Solar nebula theory
... The Sun’s outer core will expand and the Sun will become a Red Giant. Theory #1: The Earth will get engulfed by the Sun and exist no more. Theory #2: When the Sun first begins to shrink, gravitational attraction between the Earth and Sun will become less. Some scientists think the Earth may move awa ...
... The Sun’s outer core will expand and the Sun will become a Red Giant. Theory #1: The Earth will get engulfed by the Sun and exist no more. Theory #2: When the Sun first begins to shrink, gravitational attraction between the Earth and Sun will become less. Some scientists think the Earth may move awa ...
Stellarium is a simple and easy way to look at the
... years – and show what positio the stars were or are going to b in. ...
... years – and show what positio the stars were or are going to b in. ...
슬라이드 1
... 3 objects around AzTEC-3 Probably represent the progenitor of a massive central cluster galaxy (type cD) at lower redshift. - Already within the radius of a typical local cD galaxy - Dynamical timescale ~ 60 Myr (assuming σ ~ 200km/s) - Even for the objects at 95kpc, the dynamical timescale < 0.5 G ...
... 3 objects around AzTEC-3 Probably represent the progenitor of a massive central cluster galaxy (type cD) at lower redshift. - Already within the radius of a typical local cD galaxy - Dynamical timescale ~ 60 Myr (assuming σ ~ 200km/s) - Even for the objects at 95kpc, the dynamical timescale < 0.5 G ...
Red Giants
... short answer is that towards the end of a star's life, the temperature near the core rises and this causes the size of the star to expand. This is the fate of the Sun in about 5 billion years. You might want to mark your calendar!The long answer is that stars convert hydrogen to helium to produce li ...
... short answer is that towards the end of a star's life, the temperature near the core rises and this causes the size of the star to expand. This is the fate of the Sun in about 5 billion years. You might want to mark your calendar!The long answer is that stars convert hydrogen to helium to produce li ...
worksheet
... This seems like a small amount of energy but now work out the energy released by 1kg of hydrogen atoms undergoing fusion. (Hint: use percentages) ...
... This seems like a small amount of energy but now work out the energy released by 1kg of hydrogen atoms undergoing fusion. (Hint: use percentages) ...
The Universe - IES Alyanub
... (Ceres) is in the asteroid belt. Then there is Pluto, which was a planet for almost 80 years before being reclassified, and finally Eris, which is even further out of the solar system than Pluto is. Solar System Formation Everything has a beginning, and our story begins when the cloud that was the S ...
... (Ceres) is in the asteroid belt. Then there is Pluto, which was a planet for almost 80 years before being reclassified, and finally Eris, which is even further out of the solar system than Pluto is. Solar System Formation Everything has a beginning, and our story begins when the cloud that was the S ...
NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS
... inward due to gravitational forces ⦿ At the beginning of this collapse we form a SOLAR NEBULA. ...
... inward due to gravitational forces ⦿ At the beginning of this collapse we form a SOLAR NEBULA. ...
A Solar System is Born 4/29/11
... • Hubble image of protoplanetary discs in the Orion Nebula, a light-years-wide "stellar nursery" probably very similar to the primordial nebula from which our Sun formed. ...
... • Hubble image of protoplanetary discs in the Orion Nebula, a light-years-wide "stellar nursery" probably very similar to the primordial nebula from which our Sun formed. ...
1st EXAM VERSION C - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... B. light emitted over a wide range of wavelengths by dust grains that have been heated by radiation from embedded stars. C. light emitted by molecules in the dense clouds of gas surrounding the stars in the nebula. D. *red line, from recombination of electrons with nuclei in ionized hydrogen. ...
... B. light emitted over a wide range of wavelengths by dust grains that have been heated by radiation from embedded stars. C. light emitted by molecules in the dense clouds of gas surrounding the stars in the nebula. D. *red line, from recombination of electrons with nuclei in ionized hydrogen. ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main sequence. In the ain sequence, the hotter the star, the brighter it is. Not all star’s, however, follow that pattern. While some star’s are very hot, ...
