MeiosisPPT
... organisms with two sets of chromosomes 1. the two sets are said to be homologous a. chromosomes in one set have a version of themselves in the other set ...
... organisms with two sets of chromosomes 1. the two sets are said to be homologous a. chromosomes in one set have a version of themselves in the other set ...
Meiosis - Groby Bio Page
... In preparation for the next lesson write definitions for the following words: ...
... In preparation for the next lesson write definitions for the following words: ...
Cell Division Study Guide:
... Which type of reproduction produces identical offspring? ____________________ Which type of reproduction produces very different offspring?____________________ Human body cells have _______________ total chromosomes _________ of them are the sex chromosomes ...
... Which type of reproduction produces identical offspring? ____________________ Which type of reproduction produces very different offspring?____________________ Human body cells have _______________ total chromosomes _________ of them are the sex chromosomes ...
Mitosis, Cell division and aging
... 3. Which stage or phase of the cell cycle corresponds to each of the descriptions below? a) A new cell wall begins to form. cytokinesis b) The membrane of the nucleus dissolves. prophase (starts to dissolve), metaphase (finished) c) Daughter chromosomes begin to separate. anaphase d) Thick chromosom ...
... 3. Which stage or phase of the cell cycle corresponds to each of the descriptions below? a) A new cell wall begins to form. cytokinesis b) The membrane of the nucleus dissolves. prophase (starts to dissolve), metaphase (finished) c) Daughter chromosomes begin to separate. anaphase d) Thick chromosom ...
Meiosis - Tolar ISD
... • Meiosis : cell division which results in the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes • When fertilization occurs, the zygote will contain the full set of homologous chromosomes ...
... • Meiosis : cell division which results in the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes • When fertilization occurs, the zygote will contain the full set of homologous chromosomes ...
Chapter 10 / Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis I. Introduction
... 3. genes carry codes to make a single protein or many proteins 4. one or many genes may determine a particular trait 5. genes can be turned on or off ...
... 3. genes carry codes to make a single protein or many proteins 4. one or many genes may determine a particular trait 5. genes can be turned on or off ...
Sexual reproduction
... called alleles, offspring inherit one allele from each parent • offspring is combination of parental genes ...
... called alleles, offspring inherit one allele from each parent • offspring is combination of parental genes ...
Cell division Objectives
... Evaluate evidence provided by data sets to support the claim that heritable information is passed from one generation to another generation through mitosis, or meiosis followed by fertilization. State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologou ...
... Evaluate evidence provided by data sets to support the claim that heritable information is passed from one generation to another generation through mitosis, or meiosis followed by fertilization. State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologou ...
name
... 4. After the chromosomes replicate and condense they become visible during Prophase. Label this diagram of a doubled chromosome: ...
... 4. After the chromosomes replicate and condense they become visible during Prophase. Label this diagram of a doubled chromosome: ...
Ch 7 Genetic Variety
... During Synapsis (during Prophase1 to Metaphase1) 4 chromosomes form a tetrad Genetic material is exchanged by “non-sister” chromatid on homologous chromosomes ...
... During Synapsis (during Prophase1 to Metaphase1) 4 chromosomes form a tetrad Genetic material is exchanged by “non-sister” chromatid on homologous chromosomes ...
The phases of meiosis II
... • This kind of cell division, which produces gametes containing half the number of chromosomes as a parent’s body cell, is called meiosis. ...
... • This kind of cell division, which produces gametes containing half the number of chromosomes as a parent’s body cell, is called meiosis. ...
Meiosis
... cells (cleavage furrow in animal cells; cell plate in plant cells) • NO DNA replication occurs before Meiosis ...
... cells (cleavage furrow in animal cells; cell plate in plant cells) • NO DNA replication occurs before Meiosis ...
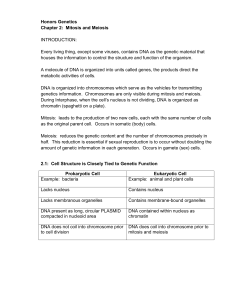
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic activities of cells. DNA is organized into chromosomes which serve as the vehicles for transmitting genetics information. Chromosomes are only visible during mitosis and meiosis. During Interphase, when the cel ...
