Stars Crossword
... 4. a singularity whose gravity is so strong that nothing can escape - not even light 5. the area surrounding a blackhole where at that point nothing can escape 9. the middle age stage of a small star like ours 11. when a very large star's outer layer explodes outward with an amazing amount of force ...
... 4. a singularity whose gravity is so strong that nothing can escape - not even light 5. the area surrounding a blackhole where at that point nothing can escape 9. the middle age stage of a small star like ours 11. when a very large star's outer layer explodes outward with an amazing amount of force ...
Kinds of Stars
... Gas and Dust in space are called Nebulae. Stable State – Stars whose diameter and radiation stay the same for millions of years. Our sun is in a stable state. When fusion doesn’t balance gravity’s force, core contracts(gets hotter) and outer layers ...
... Gas and Dust in space are called Nebulae. Stable State – Stars whose diameter and radiation stay the same for millions of years. Our sun is in a stable state. When fusion doesn’t balance gravity’s force, core contracts(gets hotter) and outer layers ...
Day 2
... Stage 3: Zero- Age Main Sequence Finally, the rate of fusion becomes high enough to establish gravitational equilibrium. At this point, fusion becomes self-sustaining and the star settles into its hydrogen burning, main sequence life. The main sequence phase is the longest phase of a star's life, a ...
... Stage 3: Zero- Age Main Sequence Finally, the rate of fusion becomes high enough to establish gravitational equilibrium. At this point, fusion becomes self-sustaining and the star settles into its hydrogen burning, main sequence life. The main sequence phase is the longest phase of a star's life, a ...
31 — Main-Sequence Stars [Revision : 1.1]
... To drive radiative flux, temperature gradient can be moderate; no need for convection So, radiative envelope In the more-massive stars (M & 10 M ), iron and nickel cause opacity peak at ∼ 200, 000 K; this ‘iron bump’ can cause thin, weak convection zone ...
... To drive radiative flux, temperature gradient can be moderate; no need for convection So, radiative envelope In the more-massive stars (M & 10 M ), iron and nickel cause opacity peak at ∼ 200, 000 K; this ‘iron bump’ can cause thin, weak convection zone ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... • Neutron stars can form powerful jets of matter and energy • Previously only thought possible with black holes • Binary system with neutron star gaining matter from white dwarf companion’s atmosphere in an accretion disk • Neutron star is tiny compared to white dwarf but is very dense and about 14 ...
... • Neutron stars can form powerful jets of matter and energy • Previously only thought possible with black holes • Binary system with neutron star gaining matter from white dwarf companion’s atmosphere in an accretion disk • Neutron star is tiny compared to white dwarf but is very dense and about 14 ...
properties of stars 2012
... Wien’s Law T = c/λm where T = temperature in kelvins, c is the speed of light, λm is the wavelength of maximum brightness. Spectral Classes There is a relationship between the temperature of a star and the appearance of the dark lines on its absorption spectrum. Star temperatures are classified, fro ...
... Wien’s Law T = c/λm where T = temperature in kelvins, c is the speed of light, λm is the wavelength of maximum brightness. Spectral Classes There is a relationship between the temperature of a star and the appearance of the dark lines on its absorption spectrum. Star temperatures are classified, fro ...
Note Taking Guide #2: Characteristics of Stars Welcome back! As
... estimate the distance to stars by a number of ways—parallax being a common means— but no method is an exact measure of distance. Estimates are just that: approximations, and, given the vast distances between objects in space, some approximations are more reliable than others. In reading through your ...
... estimate the distance to stars by a number of ways—parallax being a common means— but no method is an exact measure of distance. Estimates are just that: approximations, and, given the vast distances between objects in space, some approximations are more reliable than others. In reading through your ...
Sample final
... axis? How would you classify (composition or type) this object? In other words, what is it? Essay section part one Choose two of the following discoveries, and determine if they are surprising (not consistent with current astronomical ideas) or not surprising (consistent). In either case, state clea ...
... axis? How would you classify (composition or type) this object? In other words, what is it? Essay section part one Choose two of the following discoveries, and determine if they are surprising (not consistent with current astronomical ideas) or not surprising (consistent). In either case, state clea ...
Zairamink_Lifecycle of a Star
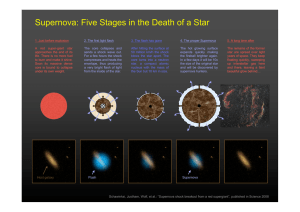
... During the time a Super Nova is around, it radiates as much energy as the sun in it’s entire life time. After a Super Nova one of two things can happen. ...
