Lecture 13
... fusing H to He in shell outside the core … but there is no H to He fusion in the core. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen fuel: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after all fusion has ceased: white dwarfs. • The white dwarf stage is the ...
... fusing H to He in shell outside the core … but there is no H to He fusion in the core. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen fuel: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after all fusion has ceased: white dwarfs. • The white dwarf stage is the ...
Stars - winterk
... way, as a nebula A nebula is a giant cloud of gas and dust Stars are created in a nebula as the gases contract due to the force of gravity, turning into a hot, dense clump As they become larger, they heat up until they reach a temperature of 10 000 000 C At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins ...
... way, as a nebula A nebula is a giant cloud of gas and dust Stars are created in a nebula as the gases contract due to the force of gravity, turning into a hot, dense clump As they become larger, they heat up until they reach a temperature of 10 000 000 C At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins ...
Astronomy 103 Exam 2 Review
... Why are there no stars of less massive than approximately 0.08 solar masses? A. They are sLll contracLng and haven’t yet reached the main sequence B. They cannot compress their cores to hydrogen fusion temperatures C. Their mass is so small that deuterium fusion blasts them apart D. Non ...
... Why are there no stars of less massive than approximately 0.08 solar masses? A. They are sLll contracLng and haven’t yet reached the main sequence B. They cannot compress their cores to hydrogen fusion temperatures C. Their mass is so small that deuterium fusion blasts them apart D. Non ...
It all began with a Big Bang!
... Telescopes now begin to find galaxies that were created about one billion years after the Big Bang. These small galaxies are much closer together than galaxies are today. ...
... Telescopes now begin to find galaxies that were created about one billion years after the Big Bang. These small galaxies are much closer together than galaxies are today. ...
TAP 705-3: The parsec - Teaching Advanced Physics
... TAP 705-3: The parsec A unit of distance in common use amongst astronomers is the parsec. As the Earth moves in its orbit around the Sun, the position of nearby stars against the background of very distant stars seems to change. ...
... TAP 705-3: The parsec A unit of distance in common use amongst astronomers is the parsec. As the Earth moves in its orbit around the Sun, the position of nearby stars against the background of very distant stars seems to change. ...
What Is a Star
... billions of years. Our sun was born about 4.6 billion years ago. It is in the middle of its life cycle. It will live for at least another five billion years. ...
... billions of years. Our sun was born about 4.6 billion years ago. It is in the middle of its life cycle. It will live for at least another five billion years. ...
Astronomy 112: Physics of Stars Problem set 2: Due April 29 1. Time
... 8. Polytropes: Helium burning: We shall see later that after they finish central and shell hydrogen burning, many stars, including the sun, go on to ignite helium burning in their centers at a temperature ∼ 1.5×108 K. (aside: This temperature does not vary very much due to the extreme temperature se ...
... 8. Polytropes: Helium burning: We shall see later that after they finish central and shell hydrogen burning, many stars, including the sun, go on to ignite helium burning in their centers at a temperature ∼ 1.5×108 K. (aside: This temperature does not vary very much due to the extreme temperature se ...
Living alongside Monsters: Matter around Central Massive Black Holes Q. Daniel Wang
... M31*, a scaled-up version of Sgr A* activities. • Cool gas in the nuclear regions of M31 and our GC both has a small filling factor and are embedded in hot gas. • Evaporation of cool gas by hot gas may lead to the starvation of SMBHs • The mass-loaded hot gas undergoes outflows, affecting the glo ...
... M31*, a scaled-up version of Sgr A* activities. • Cool gas in the nuclear regions of M31 and our GC both has a small filling factor and are embedded in hot gas. • Evaporation of cool gas by hot gas may lead to the starvation of SMBHs • The mass-loaded hot gas undergoes outflows, affecting the glo ...
Distance to Stars
... km/s – 1 light year = the distance a ray of light travels in 1 year. 9.5 trillion km. Horsehead Nebula is 1,500 light years away) ...
... km/s – 1 light year = the distance a ray of light travels in 1 year. 9.5 trillion km. Horsehead Nebula is 1,500 light years away) ...
CoRoT: a space project to listen to the songs of the stars
... Many stars can vibrate in different modes like a musical instrument. For example, vibrations detected on the surface of the Sun have been well known for more than three decades. The stellar pulsations are difficult to detect as the stars are very distant and the periods in Sun-like stars are only fe ...
... Many stars can vibrate in different modes like a musical instrument. For example, vibrations detected on the surface of the Sun have been well known for more than three decades. The stellar pulsations are difficult to detect as the stars are very distant and the periods in Sun-like stars are only fe ...
