Name: 11.4 – Meiosis CHROMOSOME NUMBER How many sets of
... 29. TRUE/FALSE: The chromosomes pair to form tetrads, because the homologous pairs were already separated during meiosis I. ____ Metaphase II 30. True or False: Chromosomes line up in the center of each cell. ____ Anaphase II 31. True/false: The paired chromosomes separate. ____ Telophase II and Cyt ...
... 29. TRUE/FALSE: The chromosomes pair to form tetrads, because the homologous pairs were already separated during meiosis I. ____ Metaphase II 30. True or False: Chromosomes line up in the center of each cell. ____ Anaphase II 31. True/false: The paired chromosomes separate. ____ Telophase II and Cyt ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
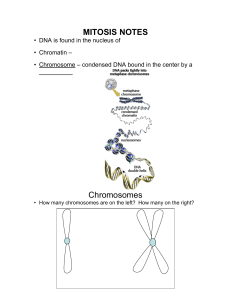
... f. Histone –The small protein that binds to the DNA, contributing to the chromatin structure g. Centromere- The central region that joins two sister chromatids h. Centrosome- The microtubule organizing center present in the cytoplasm i. Homologous Chromosomes- Chromosomes that possess genes coding f ...
... f. Histone –The small protein that binds to the DNA, contributing to the chromatin structure g. Centromere- The central region that joins two sister chromatids h. Centrosome- The microtubule organizing center present in the cytoplasm i. Homologous Chromosomes- Chromosomes that possess genes coding f ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... f. Histone –The small protein that binds to the DNA, contributing to the chromatin structure g. Centromere- The central region that joins two sister chromatids h. Centrosome- The microtubule organizing center present in the cytoplasm i. Homologous Chromosomes- Chromosomes that possess genes coding f ...
... f. Histone –The small protein that binds to the DNA, contributing to the chromatin structure g. Centromere- The central region that joins two sister chromatids h. Centrosome- The microtubule organizing center present in the cytoplasm i. Homologous Chromosomes- Chromosomes that possess genes coding f ...
Meiosis
... Interphase I Cell undergoes regular metabolic processes and protein synthesis. Organelles double in number. DNA replicates and becomes uncoiled. 2n genetic compliment ...
... Interphase I Cell undergoes regular metabolic processes and protein synthesis. Organelles double in number. DNA replicates and becomes uncoiled. 2n genetic compliment ...
MEIOSIS NOTES
... Meiosis is a form of cell division that splits the number of chromosomes in half when forming specialized reproductive cells, called gametes. Meiosis has two divisions of the nucleus, called meiosis I and meiosis II. MEIOSIS I Prophase I: The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks do ...
... Meiosis is a form of cell division that splits the number of chromosomes in half when forming specialized reproductive cells, called gametes. Meiosis has two divisions of the nucleus, called meiosis I and meiosis II. MEIOSIS I Prophase I: The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks do ...
Study Guide for Chapter 9 – Cell Division
... - Calculations: If given one of the following numbers can figure out the rest: sister chromatids, chromosomes, haploid number, diploid number - Meiosis o Compare and contrast to mitosis at least two ways each o Identify the various parts Meiosis I and Meiosis II- similarities and differences. o Voca ...
... - Calculations: If given one of the following numbers can figure out the rest: sister chromatids, chromosomes, haploid number, diploid number - Meiosis o Compare and contrast to mitosis at least two ways each o Identify the various parts Meiosis I and Meiosis II- similarities and differences. o Voca ...
Meiosis - DiBiasioScience
... Telophase I • Each pole now has haploid set of chromosomes. • Cytokinesis occurs and two haploid daughter cells are formed. ...
... Telophase I • Each pole now has haploid set of chromosomes. • Cytokinesis occurs and two haploid daughter cells are formed. ...
Prophase I (cont`d)
... The random separation of homologous chromosomes is called independent assortment. ...
... The random separation of homologous chromosomes is called independent assortment. ...
Meiosis What is an “n”?
... • Cytoplasm splits to separate the • Each of the 4 daughter cells is a new gamete with genetic information different from either parent! ...
... • Cytoplasm splits to separate the • Each of the 4 daughter cells is a new gamete with genetic information different from either parent! ...
CHAPTER 2
... 1. A diploid eukaryotic cell has ten chromosomes (five per set). As a group, take turns having one student draw the cell as it would look during a phase of mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II; then have the other students guess which phase it is. Answer: It’s not possible to give a direct answer, but ...
... 1. A diploid eukaryotic cell has ten chromosomes (five per set). As a group, take turns having one student draw the cell as it would look during a phase of mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II; then have the other students guess which phase it is. Answer: It’s not possible to give a direct answer, but ...