... It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main sequence. In the ain sequence, the hotter the star, the brighter it is. Not all star’s, however, follow that pattern. While some star’s are very hot, ...
R - AMUSE code
... (which we derived). We know the surface temperature (Teff=5780K) is much smaller than its minimum mean temperature (2×106 K). Thus we make two approximations for the surface boundary conditions: ρM=M, ρ = 0 kg/m3 and T = 0K at r=rs i.e. that the star does have a sharp boundary with the surrounding v ...
... (which we derived). We know the surface temperature (Teff=5780K) is much smaller than its minimum mean temperature (2×106 K). Thus we make two approximations for the surface boundary conditions: ρM=M, ρ = 0 kg/m3 and T = 0K at r=rs i.e. that the star does have a sharp boundary with the surrounding v ...
Chapter19
... fusion. By the time the center of the star becomes hot enough for helium fusion, all of the hydrogen has been fused into helium. Their nuclei have greater positive charges than hydrogen, so a higher temperature is required for the nuclei to have enough energy to overcome the repulsive electrical for ...
... fusion. By the time the center of the star becomes hot enough for helium fusion, all of the hydrogen has been fused into helium. Their nuclei have greater positive charges than hydrogen, so a higher temperature is required for the nuclei to have enough energy to overcome the repulsive electrical for ...
Stellar Deaths - Mid
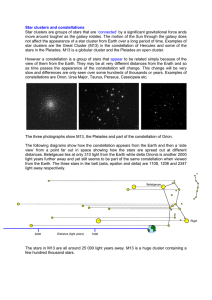
... 1) formed at about same time 2) are at about the same distance 3) have same chemical composition The ONLY variable property among stars in a cluster is mass! ...
... 1) formed at about same time 2) are at about the same distance 3) have same chemical composition The ONLY variable property among stars in a cluster is mass! ...
Document
... • Betelgeuse is the only star big enough to directly see its surface with a normal telescope. ...
... • Betelgeuse is the only star big enough to directly see its surface with a normal telescope. ...
Star Vocabulary
... 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- change in the observed frequency of a wave when it moves toward or away from ...
... 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- change in the observed frequency of a wave when it moves toward or away from ...
Study Guide for 3RD Astronomy Exam
... Solve problems relating to the relative brightness or luminosity of two stars given their m or M values. Determine the hottest and coolest stars from a list of stars with their spectral types. Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class and identifying if the star is in t ...
... Solve problems relating to the relative brightness or luminosity of two stars given their m or M values. Determine the hottest and coolest stars from a list of stars with their spectral types. Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class and identifying if the star is in t ...
Stars, Galaxies & Universe
... • Stars that are less than 1.4 solar masses will shrink to a white dwarf. • Stars between 1.4 -3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and leave a ...
... • Stars that are less than 1.4 solar masses will shrink to a white dwarf. • Stars between 1.4 -3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and leave a ...
PREVIEW-Reading Quiz 06 - Chapter 12
... "Quantum mechanics restricts the number of electrons that can have low energy. Basically, each electron must occupy its own energy state. When electrons are packed together, as they are in a white dwarf, the number of available low energy states is too small and many electrons are forced into high e ...
... "Quantum mechanics restricts the number of electrons that can have low energy. Basically, each electron must occupy its own energy state. When electrons are packed together, as they are in a white dwarf, the number of available low energy states is too small and many electrons are forced into high e ...
Introduction to the Earth
... Black holes If the star was bigger than 30 times the mass of the sun The left over core becomes so dense that light can’t escape its gravity. Becomes a black hole. Grab any nearby matter and get bigger As matter falls in, it gives off x-rays. That’s how they find them ...
... Black holes If the star was bigger than 30 times the mass of the sun The left over core becomes so dense that light can’t escape its gravity. Becomes a black hole. Grab any nearby matter and get bigger As matter falls in, it gives off x-rays. That’s how they find them ...
The Milky Way - Midlandstech
... Guidepost Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main sequence and their old age as they swell to become giant stars. Here you will answer three essential questions: • What happens ...
... Guidepost Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main sequence and their old age as they swell to become giant stars. Here you will answer three essential questions: • What happens ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.