Chapter 20: Stellar Evolution: The Death of Stars PowerPoint
... – Each successive fusion step produces less energy – All elements heavier than iron require energy input • Core fusion cannot produce elements heavier than iron • All heavier elements are produced by other processes ...
... – Each successive fusion step produces less energy – All elements heavier than iron require energy input • Core fusion cannot produce elements heavier than iron • All heavier elements are produced by other processes ...
Comets, Meteors, and Meteoroids
... It is always exciting to see a falling star. It is gone almost as soon as you see it. You point to where it was and stare at the dark sky. You hope that you will see another falling star. What is a falling star? A falling star is not a star at all. It is not even part of a star. Stars do not fall. O ...
... It is always exciting to see a falling star. It is gone almost as soon as you see it. You point to where it was and stare at the dark sky. You hope that you will see another falling star. What is a falling star? A falling star is not a star at all. It is not even part of a star. Stars do not fall. O ...
Letter to the Editor ASTRONOMY ASTROPHYSICS
... (the Antennae). The tidal dwarf consists of a chain of nebulae ionized by recently formed massive stars, which are embedded in an envelope of HI gas and low surface brightness optical emission. Since this object is at the tip of one of the tidal tails, star formation on a scale similar to star formi ...
... (the Antennae). The tidal dwarf consists of a chain of nebulae ionized by recently formed massive stars, which are embedded in an envelope of HI gas and low surface brightness optical emission. Since this object is at the tip of one of the tidal tails, star formation on a scale similar to star formi ...
D2 Stellar characteristics and stellar evolution
... times larger. If placed at the center of our Solar System, it would extend past the orbit of Jupiter (has an immense but highly variable, outer atmosphere ). As a massive red supergiant, it is nearing the end of its life and will soon become a supernova ...
... times larger. If placed at the center of our Solar System, it would extend past the orbit of Jupiter (has an immense but highly variable, outer atmosphere ). As a massive red supergiant, it is nearing the end of its life and will soon become a supernova ...
Properties of Stars Name
... 2. Using a colored pencil of your choosing (preferably RED), graph each of the NEAREST STARS (listed in figure 21.1) on the H-R diagram (fig. 21.3). 3. Using a colored pencil of your choosing (preferably BLUE), graph each of the BRIGHTEST STARS as seen from Earth (listed in figure 21.2) on the H-R D ...
... 2. Using a colored pencil of your choosing (preferably RED), graph each of the NEAREST STARS (listed in figure 21.1) on the H-R diagram (fig. 21.3). 3. Using a colored pencil of your choosing (preferably BLUE), graph each of the BRIGHTEST STARS as seen from Earth (listed in figure 21.2) on the H-R D ...
T = 5800 K
... radiation law. It is displayed as a graph on the following slide. The temperature scale used by physicists and astronomers is the absolute Kelvin scale. The temperature at which a body can emit no energy is absolute zero. One Kelvin = 1 Celsius degree = 1.8 Fahrenheit degree. The freezing point of w ...
... radiation law. It is displayed as a graph on the following slide. The temperature scale used by physicists and astronomers is the absolute Kelvin scale. The temperature at which a body can emit no energy is absolute zero. One Kelvin = 1 Celsius degree = 1.8 Fahrenheit degree. The freezing point of w ...
the_young_astronomers_newsletter-NL1304-F
... fingerprints, or spectra, of a distant system's four red exoplanets, which orbit a star 128 light years away from Earth. These warm, red planets (HR 8799) are unlike any other known object in our universe. All four planets have different spectra, and all four are peculiar. They said that the spectra ...
... fingerprints, or spectra, of a distant system's four red exoplanets, which orbit a star 128 light years away from Earth. These warm, red planets (HR 8799) are unlike any other known object in our universe. All four planets have different spectra, and all four are peculiar. They said that the spectra ...
universe.pps - Prophet Muhammad For All
... The map shows several stars visible with the naked eye which are located deep within the Orion arm. The most notable group of stars here are main stars in the constellation of Orion -from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant -stars, thousands of time ...
... The map shows several stars visible with the naked eye which are located deep within the Orion arm. The most notable group of stars here are main stars in the constellation of Orion -from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant -stars, thousands of time ...
The Kinematics of Star Formation: Theory and Observation in the
... core accretion (Federrath & Klessen, 2012). In this model pre-stellar cores are created by supersonic turbulence, but they then decouple from the surrounding gas flows so that the mass of the stellar system that forms is proportional to the mass of the initial pre-stellar core. This idea is supporte ...
... core accretion (Federrath & Klessen, 2012). In this model pre-stellar cores are created by supersonic turbulence, but they then decouple from the surrounding gas flows so that the mass of the stellar system that forms is proportional to the mass of the initial pre-stellar core. This idea is supporte ...
