uncorrected page proofs
... ‘naked lady’ is due to the fact that after the leaves of the plant appear in spring they die off, and the flowers appear in autumn on their own (see figure 14.2). This simple but beautiful plant is poisonous. Deaths have occurred, often after a person has mistaken the plant for wild garlic and eaten ...
... ‘naked lady’ is due to the fact that after the leaves of the plant appear in spring they die off, and the flowers appear in autumn on their own (see figure 14.2). This simple but beautiful plant is poisonous. Deaths have occurred, often after a person has mistaken the plant for wild garlic and eaten ...
Single-Gene Inheritance Single-Gene Inheritance
... 3. The gene comes in two forms called alleles. If the gene is phonetically called a “wye” gene, then the two alleles can be represented by Y (standing for the yellow phenotype) and y (standing for the green phenotype). 4. A plant can be either Y/Y, y/y, or Y/y. The slash shows that the alleles are a ...
... 3. The gene comes in two forms called alleles. If the gene is phonetically called a “wye” gene, then the two alleles can be represented by Y (standing for the yellow phenotype) and y (standing for the green phenotype). 4. A plant can be either Y/Y, y/y, or Y/y. The slash shows that the alleles are a ...
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
... How do you get so many differences in traits? • Well, let’s start at the very beginning…a very good place to start. • If you look at the DNA of any cell, you will find that each strand has a pair or partner. • These are called homologous pairs • One of the chromosomes from a pair comes from mom, ...
... How do you get so many differences in traits? • Well, let’s start at the very beginning…a very good place to start. • If you look at the DNA of any cell, you will find that each strand has a pair or partner. • These are called homologous pairs • One of the chromosomes from a pair comes from mom, ...
Bio 111 Handout for Genetics 1 Bio 111 iClicker Question #1
... homozygous = both alleles are the same type (ex. “RR rr”) a.k.a “true-breeding” homozygote = an organism that is homozygous heterozygous = both alleles are different (ex. “Rr”) heterozygote = an organism that is heterozygous haploid = having only one allele of each gene; sometimes abbreviated “N”. G ...
... homozygous = both alleles are the same type (ex. “RR rr”) a.k.a “true-breeding” homozygote = an organism that is homozygous heterozygous = both alleles are different (ex. “Rr”) heterozygote = an organism that is heterozygous haploid = having only one allele of each gene; sometimes abbreviated “N”. G ...
Replication Protein A (RPA1a) Is Required for Meiotic and Somatic
... functional megaspore. E, Mononucleate embryo sac formation stage. F to H, Embryo sac mitosis stage. The functional megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions to yield a two-nucleate (arrowheads) embryo sac (F), four-nucleate (arrowheads) embryo sac (G), and eight-nucleate embryo sac (H), respective ...
... functional megaspore. E, Mononucleate embryo sac formation stage. F to H, Embryo sac mitosis stage. The functional megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions to yield a two-nucleate (arrowheads) embryo sac (F), four-nucleate (arrowheads) embryo sac (G), and eight-nucleate embryo sac (H), respective ...
File
... Mendel carried out his experiments in three steps: • 1. Mendel allowed each variety of garden pea to selfpollinate for several generations. This method ensured that each variety was true-breeding (purebred) for a particular trait; that is all the offspring would show only one form of a particular ...
... Mendel carried out his experiments in three steps: • 1. Mendel allowed each variety of garden pea to selfpollinate for several generations. This method ensured that each variety was true-breeding (purebred) for a particular trait; that is all the offspring would show only one form of a particular ...
Document
... testcross also reveals something new: there is approximately a 1:1 ratio not only between the two parental types, but also between the two nonparental types. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a. 03-04 prof S. Presciuttini ...
... testcross also reveals something new: there is approximately a 1:1 ratio not only between the two parental types, but also between the two nonparental types. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a. 03-04 prof S. Presciuttini ...
Lesson Plan - Colorado FFA
... Chromosomes are not clearly discerned in the nucleus, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be visible. Prophase. Chromatin in the nucleus begins to condense and becomes visible in the light microscope as chromosomes. The nuclear membrane dissolves and the chromosomes begin moving. Metaphase ...
