Lesson 37 questions – Gravitational Field - science
... Binary stars separated by a distance of 1x1011m have been observed with an orbital period of 100 days. Calculate the mass of each star. ...
... Binary stars separated by a distance of 1x1011m have been observed with an orbital period of 100 days. Calculate the mass of each star. ...
Measuring Distance with Spectroscopic Parallax
... 2. There are 9.46!1015 meters in one light-year. Convert your distances to lightyears by dividing the distance in meters by this number. 3. Recall that our Milky Way galaxy is 100,000 light-years across. For each of your stars, use the space below to explain whether it is most likely inside our gala ...
... 2. There are 9.46!1015 meters in one light-year. Convert your distances to lightyears by dividing the distance in meters by this number. 3. Recall that our Milky Way galaxy is 100,000 light-years across. For each of your stars, use the space below to explain whether it is most likely inside our gala ...
B. protostar - University of Maryland Astronomy
... A. Carbon dioxide is the main ingredient of all planetary atmospheres. B. Carbon is versatile in forming complex, long-chain molecules. C. No other atom can combine easily with hydrogen and helium, the most abundant elements in the universe. D. Most rocks on Earth’s surface are composed primarily of ...
... A. Carbon dioxide is the main ingredient of all planetary atmospheres. B. Carbon is versatile in forming complex, long-chain molecules. C. No other atom can combine easily with hydrogen and helium, the most abundant elements in the universe. D. Most rocks on Earth’s surface are composed primarily of ...
11-Massive Stars
... to understand the complex bipolar outflows in massive star formation and proof will require interferometer observations. The outflows are difficult to study because multiple outflows often emanate from the same large scale core. Clusters of stars form simultaneously in a core and the outflows origin ...
... to understand the complex bipolar outflows in massive star formation and proof will require interferometer observations. The outflows are difficult to study because multiple outflows often emanate from the same large scale core. Clusters of stars form simultaneously in a core and the outflows origin ...
Stellar Evolution
... • Mass of Sun • Radius of Earth • Hot as Sun’s core • A million times denser than lead • Slowly cool off ...
... • Mass of Sun • Radius of Earth • Hot as Sun’s core • A million times denser than lead • Slowly cool off ...
STScI 2005
... • Stars generally form with a frequency that decreases with increasing mass for masses greater than ~1 M: ...
... • Stars generally form with a frequency that decreases with increasing mass for masses greater than ~1 M: ...
Stats talk - Harvard University
... • To avoid implosion stars must generate energy from fusion reactions •The stages of stars are determined by the type of fuel left: hydrogen, helium, carbon etc ...
... • To avoid implosion stars must generate energy from fusion reactions •The stages of stars are determined by the type of fuel left: hydrogen, helium, carbon etc ...
13 - Joe Griffin Media Ministries
... Although my emphasis was on the star observed by the Magi, I did touch on this a couple of times while explaining the Carousel. The Enochian School teaches that the starry story begins with Virgo (virgin birth) and ends with Leo (Second Advent) and in between is the angelic conflict being resolved b ...
... Although my emphasis was on the star observed by the Magi, I did touch on this a couple of times while explaining the Carousel. The Enochian School teaches that the starry story begins with Virgo (virgin birth) and ends with Leo (Second Advent) and in between is the angelic conflict being resolved b ...
Homework #3 MHC Astronomy 100/101/110 Prof. Stage For ALL the
... explain your reasoning. Answers without work will lose points. This assignment is worth 40 points total, with an extra‐credit question worth up to an additional 4 points. You do not need to type this entire assignment. Some of the problems are more easily written out by hand. Just be neat! 1. U ...
... explain your reasoning. Answers without work will lose points. This assignment is worth 40 points total, with an extra‐credit question worth up to an additional 4 points. You do not need to type this entire assignment. Some of the problems are more easily written out by hand. Just be neat! 1. U ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Fall 2001 Professor: ER Capriotti
... glowing because they are hot, the one that emits the most light from each unit area of surface will also A. absorb light hitting it most efficiently. B. appear bluest. C. appear faintest. D. appear reddest. 47. The first double stars were discovered by A. Herschel B. Galileo C. Newton D. Copernicus ...
... glowing because they are hot, the one that emits the most light from each unit area of surface will also A. absorb light hitting it most efficiently. B. appear bluest. C. appear faintest. D. appear reddest. 47. The first double stars were discovered by A. Herschel B. Galileo C. Newton D. Copernicus ...
I CAN SEE THE STARS IN YOUR EYES
... Your space craft begins to travel at the speed of light, taking you towards the sun. Traveling at this speed, the trip from Earth to the sun, a distance of 93 million miles, would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet, to get to the next closest star, Proxima Centauri, would ...