Volume 20 Number 10 September 2012
... yellow and is mostly made up of old stars. Around the outside of the galaxy many much fainter and more distant galaxies can also be seen. A supernova is near the bottom of the image. See: http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1231/ ...
... yellow and is mostly made up of old stars. Around the outside of the galaxy many much fainter and more distant galaxies can also be seen. A supernova is near the bottom of the image. See: http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1231/ ...
Big Bang Theory
... stars (much bigger than our sun) explode and immense energy is released (equal to a ...
... stars (much bigger than our sun) explode and immense energy is released (equal to a ...
Teacher Guide - Astronomy Outreach at UT Austin
... Read the following to students: “Our galaxy, by conservative estimates, contains 100 billion stars. The small number of stars we can see at night are the nearby stars in our tiny neighborhood of our galaxy. Stars are not eternal, but live long lives compared to our lifetime. Over time they change. J ...
... Read the following to students: “Our galaxy, by conservative estimates, contains 100 billion stars. The small number of stars we can see at night are the nearby stars in our tiny neighborhood of our galaxy. Stars are not eternal, but live long lives compared to our lifetime. Over time they change. J ...
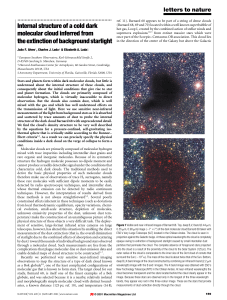
Internal structure of a cold dark molecular cloud inferred
... Molecular clouds are primarily composed of molecular hydrogen mixed with trace impurities including interstellar dust grains and rare organic and inorganic molecules. Because of its symmetric structure the hydrogen molecule possesses no dipole moment and cannot produce a readily detectable signal un ...
... Molecular clouds are primarily composed of molecular hydrogen mixed with trace impurities including interstellar dust grains and rare organic and inorganic molecules. Because of its symmetric structure the hydrogen molecule possesses no dipole moment and cannot produce a readily detectable signal un ...
Day-7
... Work with a partner Read the instructions and questions carefully Discuss your answers with each other. ...
... Work with a partner Read the instructions and questions carefully Discuss your answers with each other. ...
Day 9 - Ch. 4 -
... • Stars produce the heavier elements. • Formation of the Solar System (stardust, gravity, rotation, heat, and collisions). • Comparative Planetology (characteristics of the planets of the solar system). • Debris and remnants in the solar system. • Extrasolar planets (outside the solar system). ...
... • Stars produce the heavier elements. • Formation of the Solar System (stardust, gravity, rotation, heat, and collisions). • Comparative Planetology (characteristics of the planets of the solar system). • Debris and remnants in the solar system. • Extrasolar planets (outside the solar system). ...
Problem 4: magnitude of the star?
... E. Red giant __C___8. A blackbody radiates with a temperature T=3K. The signal is strongest for a wavelength near A. 1 nm B. 1 µm C. 1 mm D. 1 cm E. 1 m __E___9. A patch of sky shows a dark region nearly devoid of stars when viewed in visible light. However, an infrared image shows a small area with ...
... E. Red giant __C___8. A blackbody radiates with a temperature T=3K. The signal is strongest for a wavelength near A. 1 nm B. 1 µm C. 1 mm D. 1 cm E. 1 m __E___9. A patch of sky shows a dark region nearly devoid of stars when viewed in visible light. However, an infrared image shows a small area with ...
Measuring the Stars
... • Giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 times the Sun’s • Dwarf stars have radii equal to, or less than, the Sun’s • Supergiant stars have radii more than 100 times the Sun’s ...
... • Giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 times the Sun’s • Dwarf stars have radii equal to, or less than, the Sun’s • Supergiant stars have radii more than 100 times the Sun’s ...
Stars III The Hertzsprung
... As of May 2016, over 200 interstellar molecules have been detected in space, mostly at radio (rotation) and infrared (vibration) wavelengths ...
... As of May 2016, over 200 interstellar molecules have been detected in space, mostly at radio (rotation) and infrared (vibration) wavelengths ...
The Life Cycles of Stars, Part I
... The Life Cycles of Stars, Part I I. Star Birth and Life Imagine an enormous cloud of gas and dust many light-years across. Gravity, as it always does, tries to pull the materials together. A few grains of dust collect a few more, then a few more, then more still. Eventually, enough gas and dust has ...
... The Life Cycles of Stars, Part I I. Star Birth and Life Imagine an enormous cloud of gas and dust many light-years across. Gravity, as it always does, tries to pull the materials together. A few grains of dust collect a few more, then a few more, then more still. Eventually, enough gas and dust has ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.