Unit 1 Study Questions
... Carbon atoms have a tendency to form ___ bonds. A ______ is defined as all members of a given species that occur at a given place at a given time. __________ are long molecules consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. Each monomer molecule will be connected ...
... Carbon atoms have a tendency to form ___ bonds. A ______ is defined as all members of a given species that occur at a given place at a given time. __________ are long molecules consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. Each monomer molecule will be connected ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry of Life 2.1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
... • Enzymes lower the activation energy needed to start chemical reactions. • Enzymes are involved in almost every process in living things. • Conditions such as temperature and pH can effect how well enzymes work. • Enzyme structure is important because each enzyme’s shape allows only certain reactan ...
... • Enzymes lower the activation energy needed to start chemical reactions. • Enzymes are involved in almost every process in living things. • Conditions such as temperature and pH can effect how well enzymes work. • Enzyme structure is important because each enzyme’s shape allows only certain reactan ...
Recitation 2 Solutions
... Also, if carbohydrates were stored as monosaccharides, instead of polysaccharides, they would exert much higher osmotic pressure on the cell. For example 1000 glucose molecule would exert 1000 times the osmotic pressure of a single glycogen molecule, causing water to move in. If it were not for poly ...
... Also, if carbohydrates were stored as monosaccharides, instead of polysaccharides, they would exert much higher osmotic pressure on the cell. For example 1000 glucose molecule would exert 1000 times the osmotic pressure of a single glycogen molecule, causing water to move in. If it were not for poly ...
solutions and molarity for votech
... A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout May be solids, liquids and/or gases Also called a solution Salt and water Ice tea mix and water ...
... A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout May be solids, liquids and/or gases Also called a solution Salt and water Ice tea mix and water ...
Solute
... Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellular membranes. 47. Name the macromolecule whose function includes structural contributions, communication, and defense against disease. 48. Proteins ar ...
... 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellular membranes. 47. Name the macromolecule whose function includes structural contributions, communication, and defense against disease. 48. Proteins ar ...
Biological Molecules- You are What You Eat:
... from ____________. Another example is fructose. Disaccharides have ___ sugars. An example is ___________________ ...
... from ____________. Another example is fructose. Disaccharides have ___ sugars. An example is ___________________ ...
Introduction to Molecules
... An understanding of the structure and function of biological molecules is necessary in many branches of biology, especially biochemistry, physiology, and molecular genetics. ...
... An understanding of the structure and function of biological molecules is necessary in many branches of biology, especially biochemistry, physiology, and molecular genetics. ...
CB098-008.22_Biochemistry
... DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. DNA is the Genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents. Gene (a characteristic) is a segment of DNA molecule that carries the instructions for amino acid sequence of proteins. DNA is made of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of 3 parts (a Phosphate, ...
... DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. DNA is the Genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents. Gene (a characteristic) is a segment of DNA molecule that carries the instructions for amino acid sequence of proteins. DNA is made of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of 3 parts (a Phosphate, ...
Aromatic Amino Acids
... absorbance of ultraviolet light (ca. 280 nm) by proteins. Tyrosine is the only one of the aromatic amino acids with an ionizable side chain. Tyrosine is one of three hydroxyl containing amino acids. ...
... absorbance of ultraviolet light (ca. 280 nm) by proteins. Tyrosine is the only one of the aromatic amino acids with an ionizable side chain. Tyrosine is one of three hydroxyl containing amino acids. ...
cell molecules
... that is dissolved is the solute. • In our example, water is the solvent and sugar the solute. ...
... that is dissolved is the solute. • In our example, water is the solvent and sugar the solute. ...
Membrane Proteins Integral membrane proteins often contain
... Integral membrane proteins often contain helical segments of appropriate length to span the lipid bilayer. In a protein that has a single segment that spans the membrane, the helix usually only contains hydrophobic residues and is called a single-span membrane protein. In transmembrane proteins with ...
... Integral membrane proteins often contain helical segments of appropriate length to span the lipid bilayer. In a protein that has a single segment that spans the membrane, the helix usually only contains hydrophobic residues and is called a single-span membrane protein. In transmembrane proteins with ...
