File
... This week, we will first discuss what will happen when the Sun dies: It will follow the same path as other single lightweight stars, stars born with up to about 10 (but possibly as low as 8) times the mass of the Sun. They will go through planetary nebula (see figure) and white-dwarf stages. Then we ...
... This week, we will first discuss what will happen when the Sun dies: It will follow the same path as other single lightweight stars, stars born with up to about 10 (but possibly as low as 8) times the mass of the Sun. They will go through planetary nebula (see figure) and white-dwarf stages. Then we ...
Week 11 notes
... two gaseous phases (warm, diffuse phase of the ISM): T ~ 10 to 100 K; n ~ 1 to 100 atoms/cm3 ...
... two gaseous phases (warm, diffuse phase of the ISM): T ~ 10 to 100 K; n ~ 1 to 100 atoms/cm3 ...
Document
... The neutrino detectors capable to separate the contributions from different types of neutrino in the registered signal are of great value for detection of neutrino signal from gravitational collapses in our Galaxy. Such detectors are those that contain scintillator+Fe, for example, LSD (Mont Blanc) ...
... The neutrino detectors capable to separate the contributions from different types of neutrino in the registered signal are of great value for detection of neutrino signal from gravitational collapses in our Galaxy. Such detectors are those that contain scintillator+Fe, for example, LSD (Mont Blanc) ...
Stability of hot neutron stars
... presence of the Urca shell the energy losses owing to neutrino emission and the entropy increase resulting from non-equilibrium beta reactions are much smaller than the rate of decrease of the energy of pulsations by the excitation of shortwavelength acoustic waves. The dissipation of the vibrationa ...
... presence of the Urca shell the energy losses owing to neutrino emission and the entropy increase resulting from non-equilibrium beta reactions are much smaller than the rate of decrease of the energy of pulsations by the excitation of shortwavelength acoustic waves. The dissipation of the vibrationa ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... orbital period squared is proportional to semi-major axis cubed • P2 = a3 ...
... orbital period squared is proportional to semi-major axis cubed • P2 = a3 ...
Chapter 9 “The Family of Stars “
... spectroscopic: only by taking a spectrum can we see there are two stars. Astronomers wait to see how long it takes for spectral lines to return to their starting positions. - c. eclipsing: stars eclipse one another. Astronomers study the light curves from each star. ...
... spectroscopic: only by taking a spectrum can we see there are two stars. Astronomers wait to see how long it takes for spectral lines to return to their starting positions. - c. eclipsing: stars eclipse one another. Astronomers study the light curves from each star. ...
The Solar System - Astronomy - The University of Texas at Austin
... ~2,400km; however, Pluto (and Sedna) itself may be just a bigger version of the KBOs. • The peculiarity of Pluto can be seen from its orbit around the Sun: while the other planet‘s orbits are nearly circular, Pluto’s is highly elongated, arguing for a different formation process for Pluto. ...
... ~2,400km; however, Pluto (and Sedna) itself may be just a bigger version of the KBOs. • The peculiarity of Pluto can be seen from its orbit around the Sun: while the other planet‘s orbits are nearly circular, Pluto’s is highly elongated, arguing for a different formation process for Pluto. ...
Winter - Dark Sky Discovery
... The plough is perhaps the most easily recognised group of stars in the northern sky and it is a very useful ‘skymark’. The plough is always above the horizon and allows us to find Polaris, or the Pole Star. If you imagine the plough as a saucepan, then you can follow the two stars furthest from the ...
... The plough is perhaps the most easily recognised group of stars in the northern sky and it is a very useful ‘skymark’. The plough is always above the horizon and allows us to find Polaris, or the Pole Star. If you imagine the plough as a saucepan, then you can follow the two stars furthest from the ...
Int. Sci. 9 - Universe Powerpoint
... • As a protostar contracts, its internal pressure & temp continue to rise • A star is formed when a contracting cloud of gas & dust becomes so dense & hot that nuclear fusion begins • New stars enter the Main Sequence stage ...
... • As a protostar contracts, its internal pressure & temp continue to rise • A star is formed when a contracting cloud of gas & dust becomes so dense & hot that nuclear fusion begins • New stars enter the Main Sequence stage ...
Ay 112 Midterm review
... have distinctively different HR diagrams. If two open clusters have different turn off masses, the one with the heaviest main sequence star still remaining will be the younger. ...
... have distinctively different HR diagrams. If two open clusters have different turn off masses, the one with the heaviest main sequence star still remaining will be the younger. ...
luminosity1
... given element is in a star. • HD 161817 has much less of all the elements, other than Hydrogen and Helium, than the Sun. • In fact, it has about 0.03 the value of the Sun for all 90 elements. That is 3% the amount in the Sun. The most deficient star known has about 0.001% the Sun. • There are also s ...
... given element is in a star. • HD 161817 has much less of all the elements, other than Hydrogen and Helium, than the Sun. • In fact, it has about 0.03 the value of the Sun for all 90 elements. That is 3% the amount in the Sun. The most deficient star known has about 0.001% the Sun. • There are also s ...
20_LectureOutline
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a su ...
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a su ...
