The HR Diagram (PowerPoint version)
... They are ~ 2/3 H, ~ 1/3 He, with just a few percent of everything else (at least in the outer parts, which is what the spectrum tells us about) Incidentally, helium was first detected in the solar spectrum (hence its name, from the Greek ‘helios’) before it was found naturally on Earth. ...
... They are ~ 2/3 H, ~ 1/3 He, with just a few percent of everything else (at least in the outer parts, which is what the spectrum tells us about) Incidentally, helium was first detected in the solar spectrum (hence its name, from the Greek ‘helios’) before it was found naturally on Earth. ...
Document
... that there is a black hole that came from a massive star: – Strong X-ray sources (usually flares). – Optically dark objects (that is, only one star is seen in the spectrum, and it is the mass-losing one). – Masses too large to be a white dwarf or a neutron star. ...
... that there is a black hole that came from a massive star: – Strong X-ray sources (usually flares). – Optically dark objects (that is, only one star is seen in the spectrum, and it is the mass-losing one). – Masses too large to be a white dwarf or a neutron star. ...
Death of Massive Stars
... • Any event that takes place inside the Schwarzchild radius of a black hole can never be seen by the outside universe. The Schwarzchild radius is effectively the boundary of the black hole (its surface), and is called the event horizon. • The only things we can tell about the matter inside the black ...
... • Any event that takes place inside the Schwarzchild radius of a black hole can never be seen by the outside universe. The Schwarzchild radius is effectively the boundary of the black hole (its surface), and is called the event horizon. • The only things we can tell about the matter inside the black ...
The light curves for a nova look like the following.
... SN1987a has provided us with a great wealth of information about supernova physics, and help to largely experimentally confirm the basic predictions of the core-bounce picture (although with good ...
... SN1987a has provided us with a great wealth of information about supernova physics, and help to largely experimentally confirm the basic predictions of the core-bounce picture (although with good ...
Galaxy clusters - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... source, we can figure out the total mass in the lens. This provides an independent confirmation of dark matter. • A lense can act as a huge telescope. The deepest images of the most distant galaxies are obtained with clusters acting as gravitational lenses. ...
... source, we can figure out the total mass in the lens. This provides an independent confirmation of dark matter. • A lense can act as a huge telescope. The deepest images of the most distant galaxies are obtained with clusters acting as gravitational lenses. ...
Orion-pr-2009 - Astrophysics Research Institute
... does not see is an enormous cloud of molecules and dust particles that hide a vast region where young stars are currently being born. On the sky, the region – known to astronomers as the Orion Molecular Cloud -- is more than 20 times the angular size of the full moon, spanning from far above the hun ...
... does not see is an enormous cloud of molecules and dust particles that hide a vast region where young stars are currently being born. On the sky, the region – known to astronomers as the Orion Molecular Cloud -- is more than 20 times the angular size of the full moon, spanning from far above the hun ...
Nebular theory
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
Power Point of Slides I never Got to
... How to see this without too much math? Concept is “center of mass”, and the more massive the nucleus, the closer the center of mass will be to it. This means for the same separation, since both orbit the center of mass, the electron will go faster for the heavier nucleus case since the nucleus trave ...
... How to see this without too much math? Concept is “center of mass”, and the more massive the nucleus, the closer the center of mass will be to it. This means for the same separation, since both orbit the center of mass, the electron will go faster for the heavier nucleus case since the nucleus trave ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West, Use the simplified celestial sphere diagram to determine the visibility of an object and its maximum altitude, given its declination at any latitude on the Earth, Use the fact that the Earth rotates 1 ...
... Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West, Use the simplified celestial sphere diagram to determine the visibility of an object and its maximum altitude, given its declination at any latitude on the Earth, Use the fact that the Earth rotates 1 ...
a High-Mass Protostar with a Rotating Disk.
... the disk (Fig 2), we have not found any evidence for more than one active star formation center in the NGC 7538 S cloud core. The DCN map shows a secondary peak 600 to the northwest of the protostar (at Vlsr ∼ −59 km s−1 ), which is also evident in the continuum map. However, whether this is a separ ...
... the disk (Fig 2), we have not found any evidence for more than one active star formation center in the NGC 7538 S cloud core. The DCN map shows a secondary peak 600 to the northwest of the protostar (at Vlsr ∼ −59 km s−1 ), which is also evident in the continuum map. However, whether this is a separ ...
