Solution key
... twice the redshift of Galaxy #2. The apparent magnitude of Galaxy #1 minus the apparent magnitude for Galaxy #2 is A. -1.5 B. -0.75 C. 0 D. +0.75 E. +1.5 ___B___8. Which is oldest? A. M1 B. M3 C. M45 D. M67 E. The Solar System ___C___9. A star moves horizontally and to the right on an HR diagram. Wh ...
... twice the redshift of Galaxy #2. The apparent magnitude of Galaxy #1 minus the apparent magnitude for Galaxy #2 is A. -1.5 B. -0.75 C. 0 D. +0.75 E. +1.5 ___B___8. Which is oldest? A. M1 B. M3 C. M45 D. M67 E. The Solar System ___C___9. A star moves horizontally and to the right on an HR diagram. Wh ...
Star A
... stars we observe are quite young—less than a few tens of millions of years old. The reason is that their nuclear reactions proceed so rapidly that their fuel is quickly depleted despite their large masses. At the opposite end of the main sequence, the low core density and temperature of an 0.1-solar ...
... stars we observe are quite young—less than a few tens of millions of years old. The reason is that their nuclear reactions proceed so rapidly that their fuel is quickly depleted despite their large masses. At the opposite end of the main sequence, the low core density and temperature of an 0.1-solar ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17)
... Knowing the apparent brightness (really easy to measure) and luminosity, this gives the distance (review earlier material if you don’t understand this), without having to get a trigonometric parallax. Distances obtained in this way are called “spectroscopic parallaxes.” (In “spectroscopic parallax” ...
... Knowing the apparent brightness (really easy to measure) and luminosity, this gives the distance (review earlier material if you don’t understand this), without having to get a trigonometric parallax. Distances obtained in this way are called “spectroscopic parallaxes.” (In “spectroscopic parallax” ...
Sample Answer Sheet for The 10 Tourist Wonders of the
... As much as 90% of the star’s material can be thrown off during the explosion and, in the process, new (heavier) elements are made, and then distributed at high speed into the Galaxy. In many ways, life on Earth owes its existence to supernovae and the fact that they “recycle” the material of early g ...
... As much as 90% of the star’s material can be thrown off during the explosion and, in the process, new (heavier) elements are made, and then distributed at high speed into the Galaxy. In many ways, life on Earth owes its existence to supernovae and the fact that they “recycle” the material of early g ...
From Dust to Planetesimals
... 1. To find clues on the planet formation mechanisms & time scales 2. To identify signatures of planet-forming protostellar disks ...
... 1. To find clues on the planet formation mechanisms & time scales 2. To identify signatures of planet-forming protostellar disks ...
Read
... Read: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is an important tool in the study of stars. In the early 1900’s the two astronomers investigated nearby stars and found a relationship between their color and brightness. This work lead to the important discovery that the brightness of a star is related to the t ...
... Read: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is an important tool in the study of stars. In the early 1900’s the two astronomers investigated nearby stars and found a relationship between their color and brightness. This work lead to the important discovery that the brightness of a star is related to the t ...
Unit 4: Astronomy
... 3. Describe a couple of ways that our atmosphere interferes with the observation of objects in space and a couple of ways that astronomers can reduce or eliminate this interference. 4. What is a “non-optical telescope”? Describe a couple of advantages to using one of these in addition to an optical ...
... 3. Describe a couple of ways that our atmosphere interferes with the observation of objects in space and a couple of ways that astronomers can reduce or eliminate this interference. 4. What is a “non-optical telescope”? Describe a couple of advantages to using one of these in addition to an optical ...
Powerpoint for today
... Effective Temperature ~ 1/mass Universe cools with time, so that after 1021 y, the Universe is cooler than a 1 solar mass black hole (10-7 K) After 1035 y, even 1 billion solar mass black holes have begun to evaporate. ...
... Effective Temperature ~ 1/mass Universe cools with time, so that after 1021 y, the Universe is cooler than a 1 solar mass black hole (10-7 K) After 1035 y, even 1 billion solar mass black holes have begun to evaporate. ...
mass of star
... Effective Temperature ~ 1/mass Universe cools with time, so that after 1021 y, the Universe is cooler than a 1 solar mass black hole (10-7 K) After 1035 y, even 1 billion solar mass black holes have begun to evaporate. ...
... Effective Temperature ~ 1/mass Universe cools with time, so that after 1021 y, the Universe is cooler than a 1 solar mass black hole (10-7 K) After 1035 y, even 1 billion solar mass black holes have begun to evaporate. ...
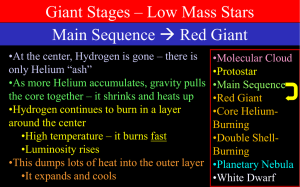
Giant Stars
... •It doesn’t produce much energy – Helium gets used up fast •Eventually, Helium is completely used up and we have a Carbon/Oxygen core left •50 Myr for the Sun •The star enters Double Shell-Burning ...