A little bit more to do. Stefan
... given element is in a star. • HD 161817 has much less of all the elements, other than Hydrogen and Helium, than the Sun. • In fact, it has about 0.03 the value of the Sun for all 90 elements. That is 3% the amount in the Sun. The most deficient star known has about 0.001% the Sun. • There are also s ...
... given element is in a star. • HD 161817 has much less of all the elements, other than Hydrogen and Helium, than the Sun. • In fact, it has about 0.03 the value of the Sun for all 90 elements. That is 3% the amount in the Sun. The most deficient star known has about 0.001% the Sun. • There are also s ...
Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date
... the components. Single lined eclipsing binary systems via radial velocity technique give us a unique opportunity to study the low mass end of the main sequence as companions to brighter primaries. Despite a large number of low mass stars present in our galaxy, masses and radii for these stars are st ...
... the components. Single lined eclipsing binary systems via radial velocity technique give us a unique opportunity to study the low mass end of the main sequence as companions to brighter primaries. Despite a large number of low mass stars present in our galaxy, masses and radii for these stars are st ...
Take-home midterm, due Fri 3/16
... What is the orbital period of that planet? Can you tel anything about the mass of that planet, just from knowing its orbital period? 3. Interstellar dust grains have typical masses of approximately 1x10-17 kg. Find the rms speed of a dust grain in an interstellar molecular cloud whose temprature is ...
... What is the orbital period of that planet? Can you tel anything about the mass of that planet, just from knowing its orbital period? 3. Interstellar dust grains have typical masses of approximately 1x10-17 kg. Find the rms speed of a dust grain in an interstellar molecular cloud whose temprature is ...
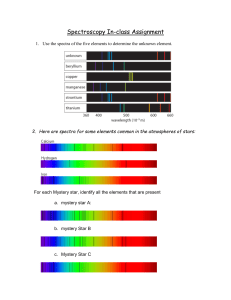
Triangulation and Spectroscopy In-class Assignment
... can stretch or crunch together depending on the relative position of objects. That said, we don't notice it on daily-life-sized scale because light travels so much faster than the speed of sound — a million times faster, ESA noted. American astronomer Edwin Hubble (who the Hubble Space Telescope is ...
... can stretch or crunch together depending on the relative position of objects. That said, we don't notice it on daily-life-sized scale because light travels so much faster than the speed of sound — a million times faster, ESA noted. American astronomer Edwin Hubble (who the Hubble Space Telescope is ...
Astronomy in the secondary school classroom
... study of matter beyond Earth – planets in the Solar System, stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, galaxies in the Universe, and diffuse matter between these concentrations. The perspective is rooted from our viewpoint on or near Earth using telescopes or robotic probes. Astrophysics (astro = star, physis = ...
... study of matter beyond Earth – planets in the Solar System, stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, galaxies in the Universe, and diffuse matter between these concentrations. The perspective is rooted from our viewpoint on or near Earth using telescopes or robotic probes. Astrophysics (astro = star, physis = ...
1 How luminous are stars?
... We measure mass using gravity Direct mass measurements are possible only for stars in binary star systems ...
... We measure mass using gravity Direct mass measurements are possible only for stars in binary star systems ...
Spectroscopy – the study of the colors of light (the spectrum) given
... Spectroscopy – the study of the colors of light (the spectrum) given off by luminous objects. Stars have absorption lines at different wavelengths where the energy is precisely correct to excite the electrons to a new level. ...
... Spectroscopy – the study of the colors of light (the spectrum) given off by luminous objects. Stars have absorption lines at different wavelengths where the energy is precisely correct to excite the electrons to a new level. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram—key to understanding properties of stars. 26 Sept
... – A show highlighting the current sky, spectacular gatherings of Venus with the moon and other planets in coming months. See what Galileo saw through his telescope 400 years ago— the Milky Way and the Pleiades, details on the moon, the four moons of Jupiter, the phases of Venus, and the mysterious d ...
... – A show highlighting the current sky, spectacular gatherings of Venus with the moon and other planets in coming months. See what Galileo saw through his telescope 400 years ago— the Milky Way and the Pleiades, details on the moon, the four moons of Jupiter, the phases of Venus, and the mysterious d ...
wk11noQ
... two gaseous phases (warm, diffuse phase of the ISM): T ~ 10 to 100 K; n ~ 1 to 100 atoms/cm3 ...
... two gaseous phases (warm, diffuse phase of the ISM): T ~ 10 to 100 K; n ~ 1 to 100 atoms/cm3 ...
The H-R Diagram
... • Main Sequence is a mass sequence, lower right to upper left is rising mass. Luminosity goes as (Mass)3.5 on the main sequence • Lowest mass star=0.08Msun, lower than that can’t fuse hydrogen • Highest mass stars ~150Msun, higher mass would be so luminous they’d blow excess mass back out to space • ...
... • Main Sequence is a mass sequence, lower right to upper left is rising mass. Luminosity goes as (Mass)3.5 on the main sequence • Lowest mass star=0.08Msun, lower than that can’t fuse hydrogen • Highest mass stars ~150Msun, higher mass would be so luminous they’d blow excess mass back out to space • ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.















![Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747311_2-a6f8878211ea1c8526dde4b9d41aac5c-300x300.png)