Only-Knowing - Department of Computer Science
... of DL in terms of an underlying model of belief, but also the relationship among these three different forms of nonmonotonic reasoning, all within a classical monotonic logic characterized semantically in terms of possible worlds. This is not the first time AEL and DL have been compared in a modal s ...
... of DL in terms of an underlying model of belief, but also the relationship among these three different forms of nonmonotonic reasoning, all within a classical monotonic logic characterized semantically in terms of possible worlds. This is not the first time AEL and DL have been compared in a modal s ...
Prof - University of Alberta
... Archimedean continua – the point-based system, SP, and the stretch-based system, SI – for the following reasons: 1. It enables us to formulate all the axioms of each system in one and the same language; 2. It makes it possible to apply, without any modification, Arsenijević's two sets of rules for t ...
... Archimedean continua – the point-based system, SP, and the stretch-based system, SI – for the following reasons: 1. It enables us to formulate all the axioms of each system in one and the same language; 2. It makes it possible to apply, without any modification, Arsenijević's two sets of rules for t ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Expert Systems
... • Defines a set of algebraic expressions to manipulate those symbols. • Using axioms, theorems can be constructed. ...
... • Defines a set of algebraic expressions to manipulate those symbols. • Using axioms, theorems can be constructed. ...
Chapter 7 - CSUDH Computer Science
... – for ( =; []; ) do statements
– varies from the initial value to the termination, each loop
varies with a stepwise
– Step can be omitted, default value is 1
...
... – for ( =
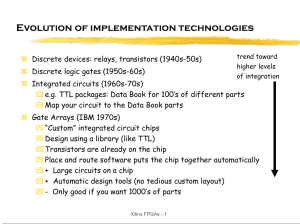
Introduction to ASIC Design
... buffer storage etc.) As control to routing and configuration switches ...
... buffer storage etc.) As control to routing and configuration switches ...
CIS 730 (Introduction to Artificial Intelligence) Lecture
... – Knowledge Bases (KB) and KB agents – Motivating example: Wumpus World – Syntax of propositional calculus – Elements of logic in general • Syntax: What constitutes legitimate sentences aka well-formed formulae? • Semantics: What constitutes logical entailment? • Proof theory: What constitutes prova ...
... – Knowledge Bases (KB) and KB agents – Motivating example: Wumpus World – Syntax of propositional calculus – Elements of logic in general • Syntax: What constitutes legitimate sentences aka well-formed formulae? • Semantics: What constitutes logical entailment? • Proof theory: What constitutes prova ...
Planning with Different Forms of Domain
... a means of representing and reasoning with this knowledge. In the past, planners such as TLPlan and TALplan have exploited domain-dependent temporal knowledge; SHOP and various hierarchical task network (HTN) planners have exploited domain-dependent hierarchical and partial-order knowledge; and sati ...
... a means of representing and reasoning with this knowledge. In the past, planners such as TLPlan and TALplan have exploited domain-dependent temporal knowledge; SHOP and various hierarchical task network (HTN) planners have exploited domain-dependent hierarchical and partial-order knowledge; and sati ...
Rule-Based Classifiers
... this applicant gets a loan. From this you should understand why phrases such as forwards-chaining, bottom-up reasoning and data-driven reasoning are used. 3.2.2 Backwards-chaining The second method we look at goes by the names backwards-chaining, top-down reasoning, goal-driven reasoning and hypothe ...
... this applicant gets a loan. From this you should understand why phrases such as forwards-chaining, bottom-up reasoning and data-driven reasoning are used. 3.2.2 Backwards-chaining The second method we look at goes by the names backwards-chaining, top-down reasoning, goal-driven reasoning and hypothe ...
Lecture Slides
... • Violating the above policies is PLAGIARISM (cheating). • Cheating will typically result in automatic failure of this course and possible expulsion from the CS program. • It is much better to leave a problem blank than to cheat! – Usually ~60% is a B and ~80% is an A. – However, cheating earns you ...
... • Violating the above policies is PLAGIARISM (cheating). • Cheating will typically result in automatic failure of this course and possible expulsion from the CS program. • It is much better to leave a problem blank than to cheat! – Usually ~60% is a B and ~80% is an A. – However, cheating earns you ...
6.034 Artificial Intelligence by T. Lozano
... Another way to look at the process we have just gone through is as a form of tree search. In this search space, the states are goals, that is, the literals that appear on our stack. The edges (shown with a green dot in the middle of each edge) are the rules or facts. However, there is one complicati ...
... Another way to look at the process we have just gone through is as a form of tree search. In this search space, the states are goals, that is, the literals that appear on our stack. The edges (shown with a green dot in the middle of each edge) are the rules or facts. However, there is one complicati ...
Lecture slides
... compatible with OCaml, so don’t use it for homework) – Warning: OCaml has a STEEP learning curve! – Pre-homework: Install OCaml • Go to the course website and follow the instructions entitled “To Prepare for the Course…” by next time ...
... compatible with OCaml, so don’t use it for homework) – Warning: OCaml has a STEEP learning curve! – Pre-homework: Install OCaml • Go to the course website and follow the instructions entitled “To Prepare for the Course…” by next time ...
The cognitive and the social - Christophe Heintz
... reasoning while at the same time being conscious about the problem of psychologism, so I think he is a good representative of the theories that I intend to criticise. In “A Border dispute” (1986) Macnamara called for a research program based on the idea that the mind contains some innate devices fro ...
