Evidence for the Big Bang
... a rushing to fill empty space The WHOLE universe is expanding - there is no empty space ...
... a rushing to fill empty space The WHOLE universe is expanding - there is no empty space ...
Supernova - Mid-Pacific Institute
... supported by the release of nuclear energy. If the star is particularly massive, then its core will collapse and in so doing will release a huge amount of energy. This will cause a blast wave that ejects the star's envelope into interstellar space. ...
... supported by the release of nuclear energy. If the star is particularly massive, then its core will collapse and in so doing will release a huge amount of energy. This will cause a blast wave that ejects the star's envelope into interstellar space. ...
Instruments and Science Programs - California State University
... will be an education. We intend to observe more novae, but this is a target-of-opportunity program: if no novae are having eruptions when we want to observe, we can’t get data. Then again, summer is nova season, since they are concentrated in the Galactic plane and center, so we won’t have to wait ...
... will be an education. We intend to observe more novae, but this is a target-of-opportunity program: if no novae are having eruptions when we want to observe, we can’t get data. Then again, summer is nova season, since they are concentrated in the Galactic plane and center, so we won’t have to wait ...
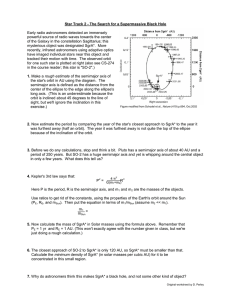
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
Test#4
... 24. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the stars of the disk component of our galaxy? a. circular orbits, b. randomly inclined orbits, c. higher metal abundance, d. young stars 25. As matter streams into a black hole it usually forms what kind of structure a) accretion disk, b) spher ...
... 24. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the stars of the disk component of our galaxy? a. circular orbits, b. randomly inclined orbits, c. higher metal abundance, d. young stars 25. As matter streams into a black hole it usually forms what kind of structure a) accretion disk, b) spher ...
large PDF file
... – a red giant when shell hydrogen fusion begins – a horizontal-branch star when core helium fusion begins – an asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star when the helium in the core is exhausted and shell helium fusion ...
... – a red giant when shell hydrogen fusion begins – a horizontal-branch star when core helium fusion begins – an asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star when the helium in the core is exhausted and shell helium fusion ...
Chapter 20 Notes (smaller PDF file)
... – a red giant when shell hydrogen fusion begins – a horizontal-branch star when core helium fusion begins – an asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star when the helium in the core is exhausted and shell helium fusion ...
... – a red giant when shell hydrogen fusion begins – a horizontal-branch star when core helium fusion begins – an asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star when the helium in the core is exhausted and shell helium fusion ...
The Ultraluminous X-ray Source in Holmberg IX and its Environment
... mass black holes (IMBHs) having 102 to 105 solar masses (Colbert & Mushotzky 1999) or non-isotropic emission beamed into our line-of-sight (King et al. 2001). Here, we are interested in one of these objects, Holmberg IX X-1, located at a distance of 3.6 Mpc in a dwarf galaxy companion of M81. Miller ...
... mass black holes (IMBHs) having 102 to 105 solar masses (Colbert & Mushotzky 1999) or non-isotropic emission beamed into our line-of-sight (King et al. 2001). Here, we are interested in one of these objects, Holmberg IX X-1, located at a distance of 3.6 Mpc in a dwarf galaxy companion of M81. Miller ...
Wien`s law - Uplift Education
... Solutions to Olber’s paradox • Perhaps the Universe is not infinite. But current model of the Universe is that it is infinite. • Perhaps the light is absorbed before it gets to us. But then Universe would warm up and eventually reradiate energy. Real help: the Big Bang model leads to the idea that t ...
... Solutions to Olber’s paradox • Perhaps the Universe is not infinite. But current model of the Universe is that it is infinite. • Perhaps the light is absorbed before it gets to us. But then Universe would warm up and eventually reradiate energy. Real help: the Big Bang model leads to the idea that t ...
13. Star Formation
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure. • Emission lines from molecules in a cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio ...
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure. • Emission lines from molecules in a cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio ...
November 2008 - Otterbein University
... • Stars thinned out very fast at right angles to Milky Way • In the plane of the Milky Way the thinning was slower and depended upon the direction in which he looked ...
... • Stars thinned out very fast at right angles to Milky Way • In the plane of the Milky Way the thinning was slower and depended upon the direction in which he looked ...
iptfsummer2014bildsten
... • He WD cools, continues to transit the star, but the other part of the eclipse becomes less important. . . Find these in iPTF? • The lower mass star then evolves, and a similar unstable mass transfer will occur, revealing yet another He WD, most likely in a very tight binary. • Gravitational waves ...
... • He WD cools, continues to transit the star, but the other part of the eclipse becomes less important. . . Find these in iPTF? • The lower mass star then evolves, and a similar unstable mass transfer will occur, revealing yet another He WD, most likely in a very tight binary. • Gravitational waves ...
Presentation available here - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... All core collapse explosions are asymmetric, maybe produced by magnetic jets. How can this be proved? Gamma-ray bursts are caused by jets of material moving at nearly the speed of light. Do they mark the birth of black holes? At least some gamma-ray bursts (and maybe all) arise in supernova ex ...
... All core collapse explosions are asymmetric, maybe produced by magnetic jets. How can this be proved? Gamma-ray bursts are caused by jets of material moving at nearly the speed of light. Do they mark the birth of black holes? At least some gamma-ray bursts (and maybe all) arise in supernova ex ...
Stefan-Boltzmann`s law Wien`s law
... Cosmological background radiation / Cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) is microwave radiation - left over from the Big Bang that fills the universe roughly uniformly in all directions. The Big Bang predicts an expanding universe that had a very high temperature at the beginning; during the ...
... Cosmological background radiation / Cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) is microwave radiation - left over from the Big Bang that fills the universe roughly uniformly in all directions. The Big Bang predicts an expanding universe that had a very high temperature at the beginning; during the ...
Here
... depends on the initial mass of the star. • Although there is a continuous range of masses, there are 4 ranges of masses that capture all of the interesting features. ...
... depends on the initial mass of the star. • Although there is a continuous range of masses, there are 4 ranges of masses that capture all of the interesting features. ...
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... – Spirals are forming stars at a few M¤ per year, and we know that there is ~ a few x 109 M¤ of HI mass in a typical spiral ...
... – Spirals are forming stars at a few M¤ per year, and we know that there is ~ a few x 109 M¤ of HI mass in a typical spiral ...
Blackbody Radiation
... radiation law. It is displayed as a graph on the following slide. The temperature scale used by physicists and astronomers is the absolute Kelvin scale. The temperature at which a body can emit no energy is absolute zero. One Kelvin = 1 Celsius degree = 1.8 Fahrenheit degree. The freezing point of w ...
... radiation law. It is displayed as a graph on the following slide. The temperature scale used by physicists and astronomers is the absolute Kelvin scale. The temperature at which a body can emit no energy is absolute zero. One Kelvin = 1 Celsius degree = 1.8 Fahrenheit degree. The freezing point of w ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.