World War II 1942 1945
... Conclusions: The Impact of World War II ■ World War II was the biggest, most deadly, & most impactful war in world history: –Europe was destroyed by the war & lost its place as the epicenter of power in the world ...
... Conclusions: The Impact of World War II ■ World War II was the biggest, most deadly, & most impactful war in world history: –Europe was destroyed by the war & lost its place as the epicenter of power in the world ...
The Yalta and Potsdam Conference
... Meeting of the Big Three for discussion and cooperation over the future of Europe following the defeat of Nazi Germany. At the time of the conference, the Red Army was within 40 miles of Berlin, while the Allied forces in the west were recovering from the ‘Battle of the Bulge’ in the Ardennes. Roose ...
... Meeting of the Big Three for discussion and cooperation over the future of Europe following the defeat of Nazi Germany. At the time of the conference, the Red Army was within 40 miles of Berlin, while the Allied forces in the west were recovering from the ‘Battle of the Bulge’ in the Ardennes. Roose ...
Lesson 14: The Cold War
... severe and threatening. President Harry S. Truman, who had succeeded Franklin Roosevelt as president after the latter’s death in April 1945, found himself in an increasingly difficult and complex battle against communism. Dwight D. Eisenhower, who succeeded Truman as president in 1952, inherited the ...
... severe and threatening. President Harry S. Truman, who had succeeded Franklin Roosevelt as president after the latter’s death in April 1945, found himself in an increasingly difficult and complex battle against communism. Dwight D. Eisenhower, who succeeded Truman as president in 1952, inherited the ...
Major Events and Battles Summary
... In 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union sign a non-aggression pact. Adolf Hitler and Josef Stalin agree not to invade each other's borders. This leaves Hitler free to focus his efforts on conquering Western Europe. The two leaders secretly plan to divide Poland and other parts of Eastern Europe betwee ...
... In 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union sign a non-aggression pact. Adolf Hitler and Josef Stalin agree not to invade each other's borders. This leaves Hitler free to focus his efforts on conquering Western Europe. The two leaders secretly plan to divide Poland and other parts of Eastern Europe betwee ...
... After learning that the Japanese had attacked Pearl Harbor, thus ensuring that the United States would enter World War II, Prime Minister Winston Churchill breathed a sigh of relief. "Hitler's fate was sealed," he would later recall. "Mussolini's fate was sealed. As for the Japanese, they would be g ...
Ch 24 ppt
... were first used at Chelmno (Kulmhof) because prisoners could be killed while they were transported. ...
... were first used at Chelmno (Kulmhof) because prisoners could be killed while they were transported. ...
Part I: Fascism, Communism and World War Two
... March: Germany annexes Austria September: Germany demands part of Czechoslovakia with majority German population; British and French prime ministers, William Chamberlain and Edouard Daladier, meet in Munich, accede to German demands and pressure Czechoslovakia to yield to Hitler. The USSR is exclude ...
... March: Germany annexes Austria September: Germany demands part of Czechoslovakia with majority German population; British and French prime ministers, William Chamberlain and Edouard Daladier, meet in Munich, accede to German demands and pressure Czechoslovakia to yield to Hitler. The USSR is exclude ...
Teachers` notes - National Union of Teachers
... was anti-Communism. Hitler and other Nazi leaders believed that Communism was part of a Jewish conspiracy to destroy Germany (even though they also believed that capitalism was part of this conspiracy). This linked to the second idea: racism. The Nazis regarded the Russians and other peoples of the ...
... was anti-Communism. Hitler and other Nazi leaders believed that Communism was part of a Jewish conspiracy to destroy Germany (even though they also believed that capitalism was part of this conspiracy). This linked to the second idea: racism. The Nazis regarded the Russians and other peoples of the ...
World War II Exam—Honors A TEST NO.
... 1. Both Fascists and Nazis were anti-Communist. 2. Japan’s government ordered the military invasion of Manchuria in northern China to obtain needed resources for Japan. 3. Great Britain, France and Italy followed a policy of appeasement towards Hitler and Nazi Germany 4. In World War II, the U.S. su ...
... 1. Both Fascists and Nazis were anti-Communist. 2. Japan’s government ordered the military invasion of Manchuria in northern China to obtain needed resources for Japan. 3. Great Britain, France and Italy followed a policy of appeasement towards Hitler and Nazi Germany 4. In World War II, the U.S. su ...
Turning Points
... 1. Why was the Battle of Stalingrad the turning point on the Eastern front? 2. Why was D-Day the turning point on the Western front? 3. Describe the Allied invasion of Northern Africa. 4. List three effects of the Allied invasion of Italy. 5. THINKER: After Germany and Italy surrender, the Allied po ...