... Chromosomes are not clearly discerned in the nucleus, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be visible. Prophase. Chromatin in the nucleus begins to condense and becomes visible in the light microscope as chromosomes. The nuclear membrane dissolves and the chromosomes begin moving. Metaphase ...
Chromosomal theory of inheritance
... – Boveri: chromosomes are required for development to occur in sea urchins. – SuLon: chromosomes appear in matched pairs in grasshoppers. • “… the associa*on of maternal and paternal chromosomes in pairs ...
... – Boveri: chromosomes are required for development to occur in sea urchins. – SuLon: chromosomes appear in matched pairs in grasshoppers. • “… the associa*on of maternal and paternal chromosomes in pairs ...
Fungi
... and terrestrial habitats – Are defined by the production of sexual spores in saclike asci, which are usually contained in fruiting bodies called ascocarps – Have asexual reproduction by producing enormous numbers of asexual spores called ...
... and terrestrial habitats – Are defined by the production of sexual spores in saclike asci, which are usually contained in fruiting bodies called ascocarps – Have asexual reproduction by producing enormous numbers of asexual spores called ...
Merotelic kinetochore orientation occurs frequently during early
... Merotelic kinetochore orientation is an error that occurs when a single kinetochore becomes attached to microtubules from two spindle poles rather than just to one pole. We obtained the first evidence that merotelic kinetochore orientation occurs very frequently during early mitosis in mammalian tis ...
... Merotelic kinetochore orientation is an error that occurs when a single kinetochore becomes attached to microtubules from two spindle poles rather than just to one pole. We obtained the first evidence that merotelic kinetochore orientation occurs very frequently during early mitosis in mammalian tis ...
Genetics Heredity and Variation: *Heredity is the branch of science
... Gene mapping meaning relative positions of genes on chromosomes Calculating (CoV) crossing over value help us to produce maps for gene position on the chromosomes, by converting CoV this value into hypothetical distances along the chromosome. Ex: a (CoV) of 4% between genes A and B means that those ...
... Gene mapping meaning relative positions of genes on chromosomes Calculating (CoV) crossing over value help us to produce maps for gene position on the chromosomes, by converting CoV this value into hypothetical distances along the chromosome. Ex: a (CoV) of 4% between genes A and B means that those ...
Chemically Induced Aberrations of Mitosis in Bacteria
... After pre-drying of the surface, the suspension of organisms was streaked over the agar with a pipette in about five streaks parallel to the axis of the gradient. The plates were then incubated and the organisms examined cytologically after various periods of exposure. Any resistant colonies were cu ...
... After pre-drying of the surface, the suspension of organisms was streaked over the agar with a pipette in about five streaks parallel to the axis of the gradient. The plates were then incubated and the organisms examined cytologically after various periods of exposure. Any resistant colonies were cu ...
one-step and stepwise magnification of a bobbed lethal
... to account for ribosomal gene increase during magnification and provide an explanation for reversion of bb' chromosomes more rapidly than is permitted by single events of unequal sister strand exchange. During the course of this study we also analyzed several stepwise bb'" chromosomes. These stepwis ...
... to account for ribosomal gene increase during magnification and provide an explanation for reversion of bb' chromosomes more rapidly than is permitted by single events of unequal sister strand exchange. During the course of this study we also analyzed several stepwise bb'" chromosomes. These stepwis ...
early RNs, crossing over initiates, then synapsis begins Chiasmata
... maize genome) is recombinationally inactive – even when in homozygous state. Also highly methylated. • Perhaps 2 levels of control – chromatin state (exposed chromosome regions more easily accessed by enzymes) plus sequence similarity. ...
... maize genome) is recombinationally inactive – even when in homozygous state. Also highly methylated. • Perhaps 2 levels of control – chromatin state (exposed chromosome regions more easily accessed by enzymes) plus sequence similarity. ...
Evolutionary Origin and Adaptive Function of Meiosis
... derived from the two bacterial cells align and undergo genetic recombination (exchange of genetic information); (3) the new recombined chromosome is passed on to progeny bacteria. Meiosis in diploid eukaryotic cells can similarly be viewed as occurring by three steps. These steps are: (1) gametes un ...
... derived from the two bacterial cells align and undergo genetic recombination (exchange of genetic information); (3) the new recombined chromosome is passed on to progeny bacteria. Meiosis in diploid eukaryotic cells can similarly be viewed as occurring by three steps. These steps are: (1) gametes un ...
