GENETICS!!!
... line up next to each other and crossing over occurs. This is an exchange of segments. ...
... line up next to each other and crossing over occurs. This is an exchange of segments. ...
Mendel and Meiosis - Bishop Ireton High School
... Cell splits End up with cell with 46 chromosomes Not done yet- split again to get to magic #23! ...
... Cell splits End up with cell with 46 chromosomes Not done yet- split again to get to magic #23! ...
AP Biology Review Chapters 9-10 Review Questions Chapter
... 4. Explain how the cell prepares the chromosomes and centrosomes prior to nuclear division. 5. Describe the major events that occur during each phase of mitosis. 6. Summarize the differences between cytokinesis in animal and plant cells, and explain why the difference is necessary. 7. List the major ...
... 4. Explain how the cell prepares the chromosomes and centrosomes prior to nuclear division. 5. Describe the major events that occur during each phase of mitosis. 6. Summarize the differences between cytokinesis in animal and plant cells, and explain why the difference is necessary. 7. List the major ...
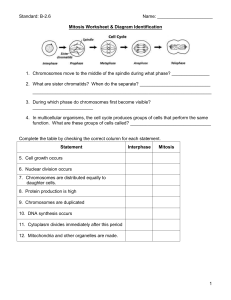
Cell Cycle Stages Worksheet
... phase of in which chromosomes line up in singles along the center of cell ...
... phase of in which chromosomes line up in singles along the center of cell ...
1. According to Model 1, in what type of orga
... 7. Cells with a full set of chromosomes are referred to as diploid or 2n, whereas cells with half the chromosomes are haploid or n. At which stage(s) of meiosis I are the cells diploid and at which stage(s) are they haploid? ...
... 7. Cells with a full set of chromosomes are referred to as diploid or 2n, whereas cells with half the chromosomes are haploid or n. At which stage(s) of meiosis I are the cells diploid and at which stage(s) are they haploid? ...
Ch 3 Sec3
... • Meiosis II– The chromosome with their 2 chromatids move to the center of the cell – Centromeres split and chromatids separate, single chromosome move to opposite ends of the cell ...
... • Meiosis II– The chromosome with their 2 chromatids move to the center of the cell – Centromeres split and chromatids separate, single chromosome move to opposite ends of the cell ...
Frequency of Crossing over lab
... crossing over? 4. From this second small sample, calculate the map distance between the gene and centromere. 5. In what cell processes is mitosis involved? In what cell processes is meiosis involved? 6. In what type of cells does mitosis occur? In what type of cells does meiosis occur? 7. How many t ...
... crossing over? 4. From this second small sample, calculate the map distance between the gene and centromere. 5. In what cell processes is mitosis involved? In what cell processes is meiosis involved? 6. In what type of cells does mitosis occur? In what type of cells does meiosis occur? 7. How many t ...
Class 004
... The number of PAIRS of chromosomes in a cell. Represented as n. Also called haploid. Ex. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in their body cells ﴾n=23﴿ The TOTAL number of chromosomes in a cell. Represented as 2n. Ex. Humans have 46 chromosomes in each body cell ﴾2n=46﴿ ...
... The number of PAIRS of chromosomes in a cell. Represented as n. Also called haploid. Ex. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in their body cells ﴾n=23﴿ The TOTAL number of chromosomes in a cell. Represented as 2n. Ex. Humans have 46 chromosomes in each body cell ﴾2n=46﴿ ...
Steps of Meiosis
... Steps of Meiosis 4. Anaphase I - The homologous chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell - The centromere does NOT split ...
... Steps of Meiosis 4. Anaphase I - The homologous chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell - The centromere does NOT split ...
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
... Chromosomes into Gametes Homologous chromosomes can be attached to either spindle pole in prophase I, so each homologue can be packaged into either one of the two new nuclei ...
... Chromosomes into Gametes Homologous chromosomes can be attached to either spindle pole in prophase I, so each homologue can be packaged into either one of the two new nuclei ...
M. Saadatian MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES
... • At metaphase I, each homologous pair of chromosomes aligns on the metaphase plate. Each pair consists of one maternal and one paternal chromosome. • • The orientation of the homologous pair to the poles is random, so there is a 50-50 chance that a particular daughter cell produced by meiosis I wil ...
... • At metaphase I, each homologous pair of chromosomes aligns on the metaphase plate. Each pair consists of one maternal and one paternal chromosome. • • The orientation of the homologous pair to the poles is random, so there is a 50-50 chance that a particular daughter cell produced by meiosis I wil ...