... 1. Why was the Battle of Stalingrad the turning point on the Eastern front? 2. Why was D-Day the turning point on the Western front? 3. Describe the Allied invasion of Northern Africa. 4. List three effects of the Allied invasion of Italy. 5. THINKER: After Germany and Italy surrender, the Allied po ...
The Cold War - International School Bangkok | PowerSchool Learning
... USSR & her allies (communism). Main weapons used: propaganda, diplomatic manoeuvring, regional conflicts. Main event: Gorbachev? 1945: 1). Germany zoned between 4 allies - Berlin, in the eastern (Soviet) zone, jointly occupied by the 4 powers. 2). Prologue to Soviet sphere of influence in eastern Eu ...
... USSR & her allies (communism). Main weapons used: propaganda, diplomatic manoeuvring, regional conflicts. Main event: Gorbachev? 1945: 1). Germany zoned between 4 allies - Berlin, in the eastern (Soviet) zone, jointly occupied by the 4 powers. 2). Prologue to Soviet sphere of influence in eastern Eu ...
File
... On the morning of June 5, after his meteorologist predicted improved conditions for the following day, Eisenhower gave the go-ahead for Operation Overlord. He told the troops: “You are about to embark upon the Great Crusade, toward which we have striven these many months. The eyes of the world are u ...
... On the morning of June 5, after his meteorologist predicted improved conditions for the following day, Eisenhower gave the go-ahead for Operation Overlord. He told the troops: “You are about to embark upon the Great Crusade, toward which we have striven these many months. The eyes of the world are u ...
Axis Powers - Endeavor Charter School
... (government), Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party came to gain control of Germany’s future. Over the next 5 years, Germany would violate the Treaty of Versailles on numerous occasions. By August of 1939, Germany will have begun forming an “axis” of power with the countries of Japan, Italy, and Russia (s ...
... (government), Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party came to gain control of Germany’s future. Over the next 5 years, Germany would violate the Treaty of Versailles on numerous occasions. By August of 1939, Germany will have begun forming an “axis” of power with the countries of Japan, Italy, and Russia (s ...
Summary: World War II
... political party called the Nazis. They believed in fascism. Hitler also encouraged racism. He blamed the Jewish people for Germany’s problems. The leaders of Germany, Italy, and Japan encouraged nationalism. They attacked other countries. Joseph Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union, and Hitler agr ...
... political party called the Nazis. They believed in fascism. Hitler also encouraged racism. He blamed the Jewish people for Germany’s problems. The leaders of Germany, Italy, and Japan encouraged nationalism. They attacked other countries. Joseph Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union, and Hitler agr ...
Dylan Cranley - rathregan.scoilnet.ie
... Under the leadership of Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), the National Socialist German Workers' Party, or Nazi Party, grew into a mass movement and ruled Germany through totalitarian means from 1933 to 1945. Founded in 1919 as the German Workers' Party, the group promoted German pride and anti-Semitism, ...
... Under the leadership of Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), the National Socialist German Workers' Party, or Nazi Party, grew into a mass movement and ruled Germany through totalitarian means from 1933 to 1945. Founded in 1919 as the German Workers' Party, the group promoted German pride and anti-Semitism, ...
Parallel Timelines
... —(Jun.) Operation Barbarossa—Germany’s three-pronged invasion of the USSR —(Dec.) United States enters the war 1942—Allied invasion of North Africa 1943—Allied invasion of Italy —USSR begins to drive the German army out of the Soviet Union 1944—(Jun. 6) D-Day; major allied invasion of Normandy, Fran ...
... —(Jun.) Operation Barbarossa—Germany’s three-pronged invasion of the USSR —(Dec.) United States enters the war 1942—Allied invasion of North Africa 1943—Allied invasion of Italy —USSR begins to drive the German army out of the Soviet Union 1944—(Jun. 6) D-Day; major allied invasion of Normandy, Fran ...
War Conference Wkst
... The Potsdam Conference, held near Berlin, July 17-August 2, 1945, was the last of the “Big Three” meetings during World War II. It was attended by Premier Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union, the new American president, Harry S. Truman, and Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain (replaced o ...
... The Potsdam Conference, held near Berlin, July 17-August 2, 1945, was the last of the “Big Three” meetings during World War II. It was attended by Premier Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union, the new American president, Harry S. Truman, and Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain (replaced o ...
File
... a. Service men and women were forced to leave their homes for Europe b. The loss of loved ones led people to move in with their families c. People moved to states with military bases and factories for better jobs d. People moved to the middle of the country to escape war on both coasts 22. How did n ...
... a. Service men and women were forced to leave their homes for Europe b. The loss of loved ones led people to move in with their families c. People moved to states with military bases and factories for better jobs d. People moved to the middle of the country to escape war on both coasts 22. How did n ...
