Fuzzy Logic - Authentic Leadership Center
... and stated that there was nothing to prevent the development of infinite-valued logic (Brule, 1985). It was not until 1965, when Zadeh published his seminal work (Zadeh, 1965), that the notion of an infinite-valued logic took hold. He proposed an entire new set of operations and calculus of logic an ...
... and stated that there was nothing to prevent the development of infinite-valued logic (Brule, 1985). It was not until 1965, when Zadeh published his seminal work (Zadeh, 1965), that the notion of an infinite-valued logic took hold. He proposed an entire new set of operations and calculus of logic an ...
Artificial Intelligence Applications by
... They are used for control, design, diagnosis, prediction, planning, simulation etc. Thousands of systems have been developed and are in use throughout the world. Expert systems have moved from the research labs to the general market place and industry. This has resulted from the better understanding ...
... They are used for control, design, diagnosis, prediction, planning, simulation etc. Thousands of systems have been developed and are in use throughout the world. Expert systems have moved from the research labs to the general market place and industry. This has resulted from the better understanding ...
9781111529413_PPT_ch01
... Origins of Programming Languages • Programming language: often defined as “a notation for communicating to a computer what we want it to do” • Before the mid 1940s, computer operators set switches to adjust the internal wiring of a computer to perform the requested tasks • Programming languages all ...
... Origins of Programming Languages • Programming language: often defined as “a notation for communicating to a computer what we want it to do” • Before the mid 1940s, computer operators set switches to adjust the internal wiring of a computer to perform the requested tasks • Programming languages all ...
Parts vs. the whole in the procedural logic hierarchy.
... program (2): 3: a plan or system under which action may be taken toward a goal 6 a: a plan for the programming of a mechanism (as a computer) b: a sequence of coded instructions that can be inserted into a mechanism (as a computer) or that is part of an organism A program is generally distinguished ...
... program (2): 3: a plan or system under which action may be taken toward a goal 6 a: a plan for the programming of a mechanism (as a computer) b: a sequence of coded instructions that can be inserted into a mechanism (as a computer) or that is part of an organism A program is generally distinguished ...
Handling Function Symbols in the DLV Grounder
... Traditionally, ASP has often been used as a first-order language without function symbols, similar to Datalog, in order to deal with finite structures only. More recently, also uninterpreted function symbols have been frequently considered, thus enabling a natural representation of complex and recur ...
... Traditionally, ASP has often been used as a first-order language without function symbols, similar to Datalog, in order to deal with finite structures only. More recently, also uninterpreted function symbols have been frequently considered, thus enabling a natural representation of complex and recur ...
BIT 143: C++ Programming: Data Structures
... The Robot class does not provide a predicate for testing if the Robot cannot pick up a Thing. Fortunately, any Boolean expression may be negated, or given the opposite value, by using the logical negation operator “ ! ”. In English, this is usually written and pronounced as “not”. ...
... The Robot class does not provide a predicate for testing if the Robot cannot pick up a Thing. Fortunately, any Boolean expression may be negated, or given the opposite value, by using the logical negation operator “ ! ”. In English, this is usually written and pronounced as “not”. ...
2. Case-Based Reasoning
... [email protected] www.somewhere.ac.uk Abstract This paper shows how a paper should look in Springer’s formatting style. Hence if you reuse this you’ll be using case-based reasoning to solve your formatting problems. Case-based reasoning is a methodology for problem solving, that may use any ...
... [email protected] www.somewhere.ac.uk Abstract This paper shows how a paper should look in Springer’s formatting style. Hence if you reuse this you’ll be using case-based reasoning to solve your formatting problems. Case-based reasoning is a methodology for problem solving, that may use any ...
Logic6
... Jack owns a dog. Every dog owner is an animal lover. No animal lover kills an animal. Either Jack or Curiosity killed the cat, who is named Tuna. Did Curiosity kill the cat? ...
... Jack owns a dog. Every dog owner is an animal lover. No animal lover kills an animal. Either Jack or Curiosity killed the cat, who is named Tuna. Did Curiosity kill the cat? ...
Solving Distributed Constraint Optimization Problems Using Logic
... combinations of value assignments in a decentralized manner; (ii) inference-based algorithms [37, 7], where the agents use dynamic programming to propagate aggregated information to other agents; and (iii) sampling-based algorithms [36, 34], where the agents sample the search space in a decentralize ...
... combinations of value assignments in a decentralized manner; (ii) inference-based algorithms [37, 7], where the agents use dynamic programming to propagate aggregated information to other agents; and (iii) sampling-based algorithms [36, 34], where the agents sample the search space in a decentralize ...
kb1
... isa(robin,bird). • The implementation level refers to the way in which the knowledge is encoded, (e.g., isa(robin,bird) might be encoded as a list, array, database record, etc.) ...
... isa(robin,bird). • The implementation level refers to the way in which the knowledge is encoded, (e.g., isa(robin,bird) might be encoded as a list, array, database record, etc.) ...
Slides_12
... • static classes/methods/objects: Always have the same value within a Java Virtual Machine (Java VM) • Open the ICE_12.java. Note that the main method is always a static method: It can be called on a class without instantiating an object first – Can only call static methods or make objects and call ...
... • static classes/methods/objects: Always have the same value within a Java Virtual Machine (Java VM) • Open the ICE_12.java. Note that the main method is always a static method: It can be called on a class without instantiating an object first – Can only call static methods or make objects and call ...
An Introduction of Soft Computing Approach over Hard Computing
... When it is applied to problem solving, the basic premise is that we can create an initial populations of individuals representing possible solution to a problem we are trying to solve. Each of these individuals has certain characteristics that make them more or less fit as members of the populations ...