Sex Cell (gamete) Reproduction
... iv. By contrast, the __gametes______ (or sex cells) of sexually reproducing organisms contain only a single set of chromosomes, and therefore only a single set of genes and are called __haploid_____ and can be written as N = 23, meaning that the haploid number is 23. ...
... iv. By contrast, the __gametes______ (or sex cells) of sexually reproducing organisms contain only a single set of chromosomes, and therefore only a single set of genes and are called __haploid_____ and can be written as N = 23, meaning that the haploid number is 23. ...
Cell Reproduction Xword puzzle
... 20. Reproduction involving a single parent 22. 2n chromosome number in somatic cells 24. X and Y chromosomes 26. Stage in the cell cycle when DNA is copied 29. Chromosomes that are the same size and shape and carry the genes for the same traits 32. Type of cell that enters the G0 cycle such as a bra ...
... 20. Reproduction involving a single parent 22. 2n chromosome number in somatic cells 24. X and Y chromosomes 26. Stage in the cell cycle when DNA is copied 29. Chromosomes that are the same size and shape and carry the genes for the same traits 32. Type of cell that enters the G0 cycle such as a bra ...
Laboratory Exam I - HCC Learning Web
... What is the difference between xylem and phloem? What color of the visible light spectrum is the least effective in photosynthesis (it is not absorbed)? What is paper chromatography? What is the basis of fractionation (there are 3 possible answer choices)? Which pigment acts as the reaction center m ...
... What is the difference between xylem and phloem? What color of the visible light spectrum is the least effective in photosynthesis (it is not absorbed)? What is paper chromatography? What is the basis of fractionation (there are 3 possible answer choices)? Which pigment acts as the reaction center m ...
tetrad - Cloudfront.net
... where the chromosome number is reduced by half • Gametes created (egg, sperm, pollen) • End Result: Four Haploid Cells ...
... where the chromosome number is reduced by half • Gametes created (egg, sperm, pollen) • End Result: Four Haploid Cells ...
Mitosis Phase Review Sheet
... 18. What two main changes are taking place in cell B? ____________________________ 19. Sequence the six diagrams in order from first to last. ___________________________ 20. What is the end product of mitosis? ________________________________________ 21. What is the main difference between cytokines ...
... 18. What two main changes are taking place in cell B? ____________________________ 19. Sequence the six diagrams in order from first to last. ___________________________ 20. What is the end product of mitosis? ________________________________________ 21. What is the main difference between cytokines ...
Meiosis II
... The frequency of crossing over appears to be governed largely by the distance between genes, or in this case, between the gene for spore coat color and the centromere. The probability of a crossover occurring between two particular genes on the same chromosome (linked genes) increases as the distanc ...
... The frequency of crossing over appears to be governed largely by the distance between genes, or in this case, between the gene for spore coat color and the centromere. The probability of a crossover occurring between two particular genes on the same chromosome (linked genes) increases as the distanc ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Pre-Test
... 5. Which of the following best explains why meiosis results in greater genetic diversity than mitosis? A. After meiosis, daughter cells are diploid and have twice as much genetic material, which can be divided in many more possible combinations. B. After meiosis, haploid daughter cells are fertiliz ...
... 5. Which of the following best explains why meiosis results in greater genetic diversity than mitosis? A. After meiosis, daughter cells are diploid and have twice as much genetic material, which can be divided in many more possible combinations. B. After meiosis, haploid daughter cells are fertiliz ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Figure 15.7 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: After they have replicated and become compacted in preparation for cell division, chromosomes are often shaped like an X, as in part (a) of this figure. Which proteins are primarily responsible for this X shape? ANSWER: The nuclear matrix proteins form the sc ...
... Figure 15.7 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: After they have replicated and become compacted in preparation for cell division, chromosomes are often shaped like an X, as in part (a) of this figure. Which proteins are primarily responsible for this X shape? ANSWER: The nuclear matrix proteins form the sc ...
Meiosis Warm
... a. mitosis, cytokinesis, interphase b. interphase, cytokinesis, mitosis c. interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis d. cytokinesis, mitosis, interphase 2. What process is being shown below? a. osmosis b. binary fission c. mitosis d. meiosis ...
... a. mitosis, cytokinesis, interphase b. interphase, cytokinesis, mitosis c. interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis d. cytokinesis, mitosis, interphase 2. What process is being shown below? a. osmosis b. binary fission c. mitosis d. meiosis ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.