Bernard Scott
... LRH-1 and other small molecules (on Comet using MPI and Cuda). • Want to know how these small molecules regulate the protein • Will use select compounds to do dynamics studies in hopes of elucidating (agonistic, antagonistic, is the previously discovered mode of allostery replicated or at least simi ...
... LRH-1 and other small molecules (on Comet using MPI and Cuda). • Want to know how these small molecules regulate the protein • Will use select compounds to do dynamics studies in hopes of elucidating (agonistic, antagonistic, is the previously discovered mode of allostery replicated or at least simi ...
AP BIOLOGY Unit 1 – Chemistry and Molecules of Life
... What are some of the main chemical characteristics of amino acids? What effect does the chemical characteristic have on the structure and function of a protein? Describe the directionality of a protein. What are the main functions of lipids? What are the main types of lipids? What is the common char ...
... What are some of the main chemical characteristics of amino acids? What effect does the chemical characteristic have on the structure and function of a protein? Describe the directionality of a protein. What are the main functions of lipids? What are the main types of lipids? What is the common char ...
Milk is a suspension of lipids and proteins. At... soluble because they have either a net positive or net...
... Milk is a suspension of lipids and proteins. At the pH of milk (about 6.4) these proteins are soluble because they have either a net positive or net negative charge. The charge keeps the proteins from interacting with each other by repelling each other yet and allows for sufficient solvation. The pr ...
... Milk is a suspension of lipids and proteins. At the pH of milk (about 6.4) these proteins are soluble because they have either a net positive or net negative charge. The charge keeps the proteins from interacting with each other by repelling each other yet and allows for sufficient solvation. The pr ...
Unit 14: Solutions
... the bottle is opened, there is a rapid decrease in the pressure and the solubility of carbon dioxide gas in the water is greatly reduced causing the familiar bubbling and foaming. ...
... the bottle is opened, there is a rapid decrease in the pressure and the solubility of carbon dioxide gas in the water is greatly reduced causing the familiar bubbling and foaming. ...
ppt - Avraham Samson`s Lab
... – Knowledge-based methods • Predict structure by applying statistical rules • Rules: observations made on known protein structures ...
... – Knowledge-based methods • Predict structure by applying statistical rules • Rules: observations made on known protein structures ...
Protein Stability - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Ionic contacts between an acidic and basic amino acid side chain ...
... Ionic contacts between an acidic and basic amino acid side chain ...
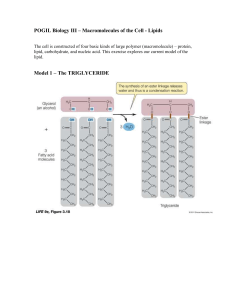
pogil 3
... The cell is constructed of four basic kinds of large polymer (macromolecule) – protein, lipid, carbohydrate, and nucleic acid. This exercise explores our current model of the ...
... The cell is constructed of four basic kinds of large polymer (macromolecule) – protein, lipid, carbohydrate, and nucleic acid. This exercise explores our current model of the ...
Seminario Tunable electronic properties of self
... Université Pierre et Marie Curie In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited spec ...
... Université Pierre et Marie Curie In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited spec ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Chemical reactions involve making and breaking bonds. Making bonds requires the input of energy. Energy is stored in molecules in the chemical bonds. Breaking bonds usually releases energy. ...
... Chemical reactions involve making and breaking bonds. Making bonds requires the input of energy. Energy is stored in molecules in the chemical bonds. Breaking bonds usually releases energy. ...
Name- Kristin Kaufmann
... 1) Compare the hydrophobic forces that hold a membrane protein in the lipid bilayer to those that help proteins fold into unique three-dimensional structures. The hydrophobic forces that hold a protein in the lipid bilayer into the membrane are interactions between the fatty acid tails and the amino ...
... 1) Compare the hydrophobic forces that hold a membrane protein in the lipid bilayer to those that help proteins fold into unique three-dimensional structures. The hydrophobic forces that hold a protein in the lipid bilayer into the membrane are interactions between the fatty acid tails and the amino ...