28. What causes waves - Summer Science Safari
... light year distance light travels in one year apparent magnitude how bright a star appears from earth galaxy largest grouping of stars in space absolute magnitude the actual brightness of a star parallax one of the ways we measure distances in space; apparent shift in a star’s location nebulae cloud ...
... light year distance light travels in one year apparent magnitude how bright a star appears from earth galaxy largest grouping of stars in space absolute magnitude the actual brightness of a star parallax one of the ways we measure distances in space; apparent shift in a star’s location nebulae cloud ...
The Origin of the Elements - Indiana University Astronomy
... About 10% of the lithium in the Universe today was also created in the Big Bang. We’re still not sure where the rest comes from. The first stars formed from this material. ...
... About 10% of the lithium in the Universe today was also created in the Big Bang. We’re still not sure where the rest comes from. The first stars formed from this material. ...
In Pictures: Journey to the Stars
... Energy easily changes from one form to another. Image credits: Eric Hamilton. ...
... Energy easily changes from one form to another. Image credits: Eric Hamilton. ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... The speed of light is a universal constant, it does not change over time or from place to place. Thought Experiment: imagine two teams of scientist measuring the speed of a beam of light. One team measures the speed from a ground. The second team measures the speed from a fast moving airplane foll ...
... The speed of light is a universal constant, it does not change over time or from place to place. Thought Experiment: imagine two teams of scientist measuring the speed of a beam of light. One team measures the speed from a ground. The second team measures the speed from a fast moving airplane foll ...
Slajd 1 - INFN-LNF
... predominantly with much longer orbital periods. Such systems are very difficult to detect, both due to very long orbital periods and due to, probably, very low luminosities (the accretion at such large orbital separations must be very inefficient). ...
... predominantly with much longer orbital periods. Such systems are very difficult to detect, both due to very long orbital periods and due to, probably, very low luminosities (the accretion at such large orbital separations must be very inefficient). ...
AAS Plenary Talk, May 2011 - National Radio Astronomy Observatory
... EVLA observations of the Barnard 5 star forming cloud: embedded filaments revealed (Pineda) The mm colors of a young binary disk system in the Orion Nebular Cluster (Ricci) Microwave observations of edge-on protoplanetary disks (Melis) First results from a 1.3cm EVLA survey of massive protos ...
... EVLA observations of the Barnard 5 star forming cloud: embedded filaments revealed (Pineda) The mm colors of a young binary disk system in the Orion Nebular Cluster (Ricci) Microwave observations of edge-on protoplanetary disks (Melis) First results from a 1.3cm EVLA survey of massive protos ...
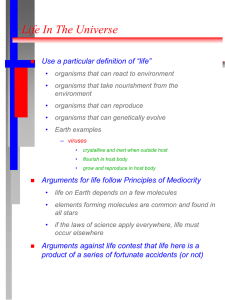
astro20 chap27 - Las Positas College
... fraction of planets with intelligent life that develops technology – don’t know how many early human civilizations failed to develop technology – the fact the many independent early civilizations did develop technology makes us believe ~ 1 ...
... fraction of planets with intelligent life that develops technology – don’t know how many early human civilizations failed to develop technology – the fact the many independent early civilizations did develop technology makes us believe ~ 1 ...
Counter-rotating Stellar Components in Simulated Disk Galaxies
... major axis shows striking bimodality. This bimodality indicates the presence of two disk components, photometrically inseparable, but counterstreaming at projected velocities of 100km/s and +150km/s (Rix et al 1992) ...
... major axis shows striking bimodality. This bimodality indicates the presence of two disk components, photometrically inseparable, but counterstreaming at projected velocities of 100km/s and +150km/s (Rix et al 1992) ...
On the nature of early-type emission line objects in NGC6611
... metallicity (Schaller et al. 1992). A part of stars in the sample (mainly the massive stars) are young and are close to the ZAMS. However, the analysis of our results demonstrates that a group (intermediate mass stars) of our NGC6611 targets have an age too old for the age of this star-formation reg ...
... metallicity (Schaller et al. 1992). A part of stars in the sample (mainly the massive stars) are young and are close to the ZAMS. However, the analysis of our results demonstrates that a group (intermediate mass stars) of our NGC6611 targets have an age too old for the age of this star-formation reg ...
Planet formation around M-dwarfs: the moving snow line and super
... (e.g. Lissauer 1993). However, both theoretical and numerical calculations show that oligarchic growth probably ends when oligarchs contain ∼50% of the total mass in solids, and dynamical friction from small objects no longer keeps the large objects in circular orbits (Goldreich et al. 2004; Kenyon ...
... (e.g. Lissauer 1993). However, both theoretical and numerical calculations show that oligarchic growth probably ends when oligarchs contain ∼50% of the total mass in solids, and dynamical friction from small objects no longer keeps the large objects in circular orbits (Goldreich et al. 2004; Kenyon ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.