... A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic activities of cells. DNA is organized into chromosomes which serve as the vehicles for transmitting genetics information. Chromosomes are only visible during mitosis and meiosis. During Interphase, when the cel ...
Meiosis
... number of chromosomes as the original cell Produces gametes (eggs & sperm) Occurs in the testes in males ...
... number of chromosomes as the original cell Produces gametes (eggs & sperm) Occurs in the testes in males ...
Cell Growth & Division - Whitman
... set of chromosomes to combine during sexual reproduction with another to form a DIPLOID cell. ...
... set of chromosomes to combine during sexual reproduction with another to form a DIPLOID cell. ...
Meiosis Formation of Gametes (Eggs & Sperm)
... chromosomes as the original cell Produces gametes (eggs & sperm) Occurs in the testes in males ...
... chromosomes as the original cell Produces gametes (eggs & sperm) Occurs in the testes in males ...
Fly Meiosis FlyMeiosis2016_2
... Diploid (2N) a cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes (all the genetic info) Gametes (sex cells) have only one set of chromosomes (half the genetic info,) considered haploid (N) Haploid gametes are produced in meiosis: look at your diagram from activity and add notations/descript ...
... Diploid (2N) a cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes (all the genetic info) Gametes (sex cells) have only one set of chromosomes (half the genetic info,) considered haploid (N) Haploid gametes are produced in meiosis: look at your diagram from activity and add notations/descript ...
Chapter 4 Cell Division - Heritage Christian School
... increase in size and accumulation of raw materials needed for the division process 2. Prophase – threadlike chromosomes (chromatin) shorten and thicken; centrioles separate and move to opposite ends of the cell; nuclear membrane disappears. (***each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids att ...
... increase in size and accumulation of raw materials needed for the division process 2. Prophase – threadlike chromosomes (chromatin) shorten and thicken; centrioles separate and move to opposite ends of the cell; nuclear membrane disappears. (***each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids att ...
Cell Division Homework w.answers
... Diploid – full set of chromosome (1 chromosome from each parent) Human 2n = 46 Haploid – Half set of chromosomes Human n = 23 5. Draw a replicated chromosome and label the sister chromatids and centromere. Sister chromatids are exact copies of each other (same genes) Centromeres hold sisters togethe ...
... Diploid – full set of chromosome (1 chromosome from each parent) Human 2n = 46 Haploid – Half set of chromosomes Human n = 23 5. Draw a replicated chromosome and label the sister chromatids and centromere. Sister chromatids are exact copies of each other (same genes) Centromeres hold sisters togethe ...
The Formation of Sex Cells
... normal number of chromosomes! The chromosome # must be reduced to half! This is Meiosis. ...
... normal number of chromosomes! The chromosome # must be reduced to half! This is Meiosis. ...
Genetics Test 1 Review
... Draw a diagram of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. Add a few different genes to the chromatids (same on both sides) and identify what the genes code for. Why are sister chromatids identical? ...
... Draw a diagram of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. Add a few different genes to the chromatids (same on both sides) and identify what the genes code for. Why are sister chromatids identical? ...
1. Life process that is crucial to the continuation of a species • 2
... 9. Type of asexual reproduction in which a knoblike structure forms on the parent and pinches off to become a new individual 10. Type of asexual reproduction found in plants, in which offspring separate from the parent plant to become individual plants 11. The ability to develop lost body parts or e ...
... 9. Type of asexual reproduction in which a knoblike structure forms on the parent and pinches off to become a new individual 10. Type of asexual reproduction found in plants, in which offspring separate from the parent plant to become individual plants 11. The ability to develop lost body parts or e ...
Chapter 7 Notes Chapter 7 Notes
... The result is that females will have two copies of the sex-linked gene while males will only have one copy of this gene. If the gene is recessive, then males only need one recessive gene to have a sex-link trait. Examples of Sex-linked Traits: ...
... The result is that females will have two copies of the sex-linked gene while males will only have one copy of this gene. If the gene is recessive, then males only need one recessive gene to have a sex-link trait. Examples of Sex-linked Traits: ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.