Exam #4_REVIEW-11042016-LW
... 60) Correns found that the inheritance of variegated color on the leaves of certain plants was determined only by the maternal parent. What phenomenon explains this pattern? Section: 15.5 61) Mitochondrial DNA is primarily involved in coding for proteins needed for protein complexes of the electron ...
... 60) Correns found that the inheritance of variegated color on the leaves of certain plants was determined only by the maternal parent. What phenomenon explains this pattern? Section: 15.5 61) Mitochondrial DNA is primarily involved in coding for proteins needed for protein complexes of the electron ...
File
... 50 : 50 ratio. All human egg cells carry a single X chro mosome (23,X). However, half of all sperm cells carry an X chromosome (23,X) and half carry a Y chromosome (23,Y). This ensures that just about half the zygotes will be males and half will be females. More than 1200 genes are found on the X c ...
... 50 : 50 ratio. All human egg cells carry a single X chro mosome (23,X). However, half of all sperm cells carry an X chromosome (23,X) and half carry a Y chromosome (23,Y). This ensures that just about half the zygotes will be males and half will be females. More than 1200 genes are found on the X c ...
Learning about the Human Genome Explore the 23andMe Browse
... Objective: In this activity, the students are introduced to the human genome and what can be observed about it by looking at chromosome data analyzed by 23andMe. They will discover that: 1. Chromosomes are numbered and organized by scientists from largest to smallest (with one exception chrom ...
... Objective: In this activity, the students are introduced to the human genome and what can be observed about it by looking at chromosome data analyzed by 23andMe. They will discover that: 1. Chromosomes are numbered and organized by scientists from largest to smallest (with one exception chrom ...
Genigames Curriculum Guide
... located in the chromosomes of each cell. An in a variety of ways replication of inherited trait of an individual can be determined that result in genetic material by one or by many genes, and a single gene can continuity of result in offspring influence more than one trait. A human cell structure and ...
... located in the chromosomes of each cell. An in a variety of ways replication of inherited trait of an individual can be determined that result in genetic material by one or by many genes, and a single gene can continuity of result in offspring influence more than one trait. A human cell structure and ...
Answers Lab 9 Mendelian Genetics
... flipping coins, we would expect to see heads 50% of the time and tails 50% of the time. But, does this always occur? Let’s explore! ...
... flipping coins, we would expect to see heads 50% of the time and tails 50% of the time. But, does this always occur? Let’s explore! ...
Student Review Sheet Biology Semester B Examination
... For a long time scientists have believed that mammals cannot survive when they have twice as much DNA as they should have. A rat species found in Argentina is challenging this belief. Scientists know that some non-mammals, such as fish and amphibians, can live with four copies of each chromosome ins ...
... For a long time scientists have believed that mammals cannot survive when they have twice as much DNA as they should have. A rat species found in Argentina is challenging this belief. Scientists know that some non-mammals, such as fish and amphibians, can live with four copies of each chromosome ins ...
Mendel`s Work - the science center
... scientific study of heredity. A new organism begins to form when egg and sperm join in the process called fertilization. Before fertilization can happen in pea plants, pollen must reach the pistil of a pea flower through pollination. Pea plants are usually self-pollinating, meaning pollen from a flo ...
... scientific study of heredity. A new organism begins to form when egg and sperm join in the process called fertilization. Before fertilization can happen in pea plants, pollen must reach the pistil of a pea flower through pollination. Pea plants are usually self-pollinating, meaning pollen from a flo ...
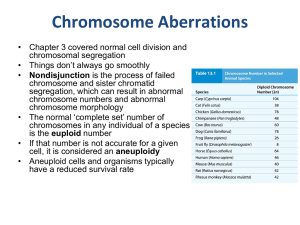
Chromosome Aberrations
... chromosome and sister chromatid segregation, which can result in abnormal chromosome numbers and abnormal chromosome morphology • The normal ‘complete set’ number of chromosomes in any individual of a species is the euploid number • If that number is not accurate for a given cell, it is considered a ...
... chromosome and sister chromatid segregation, which can result in abnormal chromosome numbers and abnormal chromosome morphology • The normal ‘complete set’ number of chromosomes in any individual of a species is the euploid number • If that number is not accurate for a given cell, it is considered a ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.