... reasoning while at the same time being conscious about the problem of psychologism, so I think he is a good representative of the theories that I intend to criticise. In “A Border dispute” (1986) Macnamara called for a research program based on the idea that the mind contains some innate devices fro ...
ppt
... • Edinburgh syntax is the basis of ISO standard. • High-level interactive language. • Logic programming language. – Based on Horn Clauses • (parent(X,Z)∧ancestor(Z,Y)) ⊃ ancestor(X,Y) ...
... • Edinburgh syntax is the basis of ISO standard. • High-level interactive language. • Logic programming language. – Based on Horn Clauses • (parent(X,Z)∧ancestor(Z,Y)) ⊃ ancestor(X,Y) ...
The Commutative/Noncommutative Linear Logic BV
... In practice, however, the more liberal proof composition mechanism of deep inference completely invalidates the techniques (and the intuition) behind cut elimination procedures in Gentzen systems. Much of the effort of these 15 years of research on deep inference went into recovering a normalisation ...
... In practice, however, the more liberal proof composition mechanism of deep inference completely invalidates the techniques (and the intuition) behind cut elimination procedures in Gentzen systems. Much of the effort of these 15 years of research on deep inference went into recovering a normalisation ...
Search and forward chaining
... Our goal is to prove that KB entails a fact, a • We use logical inference Forward chaining Backward chaining Resolution ...
... Our goal is to prove that KB entails a fact, a • We use logical inference Forward chaining Backward chaining Resolution ...
Graph Logic Model Framework for Predictive Linguistic Analysis
... condition – either one adjacent link is activated or another, while probabilities – kind of “weights” - are used to “normalize” the chances of choosing one particular link (sum of probabilities to come out from a node equals 1, note that for incoming this condition does not stand). To complete corre ...
... condition – either one adjacent link is activated or another, while probabilities – kind of “weights” - are used to “normalize” the chances of choosing one particular link (sum of probabilities to come out from a node equals 1, note that for incoming this condition does not stand). To complete corre ...
Lecture 3
... – Logic 0 can be: false, off, low, no, open switch. – Logic 1 can be: true, on, high, yes, closed switch. ...
... – Logic 0 can be: false, off, low, no, open switch. – Logic 1 can be: true, on, high, yes, closed switch. ...
Extending Logic Programs with Description Logic Expressions for
... them in the same way as other predicate symbols in P. To ensure decidability, we require that P and C be finite. Let Ω = P ∩ (A ∪ R) denote the predicate symbols shared by Π and L. Definition 1. Let L be a DL knowledge base. A logic program Π with DL expressions relative to L consists of a finite se ...
... them in the same way as other predicate symbols in P. To ensure decidability, we require that P and C be finite. Let Ω = P ∩ (A ∪ R) denote the predicate symbols shared by Π and L. Definition 1. Let L be a DL knowledge base. A logic program Π with DL expressions relative to L consists of a finite se ...
PowerPoint - University of Virginia
... Our goal is to prove that KB entails a fact, a • We use logical inference Forward chaining Backward chaining Resolution ...
... Our goal is to prove that KB entails a fact, a • We use logical inference Forward chaining Backward chaining Resolution ...
KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION AND REASONING 1
... ¯ derivability A sentence a is derivable from a set of sentences S (written ~- or) iff there is a sequenceof sentencesal ..... otn whereotn is t~, such that each t~i either is an elementof S, or a logical axiom, or follows from earlier aj’s by a rule of inference. A sentenceis a theoremif it is deri ...
... ¯ derivability A sentence a is derivable from a set of sentences S (written ~- or) iff there is a sequenceof sentencesal ..... otn whereotn is t~, such that each t~i either is an elementof S, or a logical axiom, or follows from earlier aj’s by a rule of inference. A sentenceis a theoremif it is deri ...
A Probabilistic Extension of the Stable Model
... knowledge representation. The language is also a generalization of ProbLog, and is closely related to Markov Logic Networks, which implies that the computation can be carried out by the techniques developed for them. LPMLN appears to be a natural language for probabilistic answer set programming, an ...
... knowledge representation. The language is also a generalization of ProbLog, and is closely related to Markov Logic Networks, which implies that the computation can be carried out by the techniques developed for them. LPMLN appears to be a natural language for probabilistic answer set programming, an ...
CS 561: Artificial Intelligence CS 561: Artificial Intelligence
... phenomenal, study and formalize common sense facts about the world and the problems that the world presents to the achievement of goals. ...
... phenomenal, study and formalize common sense facts about the world and the problems that the world presents to the achievement of goals. ...
An Abstract View on Modularity in Knowledge Representation
... Modularity is crucial in design, analysis and reasoning about complex systems. It has long been recognized as one of the key techniques in software development. Modularity has also played an important role in artificial intelligence and, in particular, in knowledge representation and reasoning. Form ...
... Modularity is crucial in design, analysis and reasoning about complex systems. It has long been recognized as one of the key techniques in software development. Modularity has also played an important role in artificial intelligence and, in particular, in knowledge representation and reasoning. Form ...
PDF - 1.4 MB - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... 6.034 Artificial Intelligence. Copyright © 2004 by Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Slide 11.1.7 Note that not every logical statement can be written in Horn clause form, especially if we disallow clauses with zero positive literals (consistency constraints). Importantly, one cannot have a ne ...
... 6.034 Artificial Intelligence. Copyright © 2004 by Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Slide 11.1.7 Note that not every logical statement can be written in Horn clause form, especially if we disallow clauses with zero positive literals (consistency constraints). Importantly, one cannot have a ne ...