DP11 Foundations of Astronomy
... The lives of stars are extremely long – millions, billions or even trillions of years. So how can we understand them at all, when the whole of recorded human history is less than 1% of the life of even the shortest-lived star? Luckily, we have a huge sample to work with. There are 200 billion stars ...
... The lives of stars are extremely long – millions, billions or even trillions of years. So how can we understand them at all, when the whole of recorded human history is less than 1% of the life of even the shortest-lived star? Luckily, we have a huge sample to work with. There are 200 billion stars ...
Part 2 of Our Lecture
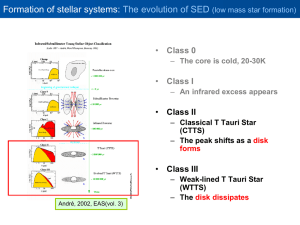
... to the same procedures followed for Tr 37) only 1 sample shows indications of active accretion (CTTS). – black dotted line : similar spectral type derived from Kenyon & Hartmann (1995) – magenta dashed line : the median disk emission in Taurus – light blue line : the median disk emission in Tr 37 ...
... to the same procedures followed for Tr 37) only 1 sample shows indications of active accretion (CTTS). – black dotted line : similar spectral type derived from Kenyon & Hartmann (1995) – magenta dashed line : the median disk emission in Taurus – light blue line : the median disk emission in Tr 37 ...
*Studying Complex Star-Forming Fields: Rosette Nebula and Monoceros Loop by Chris Hathaway and Anthony Kuchera
... idea in the contemporary star-formation theory leading astronomers to constantly look for observational evidence. Star formation appears to be clumped into a hierarchy of structures, from small stellar clusters to giant star-forming complexes. The interplay between gravity and supersonic turbulence ...
... idea in the contemporary star-formation theory leading astronomers to constantly look for observational evidence. Star formation appears to be clumped into a hierarchy of structures, from small stellar clusters to giant star-forming complexes. The interplay between gravity and supersonic turbulence ...
How do atoms interact with light?
... The spectra of stars are more complicated than pure blackbody spectra. They contain characteristic lines, called absorption lines. With what we have learned about atomic structure, we can now understand how those lines are formed. ...
... The spectra of stars are more complicated than pure blackbody spectra. They contain characteristic lines, called absorption lines. With what we have learned about atomic structure, we can now understand how those lines are formed. ...
Document
... Dr. Frank Drake is the Director of the SETI Institute's Center for the Study of Life in the Universe and also serves on the Board of Trustees of the SETI Institute as Chairman Emeritus. In 1960, as a staff member of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, he conducted the first radio search for e ...
... Dr. Frank Drake is the Director of the SETI Institute's Center for the Study of Life in the Universe and also serves on the Board of Trustees of the SETI Institute as Chairman Emeritus. In 1960, as a staff member of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, he conducted the first radio search for e ...
Binary Stars/Star Clusters
... The faster the source, the more compression/stretching Sound: frequency (pitch) of a siren gets higher as ambulance moves toward an observer (vice versa) MPP©2004 ...
... The faster the source, the more compression/stretching Sound: frequency (pitch) of a siren gets higher as ambulance moves toward an observer (vice versa) MPP©2004 ...
08 September: How far away are the closest stars?
... • From Abell “Exploration of the Universe”, 1966: “For only about 700 stars, however, are the parallaxes large enough to be measured with a precision of 10 percent or better”. • 1 percent parallaxes for only few dozen stars (p377 of book) ...
... • From Abell “Exploration of the Universe”, 1966: “For only about 700 stars, however, are the parallaxes large enough to be measured with a precision of 10 percent or better”. • 1 percent parallaxes for only few dozen stars (p377 of book) ...
Stars & Constellations
... the North Star (which always points North). Once navigators had found North, they could observe its height in the sky and hence work out their latitude (how far North / South they are). Now they know how far North they are + the direction they’re traveling ...
... the North Star (which always points North). Once navigators had found North, they could observe its height in the sky and hence work out their latitude (how far North / South they are). Now they know how far North they are + the direction they’re traveling ...
The Milky Way: Home to Star Clusters
... was the original extent of the galaxy, and that this was created first, from the primordial gas that eventually collapsed in on itself, also demonstrated by the old stars contained within the globular clusters. This matter condensed to create the central bulge, which ultimately began to rotate, crea ...
... was the original extent of the galaxy, and that this was created first, from the primordial gas that eventually collapsed in on itself, also demonstrated by the old stars contained within the globular clusters. This matter condensed to create the central bulge, which ultimately began to rotate, crea ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.