... During the time a Super Nova is around, it radiates as much energy as the sun in it’s entire life time. After a Super Nova one of two things can happen. ...
Grade 9 Science EXAM REVIEW – ASTRONOMY
... 7. What is the Big Bang theory? What are the pieces of evidence to support it? Scientists believe that at one point in time, all the matter in the universe was packed together into one small, extremely dense, hot mass under enormous pressure. The event where this mass began to move apart is called t ...
... 7. What is the Big Bang theory? What are the pieces of evidence to support it? Scientists believe that at one point in time, all the matter in the universe was packed together into one small, extremely dense, hot mass under enormous pressure. The event where this mass began to move apart is called t ...
Ch 11c and 12 ( clusters 3-31-11)
... •Contraction and heating of clouds into protostars • Hydrogen fusion stops collapse II. Leaving the Main Sequence: Hydrogen fusion stops ...
... •Contraction and heating of clouds into protostars • Hydrogen fusion stops collapse II. Leaving the Main Sequence: Hydrogen fusion stops ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Stars
... Nebulae – clouds of dust, gas, and thinly scattered matter • Stars and planets form from this interstellar matter 1. Nebulae begin to contract – Gravity squeezes particles in the nebula towards the center – Nebula shrinks – Gravitational energy is converted into heat energy ...
... Nebulae – clouds of dust, gas, and thinly scattered matter • Stars and planets form from this interstellar matter 1. Nebulae begin to contract – Gravity squeezes particles in the nebula towards the center – Nebula shrinks – Gravitational energy is converted into heat energy ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 7. Create a flow-map that shows the organization of the universe, from smallest to largest unit? star, star cluster, galaxy, galactic cluster, universe 8. The H-R diagram is based upon which 2 criteria? temperature and brightness 9. The tilt of Earth on its axis affects Climate, Seasons, length of d ...
... 7. Create a flow-map that shows the organization of the universe, from smallest to largest unit? star, star cluster, galaxy, galactic cluster, universe 8. The H-R diagram is based upon which 2 criteria? temperature and brightness 9. The tilt of Earth on its axis affects Climate, Seasons, length of d ...
Astronomy 103 – Midterm 2 – October 29, 2014
... a) Cloud A is stopped by fusion of helium to carbon and cloud K is stopped by fusion of hydrogen to helium b) Cloud K is stopped by fusion of helium to carbon and cloud A is stopped by fusion of hydrogen to helium c) Both clouds are stopped by fusion of hydrogen to helium d) Both clouds are stopped ...
... a) Cloud A is stopped by fusion of helium to carbon and cloud K is stopped by fusion of hydrogen to helium b) Cloud K is stopped by fusion of helium to carbon and cloud A is stopped by fusion of hydrogen to helium c) Both clouds are stopped by fusion of hydrogen to helium d) Both clouds are stopped ...
Seating Chart for Wednesday PHOTO ID REQUIRED! SIT IN YOUR ASSIGNED ROW!
... • Gravity = “curvature” in space. • Photons, planets etc follow shortest paths through curved space. • Analogy: 2D bug on surface that curves into an extra (3rd) ...
... • Gravity = “curvature” in space. • Photons, planets etc follow shortest paths through curved space. • Analogy: 2D bug on surface that curves into an extra (3rd) ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... the distance to these clusters and he plotted their positions. • For them to fit, the Milky Way must be around 30 kpc across. (Shapley miscalcuated to around 40 kpc. ...
... the distance to these clusters and he plotted their positions. • For them to fit, the Milky Way must be around 30 kpc across. (Shapley miscalcuated to around 40 kpc. ...
4.5.5. Black Holes
... Region II is therefore called a black hole. The spherical surface at r rS is called the event horizon. To the Minkowskian observer at r , light emitted by an ingoing particle will be redshifted by an increasing amount as the particle approaches the event horizon. Physically, one possible way t ...
... Region II is therefore called a black hole. The spherical surface at r rS is called the event horizon. To the Minkowskian observer at r , light emitted by an ingoing particle will be redshifted by an increasing amount as the particle approaches the event horizon. Physically, one possible way t ...
Figures I through VII in Section 1 on the following sheet
... List them in order of decreasing temperature (_1_). List them in order of decreasing strength of their Hydrogen lines (_2_). Which spectrum would most likely have been produced by star B from figure X (_3_)? Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure I ...
... List them in order of decreasing temperature (_1_). List them in order of decreasing strength of their Hydrogen lines (_2_). Which spectrum would most likely have been produced by star B from figure X (_3_)? Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure I ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.


![31 — Main-Sequence Stars [Revision : 1.1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015926256_1-97d746cbe97ccc13b433136b208bf071-300x300.png)