulae are the basic building blocks of the universe • They contain the elements from which stars and solar systems are built. • Most nebulae are composed of about 90% hydrogen, 10% helium, and 0.1% heavy elements such as carbon, nitrogen, magnesium, po ...
The origin, life, and death of stars
... mass, gravity will not be strong enough to compress and heat its core to the temperatures that trigger fusion If the mass is less than 0.08 x solar mass, it will form a Brown Dwarf Brown Dwarfs are not true stars, but they do give off small amounts of light as they cool ...
... mass, gravity will not be strong enough to compress and heat its core to the temperatures that trigger fusion If the mass is less than 0.08 x solar mass, it will form a Brown Dwarf Brown Dwarfs are not true stars, but they do give off small amounts of light as they cool ...
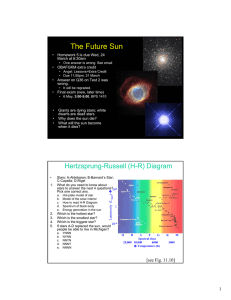
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... In what ways are HR diagrams of H+χ Perseus, Pleiades, Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Hottest stars in Perseus are hotter than hottest stars in Pleiades. b. Most stars are on the main sequence. c. NGC188 has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
... In what ways are HR diagrams of H+χ Perseus, Pleiades, Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Hottest stars in Perseus are hotter than hottest stars in Pleiades. b. Most stars are on the main sequence. c. NGC188 has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
Chapter 2 Cosmic tombstones
... Since the magnetic axis and the rotation axis are not aligned, the pulsar operates like a lighthouse an observer sees periodic pulses of radio emission According to the leading theory, this emission is produced by fast particles propagating along the magnetic field lines Particles are extracted fr ...
... Since the magnetic axis and the rotation axis are not aligned, the pulsar operates like a lighthouse an observer sees periodic pulses of radio emission According to the leading theory, this emission is produced by fast particles propagating along the magnetic field lines Particles are extracted fr ...
Stellar structure
... T ~ GMmp/kBR. For a sufficiently large value of M/R (e.g. take one solar mass and one solar radius) T is large enough (> 107 K) that nuclear reactions will take place (high density also satisfied because also M/R3 very large) -- nuclear reactions establish a pressure/temperature gradient that suppo ...
... T ~ GMmp/kBR. For a sufficiently large value of M/R (e.g. take one solar mass and one solar radius) T is large enough (> 107 K) that nuclear reactions will take place (high density also satisfied because also M/R3 very large) -- nuclear reactions establish a pressure/temperature gradient that suppo ...
Chapter 7 Review Answers
... 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have lots of dust and gas, which are the birt ...
... 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have lots of dust and gas, which are the birt ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.