... •It doesn’t produce much energy – Helium gets used up fast •Eventually, Helium is completely used up and we have a Carbon/Oxygen core left •50 Myr for the Sun •The star enters Double Shell-Burning ...
HOMEWORK #1
... #3. The Sun’s absolute visual magnitude is M=4.8. What would the Sun’s apparent magnitude be at the distance of the Andromeda galaxy, 2.5 million light-years? The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can detect stars as faint as 29 in a 10-hour long exposure – its so-called “limiting magnitude.” Could HST d ...
... #3. The Sun’s absolute visual magnitude is M=4.8. What would the Sun’s apparent magnitude be at the distance of the Andromeda galaxy, 2.5 million light-years? The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can detect stars as faint as 29 in a 10-hour long exposure – its so-called “limiting magnitude.” Could HST d ...
Word
... #3. The Sun’s absolute visual magnitude is M=4.8. What would the Sun’s apparent magnitude be at the distance of the Andromeda galaxy, 2.5 million light-years? The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can detect stars as faint as 29 in a 10-hour long exposure – its so-called “limiting magnitude.” Could HST d ...
... #3. The Sun’s absolute visual magnitude is M=4.8. What would the Sun’s apparent magnitude be at the distance of the Andromeda galaxy, 2.5 million light-years? The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can detect stars as faint as 29 in a 10-hour long exposure – its so-called “limiting magnitude.” Could HST d ...
Spectral Classification
... B stars are extremely luminous and blue. As O and B stars are so powerful, they live for a very short time. They do not stray far from the area in which they were formed as they don't have the time. They therefore tend to cluster together in what we call OB1 associations. and contains all of the con ...
... B stars are extremely luminous and blue. As O and B stars are so powerful, they live for a very short time. They do not stray far from the area in which they were formed as they don't have the time. They therefore tend to cluster together in what we call OB1 associations. and contains all of the con ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. October 2005
... approached on November 7th. The disc is approaching maximum diameter making surface features visible in small telescopes. The rotation of Mars is about half an hour slower than that of the Earth so that observations made at the same time on successive nights show only a small change in surface featu ...
... approached on November 7th. The disc is approaching maximum diameter making surface features visible in small telescopes. The rotation of Mars is about half an hour slower than that of the Earth so that observations made at the same time on successive nights show only a small change in surface featu ...
The Transient Radio Sky Astrophysical and Artificial
... Cosmic reionization and first light HI + continuum survey: galaxy evolution and dark energy ...
... Cosmic reionization and first light HI + continuum survey: galaxy evolution and dark energy ...
Notes 4, p. 1-3
... ⊲ In a non-equilibrium state, there is not enough outward force to oppose the gravitational collapse so the star begins to contract ⊲ For the star to contract, gravitational potential energy must be lost; in this case it goes into heating the star at a smaller radius (keeping the star shining) ⊲ The ...
... ⊲ In a non-equilibrium state, there is not enough outward force to oppose the gravitational collapse so the star begins to contract ⊲ For the star to contract, gravitational potential energy must be lost; in this case it goes into heating the star at a smaller radius (keeping the star shining) ⊲ The ...
Planets in different environments
... Most stars do not form in isolation but in stellar clusters. In a cluster, the protoplanetary disks and the planets are effected by: the intensive X-ray and extreme UV-radiation (XUV) from the hottest stars in the cluster, and by close encounters of the disks and the planets with other stars in ...
... Most stars do not form in isolation but in stellar clusters. In a cluster, the protoplanetary disks and the planets are effected by: the intensive X-ray and extreme UV-radiation (XUV) from the hottest stars in the cluster, and by close encounters of the disks and the planets with other stars in ...
Chapter 12 Star Stuff How do stars form?
... The star has become a red giant called a “double-shell burning star” This double-shell-burning stage is unsteady, and the fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. With each pulse, carbon gets dredged up from the core and transported into the overlying “envelope” Soon tha ...
... The star has become a red giant called a “double-shell burning star” This double-shell-burning stage is unsteady, and the fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. With each pulse, carbon gets dredged up from the core and transported into the overlying “envelope” Soon tha ...
Star Formation in the Galaxy, An Observational Overview
... accompanied by a drastic increase in the star’s luminosity. Thus begins the post-main sequence phase of stellar evolution during which the star evolves away from the main sequence while keeping its temperature roughly constant in a manner prescribed by Hayashi (Hayasi & Hoshi 1961). The inner core b ...
... accompanied by a drastic increase in the star’s luminosity. Thus begins the post-main sequence phase of stellar evolution during which the star evolves away from the main sequence while keeping its temperature roughly constant in a manner prescribed by Hayashi (Hayasi & Hoshi 1961). The inner core b ...
Pallavicini - IASF Milano
... GO programmes, are starting to cover the full age-metallicity plane of nearby open clusters. They allow addressing the question whether a cluster of a given age is representative of all clusters with the same age. ...
... GO programmes, are starting to cover the full age-metallicity plane of nearby open clusters. They allow addressing the question whether a cluster of a given age is representative of all clusters with the same age. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.