Meiosis Review
... 5. This term refers to a cell which contains 2 copies of each chromosome. (diploid) 6. This term refers to a cell that contains only one copy of each chromosome. (haploid) 7. In humans the 23rd pair of chromosomes are referred to as what? (sex chromosomes) 8. Give an example of a disorder that could ...
... 5. This term refers to a cell which contains 2 copies of each chromosome. (diploid) 6. This term refers to a cell that contains only one copy of each chromosome. (haploid) 7. In humans the 23rd pair of chromosomes are referred to as what? (sex chromosomes) 8. Give an example of a disorder that could ...
Slide 1
... female is born and Meiosis II happens for one egg each month before fertilization. Therefore the female is born with all her eggs but are not ready for ferilization until Meiosis II is completed. ...
... female is born and Meiosis II happens for one egg each month before fertilization. Therefore the female is born with all her eggs but are not ready for ferilization until Meiosis II is completed. ...
BIO 112 Review - Crossword Labs
... will occur 21. When pollen (sperm) from a plant fertilizes an egg on the same plant 24. The physical appearance of a trait 25. Offspring of the P generation parents, have only one of the two parental traits 26. Sequence of DNA that codes for one trait 27. Type of cell used in fertilization 28. Struc ...
... will occur 21. When pollen (sperm) from a plant fertilizes an egg on the same plant 24. The physical appearance of a trait 25. Offspring of the P generation parents, have only one of the two parental traits 26. Sequence of DNA that codes for one trait 27. Type of cell used in fertilization 28. Struc ...
UOPX Material
... chromosomes are depicted as condensed, although during interphase of the normal cell cycle, they are actually thing and dispersed and not visible under a light microscope. Before a cell enter meiosis, it first replicates its DNA. After DNA replication, the chromosomes are duplicated so that each has ...
... chromosomes are depicted as condensed, although during interphase of the normal cell cycle, they are actually thing and dispersed and not visible under a light microscope. Before a cell enter meiosis, it first replicates its DNA. After DNA replication, the chromosomes are duplicated so that each has ...
Meiosis - Biology Courses Server
... – Cancerous cells repeatedly divide – No stopping at the G1 checkpoint ...
... – Cancerous cells repeatedly divide – No stopping at the G1 checkpoint ...
1 - life.illinois.edu
... d. a deep understanding of the molecular basis of the structure of genes. 36. The alleles of two genes that are closely linked on a chromosome will a. usually be inherited together as they were in the parent. b. usually be separated by crossing over during Meiosis I. c. exhibit increased mutation ra ...
... d. a deep understanding of the molecular basis of the structure of genes. 36. The alleles of two genes that are closely linked on a chromosome will a. usually be inherited together as they were in the parent. b. usually be separated by crossing over during Meiosis I. c. exhibit increased mutation ra ...
Review MEIOSIS – the process of cell division in which - Room N-60
... MEIOSIS – the process of cell division in which the number of chromosomes are reduced to half through a process of separating homologous pairs. Diploid – 2 copies of each chromosome ...
... MEIOSIS – the process of cell division in which the number of chromosomes are reduced to half through a process of separating homologous pairs. Diploid – 2 copies of each chromosome ...
Mitosis, Meiosis, Cloning and Genetic Variations
... Cloned individuals are genetically identical to the parent from which they came. This is because they are formed by mitosis / asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is fusion of the sperm and egg, which have been produced through meiosis. Sexual reproduction uses meiosis to produce gametes with h ...
... Cloned individuals are genetically identical to the parent from which they came. This is because they are formed by mitosis / asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is fusion of the sperm and egg, which have been produced through meiosis. Sexual reproduction uses meiosis to produce gametes with h ...
Chapter 10: Meiosis
... Prophase I: Homologous chromosomes pair up (form tetrad); Cross over may occur; other aspects as observed in mitosis. Metaphase I: Homologous pairs align at equator (not sister chromatids). ...
... Prophase I: Homologous chromosomes pair up (form tetrad); Cross over may occur; other aspects as observed in mitosis. Metaphase I: Homologous pairs align at equator (not sister chromatids). ...
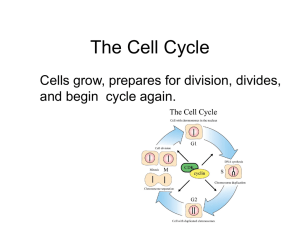
Cell Cycle Notes
... C. Cell Division (M) – division of nucleus (mitosis) & cytoplasm (cytokinesis) ...
... C. Cell Division (M) – division of nucleus (mitosis) & cytoplasm (cytokinesis) ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.