... When it is applied to problem solving, the basic premise is that we can create an initial populations of individuals representing possible solution to a problem we are trying to solve. Each of these individuals has certain characteristics that make them more or less fit as members of the populations ...
Overview of FPGAs
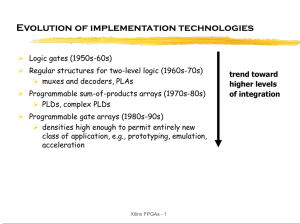
... used to connect one of a set of possible sources to input can be used to implement logic functions ...
... used to connect one of a set of possible sources to input can be used to implement logic functions ...
Curriculum Vitae
... as I am aware, this remains a rare attempt to successfully address the important practical problem of distinguishing between true exceptions and “noisy” data in non-monotonic reasoning. This research was directed by Professor Stephen Muggleton. ...
... as I am aware, this remains a rare attempt to successfully address the important practical problem of distinguishing between true exceptions and “noisy” data in non-monotonic reasoning. This research was directed by Professor Stephen Muggleton. ...
Norm-based deontic logic for access control, some
... x ∈ out p (O> , A) is Π2 -complete. 3.2.2. Reasoning about permission Permission is probably the most important notion in the specification of an access control policy. Several notions of permission are introduced in norm-based deontic logic [24–26,18]. Hansen [18] gives a unified presentation of di ...
... x ∈ out p (O> , A) is Π2 -complete. 3.2.2. Reasoning about permission Permission is probably the most important notion in the specification of an access control policy. Several notions of permission are introduced in norm-based deontic logic [24–26,18]. Hansen [18] gives a unified presentation of di ...
Connecting First-Order ASP and the Logic FO(ID) Through Reducts
... an extension of the first-order logic with inductive definitions, the logic FO(ID), as a knowledge representation formalism. A version of that language can be used according to the ASP paradigm and there are fast tools to support that use of the logic FO(ID).1 The semantics of definitions in the log ...
... an extension of the first-order logic with inductive definitions, the logic FO(ID), as a knowledge representation formalism. A version of that language can be used according to the ASP paradigm and there are fast tools to support that use of the logic FO(ID).1 The semantics of definitions in the log ...
Logics for Intelligent Agents and Multi
... of agents, after which we turn to logics that are used for specifying multi-agent systems. On the one hand these include extensions of BDI-like logics for multiple agents such as common knowledge and mutual intention, on the other hand, when there are multiple agents into play there are also issues ...
... of agents, after which we turn to logics that are used for specifying multi-agent systems. On the one hand these include extensions of BDI-like logics for multiple agents such as common knowledge and mutual intention, on the other hand, when there are multiple agents into play there are also issues ...
Towards a Logic of Rational Agency
... 4. Agents believe their intentions are possible. 5. Agents do not believe they will not bring about their intentions. 6. Under certain circumstances, agents believe they will bring about their intentions. 7. Agents need not intend all the expected side effects of their intentions. Given these criter ...
... 4. Agents believe their intentions are possible. 5. Agents do not believe they will not bring about their intentions. 6. Under certain circumstances, agents believe they will bring about their intentions. 7. Agents need not intend all the expected side effects of their intentions. Given these criter ...
Readable, writable, both, or neither? A programming language that
... of corresponding elements in any two rows or any two columns equal to one if the rows or columns are the same and equal to zero otherwise : having a transpose with which the product equals the identity matrix 3 of a linear transformation : having a matrix that is orthogonal : preserving length and d ...
... of corresponding elements in any two rows or any two columns equal to one if the rows or columns are the same and equal to zero otherwise : having a transpose with which the product equals the identity matrix 3 of a linear transformation : having a matrix that is orthogonal : preserving length and d ...
Towards a Logic of Rational Agency
... 4. Agents believe their intentions are possible. 5. Agents do not believe they will not bring about their intentions. 6. Under certain circumstances, agents believe they will bring about their intentions. 7. Agents need not intend all the expected side effects of their intentions. Given these criter ...
... 4. Agents believe their intentions are possible. 5. Agents do not believe they will not bring about their intentions. 6. Under certain circumstances, agents believe they will bring about their intentions. 7. Agents need not intend all the expected side effects of their intentions. Given these criter ...
Programming Languages (PL)
... Knowledge Area in a curriculum’s introductory courses. Curricula will differ on which topics are integrated in this fashion and which are delayed until later courses on software development and programming languages. ...
... Knowledge Area in a curriculum’s introductory courses. Curricula will differ on which topics are integrated in this fashion and which are delayed until later courses on software development and programming languages. ...
Disproving False Conjectures
... the properties of a TI abstraction with a consistent abstract space. For the domain of first-order logic, first-order monadic logic would suffice as abstract space, but equality (see Sec. 4) requires the use of second-order monadic logic. The abstraction can be intuitively explained as follows. A de ...
... the properties of a TI abstraction with a consistent abstract space. For the domain of first-order logic, first-order monadic logic would suffice as abstract space, but equality (see Sec. 4) requires the use of second-order monadic logic. The abstraction can be intuitively explained as follows. A de ...
Intorduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Dechter ICS 270A
... Requires Natural language Knowledge representation Automated reasoning Machine learning (vision, robotics) ...
... Requires Natural language Knowledge representation Automated reasoning Machine learning (vision, robotics) ...
Resolution Based Explanations for Reasoning in the Description Logic
... completed, each clause node involved in each step is translated into an entry in an explanation list consisting of its source axioms in DL. After some clean-up, e.g., deleting duplicate line, this explanation list can be further transformed into natural language style explanations. The traversal alg ...
... completed, each clause node involved in each step is translated into an entry in an explanation list consisting of its source axioms in DL. After some clean-up, e.g., deleting duplicate line, this explanation list can be further transformed into natural language style explanations. The traversal alg ...