... Your space craft begins to travel at the speed of light, taking you towards the sun. Traveling at this speed, the trip from Earth to the sun, a distance of 93 million miles, would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet, to get to the next closest star, Proxima Centauri, would ...
27.1: Characteristics of Stars
... The greater the mass of the star, the shorter its lifetime Low mass stars with an original mass of less than 8 times the sun (8 solar masses) will become Planetary Nebula. The remnant state of these stars is a white dwarf. High mass stars containing more than 8 solar masses will explode violently as ...
... The greater the mass of the star, the shorter its lifetime Low mass stars with an original mass of less than 8 times the sun (8 solar masses) will become Planetary Nebula. The remnant state of these stars is a white dwarf. High mass stars containing more than 8 solar masses will explode violently as ...
ecliptic. - Valhalla High School
... So, 360° = 24 h R.A., 15° = 1 h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Right ascension increases from west to east (note that we are looking at the exterior of the celestial sphere in the above picture). ...
... So, 360° = 24 h R.A., 15° = 1 h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Right ascension increases from west to east (note that we are looking at the exterior of the celestial sphere in the above picture). ...
Stars - Academic Computer Center
... • But as we already know we can learn a lot from light! • Light can tell us about a star’s: ...
... • But as we already know we can learn a lot from light! • Light can tell us about a star’s: ...
Astronomy Worksheet
... Notes about certain spectral classes: *In general a hot star’s spectrum looks smoother than a cooler star’s spectrum. *In very hot stars (> 10,000 K) most of the Hydrogen gas in the star’s atmosphere will be ionized. Since an ionized Hydrogen atom has no electron it cannot produce any spectral lines ...
... Notes about certain spectral classes: *In general a hot star’s spectrum looks smoother than a cooler star’s spectrum. *In very hot stars (> 10,000 K) most of the Hydrogen gas in the star’s atmosphere will be ionized. Since an ionized Hydrogen atom has no electron it cannot produce any spectral lines ...
annie jump cannon
... “In 1896 Annie Jump Cannon was hired by Professor Edward Charles Pickering, director of the Harvard College Observatory to catalogue variable stars and classify the spectra of southern [hemisphere] stars.” ...
... “In 1896 Annie Jump Cannon was hired by Professor Edward Charles Pickering, director of the Harvard College Observatory to catalogue variable stars and classify the spectra of southern [hemisphere] stars.” ...
Evolved Stellar Populations
... and bluer than younger and foreground objects. C-rich are redder than O-rich AGB stars Both criteria exclude upper-RGB stars. ...
... and bluer than younger and foreground objects. C-rich are redder than O-rich AGB stars Both criteria exclude upper-RGB stars. ...
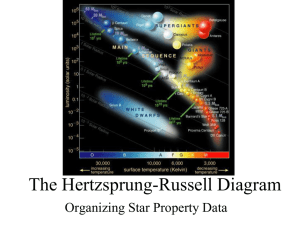
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Solar Spectrum Birth of Spectroscopy Kirchhoff`s Laws Types of
... • A, F, G stars; T = 5,000 - 12,000 K • A few more spectral lines in visual spectrum than in O & B stars – metals are readily excited & ionized at these temperatures – lines from metals in the ultraviolet • Hydrogen lines strong – temperature is high enough to excite electrons in H atoms but not to ...
... • A, F, G stars; T = 5,000 - 12,000 K • A few more spectral lines in visual spectrum than in O & B stars – metals are readily excited & ionized at these temperatures – lines from metals in the ultraviolet • Hydrogen lines strong – temperature is high enough to excite electrons in H atoms but not to ...
Ch16_MilkyWayGalaxy
... • Some energetic event, perhaps a supernova explosion, violently disturbed the center in the not-to-distant past • Deep within the core lies an incredibly small (10 AU diameter) radio source known as Sgr A* • A 5 ×106 M black hole may occupy the very center of the galaxy! ...
... • Some energetic event, perhaps a supernova explosion, violently disturbed the center in the not-to-distant past • Deep within the core lies an incredibly small (10 AU diameter) radio source known as Sgr A* • A 5 ×106 M black hole may occupy the very center of the galaxy! ...
ph607-14-a3uni - University of Kent
... in solar masses per year. 3. Describe the colour, stellar population and gas content of E, SO and Irr galaxies. 4. Explain the difference between the monolithic and hierarchical theories for the ...
... in solar masses per year. 3. Describe the colour, stellar population and gas content of E, SO and Irr galaxies. 4. Explain the difference between the monolithic and hierarchical theories for the ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.