Galaxies • Test 3 (New date) – Thurs, 9 April
... Between 7 & 16 kpc, M(R) rises linearly. There is little light beyond 7 kpc. Where there is mass there is not necessarily light from stars & gas. Extrapolate M(R) is linear beyond visible part of galaxy. ...
... Between 7 & 16 kpc, M(R) rises linearly. There is little light beyond 7 kpc. Where there is mass there is not necessarily light from stars & gas. Extrapolate M(R) is linear beyond visible part of galaxy. ...
PDF copy
... years away from the earth. It contains a supergiant star, about 25 times as massive as our Sun, and a compressed dead partn about twice as massive as the Sun but compressed to a diameter of just about 30 km. the stars orbit around each other in 4.9 ...
... years away from the earth. It contains a supergiant star, about 25 times as massive as our Sun, and a compressed dead partn about twice as massive as the Sun but compressed to a diameter of just about 30 km. the stars orbit around each other in 4.9 ...
Solar System knowledge
... The origin of the Sun and of the Solar System is connected to the condensation of a primordial cloud of gas and dust as those often seen in our galaxy. It is probable that an external event triggered the collapse of the cloud, since its parts were in equilibrium. Scientists have put forward the hypo ...
... The origin of the Sun and of the Solar System is connected to the condensation of a primordial cloud of gas and dust as those often seen in our galaxy. It is probable that an external event triggered the collapse of the cloud, since its parts were in equilibrium. Scientists have put forward the hypo ...
Herbig Ae/Be Stars
... starting point for for T Tauri stars depends on factors such as how much thermal energy is added during protostellar accretion + The youngest low mass stars are observed near the birthline, but a definitive observational test does not yet exist + D-burning is insignificant for more massive stars (M ...
... starting point for for T Tauri stars depends on factors such as how much thermal energy is added during protostellar accretion + The youngest low mass stars are observed near the birthline, but a definitive observational test does not yet exist + D-burning is insignificant for more massive stars (M ...
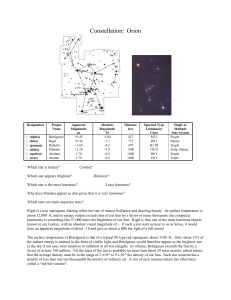
Orion
... in the sky, visible to the naked eye, and rewarding in telescopes of every size, from the smallest glasses to the greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellati ...
... in the sky, visible to the naked eye, and rewarding in telescopes of every size, from the smallest glasses to the greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellati ...
Unit 1
... kpc from the center, in one of the spiral arms. Most of the stars are concentrated in the galactic plane, or in the central bulge at the center of the galaxy Inside the bulge is the nucleus of the galaxy ...
... kpc from the center, in one of the spiral arms. Most of the stars are concentrated in the galactic plane, or in the central bulge at the center of the galaxy Inside the bulge is the nucleus of the galaxy ...
–1– 28. HIGH-MASS STAR FORMATION: THEORY 28.1. The Effects
... the values he considers. (One can show that when one generalizes the Bondi accretion model to approximately include the self gravity of the gas, the accretion rate is indeed about c 3 /G.) Bonnell and collaborators have proposed two alternative models. In the competitive accretion model (Lecture 24) ...
... the values he considers. (One can show that when one generalizes the Bondi accretion model to approximately include the self gravity of the gas, the accretion rate is indeed about c 3 /G.) Bonnell and collaborators have proposed two alternative models. In the competitive accretion model (Lecture 24) ...
Document
... Radioactive dating of meteorites (4.55 ± 109 yr) How is the age of meteorites related to the ignition of hydrogen burning, i.e., the start of the Sun’s main-sequence life? Star formation Interstellar cloud (104 m) is triggered into gravitational collapse Shock waves in galactic spiral arms or sup ...
... Radioactive dating of meteorites (4.55 ± 109 yr) How is the age of meteorites related to the ignition of hydrogen burning, i.e., the start of the Sun’s main-sequence life? Star formation Interstellar cloud (104 m) is triggered into gravitational collapse Shock waves in galactic spiral arms or sup ...