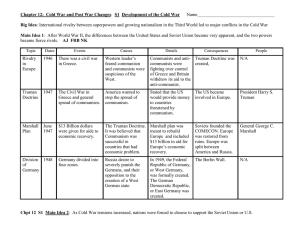
Chapter 12: Cold War and Post War Changes: S1 Development of
... 1) North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) 2) The Warsaw Pact as signed 3) Southeast Asia Treaty Organization was formed. 4) The Central Treaty Organization (CENTO) ...
... 1) North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) 2) The Warsaw Pact as signed 3) Southeast Asia Treaty Organization was formed. 4) The Central Treaty Organization (CENTO) ...
WORD
... - Hitler called for German territorial expansion by seizing lands to the east - He said Germany must cease its attempts at acquiring colonial possessions and look to the east instead - Hitler hoped lebensraum would create an German autarky that would have the strength and self-sufficiency to fight R ...
... - Hitler called for German territorial expansion by seizing lands to the east - He said Germany must cease its attempts at acquiring colonial possessions and look to the east instead - Hitler hoped lebensraum would create an German autarky that would have the strength and self-sufficiency to fight R ...
ws05-wwii-and-the-holocaust-wi2017-study-guide
... French coastline to fight Nazi Germany on the beaches of Normandy, France. - Operation Overlord - General Dwight D. Eisenhower called the operation a crusade in which "we will accept nothing less than full victory." - more than 5,000 Ships and 13,000 aircraft supported the D-Day invasion, and by day ...
... French coastline to fight Nazi Germany on the beaches of Normandy, France. - Operation Overlord - General Dwight D. Eisenhower called the operation a crusade in which "we will accept nothing less than full victory." - more than 5,000 Ships and 13,000 aircraft supported the D-Day invasion, and by day ...
WWII
... after threatening to overthrow the gov’t • Turned Italy into a fascist state • Fascism: a political system based on militarism, extreme nationalism, and blind loyalty to the state and its leader (end to FoP and all other parties) ...
... after threatening to overthrow the gov’t • Turned Italy into a fascist state • Fascism: a political system based on militarism, extreme nationalism, and blind loyalty to the state and its leader (end to FoP and all other parties) ...
The Muddled Legend of Yalta
... ruins. Refugees were a common sight, displaced by war and political turmoil. Germany itself would soon be in the hands of its former enemies. The allied Big Three leaders—President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States, Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain, and Premier Joseph Stali ...
... ruins. Refugees were a common sight, displaced by war and political turmoil. Germany itself would soon be in the hands of its former enemies. The allied Big Three leaders—President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States, Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain, and Premier Joseph Stali ...
Chapter 26 Section 4 - Home Front _ Aftermath of War
... Germany – Britain responded to the bombing of their own cities by bombing German cities. This resulted in a raids of over 1,000 planes into Cologne in 1943. The most well known bombing in Germany occurred in Dresden and resulted in 100,000 casualties in 3 days. ...
... Germany – Britain responded to the bombing of their own cities by bombing German cities. This resulted in a raids of over 1,000 planes into Cologne in 1943. The most well known bombing in Germany occurred in Dresden and resulted in 100,000 casualties in 3 days. ...
World War II and Post War Test
... C Japan engaged in wars with western Europe. D Japan became economically competitive with Britain. 2. International Violence Before WWII Japan invades Manchuria - 1931 Italy invades Ethiopia - 1935 Japan invades China - 1937 Germany annexes Czechoslovakia - 1939 Germany invades Poland - 19 ...
... C Japan engaged in wars with western Europe. D Japan became economically competitive with Britain. 2. International Violence Before WWII Japan invades Manchuria - 1931 Italy invades Ethiopia - 1935 Japan invades China - 1937 Germany annexes Czechoslovakia - 1939 Germany invades Poland - 19 ...
Western betrayal

The concept of Western betrayal refers to the view that the United Kingdom and France failed to meet their legal, diplomatic, military and moral obligations with respect to the Czech and Polish nations of Central and Eastern Europe in the prelude to and aftermath of the Second World War.In particular, it refers to Czechoslovakia's treatment during the Munich Agreement and subsequent occupation and partition by Nazi Germany, Hungary (The First Vienna Award) and Poland (Invasion of Zaolzie), as well as the failure of the Western allies to aid Poland upon its invasion by Germany and the USSR in 1939. The same concept also refers to the concessions made by the United States and the United Kingdom to the USSR during the Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam conferences, to their stance during the Warsaw Uprising, and some other events, which allocated the region to the Soviet sphere of influence and created the Eastern Bloc.Historically, such views were intertwined with some of the most significant geopolitical events of the 20th century, including the rise and empowerment of the Third Reich (Nazi Germany), the rise of the Soviet Union (USSR) as a dominant superpower with control of large parts of Europe, and various treaties, alliances, and positions taken during and after World War II, and so on into the Cold War.