FROM MOLECULAR CLOUDS TO STARS 1 Star formation and the
... also M does not vary much inside a cloud and, in first approximation, it depends on the sound speed in the cloud, that is a function of the cloud temperature [Shu, Adams & Lizano 1987]. As an example a star of 0.1 M¤, has a luminosity of ∼10-4 L¤ on MS, while during the accretion phase the same obje ...
... also M does not vary much inside a cloud and, in first approximation, it depends on the sound speed in the cloud, that is a function of the cloud temperature [Shu, Adams & Lizano 1987]. As an example a star of 0.1 M¤, has a luminosity of ∼10-4 L¤ on MS, while during the accretion phase the same obje ...
Astronomy Unit Notes
... Example: a 40 watt light bulb 10 feet away appears brighter than a 40 watt bulb 100 feet away. ...
... Example: a 40 watt light bulb 10 feet away appears brighter than a 40 watt bulb 100 feet away. ...
Chapter 18 - Stars - University of New Mexico
... Historical measurements of the size and shape of Milky Way • First attempts by Caroline & William Herschel (1785) and Kapteyn (1922) by counting stars through telescopes. • Both found MW is a flattened structure. But both put the Sun near the center. Studies limited by small telescopes, lack of und ...
... Historical measurements of the size and shape of Milky Way • First attempts by Caroline & William Herschel (1785) and Kapteyn (1922) by counting stars through telescopes. • Both found MW is a flattened structure. But both put the Sun near the center. Studies limited by small telescopes, lack of und ...
Astronomy Solar System Formation Sun and Stellar Evolution
... 11. How is the Sun’s magnetic field related to the above characteristics? 12. The Sun’s Interior a. What is the source of energy production? Have a rough idea how this process occurs 13. Why are astronomers interested in the neutrino? 14. Explain why the Sun doesn’t collapse due to its own gravity? ...
... 11. How is the Sun’s magnetic field related to the above characteristics? 12. The Sun’s Interior a. What is the source of energy production? Have a rough idea how this process occurs 13. Why are astronomers interested in the neutrino? 14. Explain why the Sun doesn’t collapse due to its own gravity? ...
Lecture 33: The Lives of Stars Astronomy 141
... Stars shine because they are hot, and need a source of energy to keep shining. Main Sequence stars are powered by the fusion of Hydrogen into Helium in their cores The more massive a star is, the shorter its lifetime. Low-Mass stars are long-lived, spend some time as Red Giants, then leave behind a ...
... Stars shine because they are hot, and need a source of energy to keep shining. Main Sequence stars are powered by the fusion of Hydrogen into Helium in their cores The more massive a star is, the shorter its lifetime. Low-Mass stars are long-lived, spend some time as Red Giants, then leave behind a ...
Earth Science 25.2A : Stellar Evolution
... The Birth of a Star: The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds. These nebulae are made up of dust and gases. ...
... The Birth of a Star: The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds. These nebulae are made up of dust and gases. ...
Exam2 Review Slides
... cools – Outer layers cool enough for carbon flakes to form – Flakes are pushed outward by radiation pressure – Flakes drag stellar gas outward with them ...
... cools – Outer layers cool enough for carbon flakes to form – Flakes are pushed outward by radiation pressure – Flakes drag stellar gas outward with them ...
(Mike Riddle CTI)-84_eng_cr_v4.0
... accepted’ theory of stellar formation may be one of a hundred unsupported dogmas which constitute a large part of present-day ...
... accepted’ theory of stellar formation may be one of a hundred unsupported dogmas which constitute a large part of present-day ...
answers2008_09_BC
... Describe the life cycle of a typical solar-mass star from its formation to its eventual demise. Relate your account to the features of the HR diagram shown. ...
... Describe the life cycle of a typical solar-mass star from its formation to its eventual demise. Relate your account to the features of the HR diagram shown. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Research in observational
... do with mass-loss. The most massive stars seem to go through unstable phases where not just the huge WR mass loss, but something altogether huger takes place. A real outburst (not a supernova) that loses many solar masses in a short time. • LBVs might be the most massive stars where radiation pressu ...
... do with mass-loss. The most massive stars seem to go through unstable phases where not just the huge WR mass loss, but something altogether huger takes place. A real outburst (not a supernova) that loses many solar masses in a short time. • LBVs might be the most massive stars where radiation pressu ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.