Cells, Transport, Mitosis, Protein Synthesis
... –DNA helix uncoils and separates into 2 chains –Each strand is a template ...
... –DNA helix uncoils and separates into 2 chains –Each strand is a template ...
Oncogenesis: abnormal developmental plasticity
... dramatic events of the human cell cycle. Already in 1879, Flemming had noticed that, “the impetus causing nuclear threads to split longitudinally acts simultaneously on all of them”. What is Flemming’s “impetus” triggering loss of cohesion between sister chromatids? What holds sisters together befor ...
... dramatic events of the human cell cycle. Already in 1879, Flemming had noticed that, “the impetus causing nuclear threads to split longitudinally acts simultaneously on all of them”. What is Flemming’s “impetus” triggering loss of cohesion between sister chromatids? What holds sisters together befor ...
Document
... * During ______________, the chromosomes move to the equator of the spindle Sister Chromatids C. Anaphase: The third stage of mitosis. * During _______________, the centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. D. Telophase: the fourth stage of mitosis. ...
... * During ______________, the chromosomes move to the equator of the spindle Sister Chromatids C. Anaphase: The third stage of mitosis. * During _______________, the centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. D. Telophase: the fourth stage of mitosis. ...
Unit A Notes #1 Cell Intro - Mr. Lesiuk
... - Abundant in cells that produce large amounts of protein for export from the cell. The combination of phospholipid-membranous structures including the Nuclear Envelope, Endoplasmic Reticulums, Cell Membrane and Golgi Apparatus; collectively work together to form what is known as the Endomembrane ...
... - Abundant in cells that produce large amounts of protein for export from the cell. The combination of phospholipid-membranous structures including the Nuclear Envelope, Endoplasmic Reticulums, Cell Membrane and Golgi Apparatus; collectively work together to form what is known as the Endomembrane ...
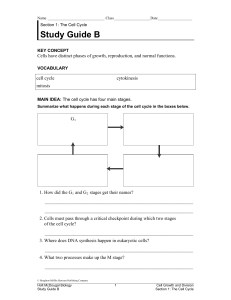
Study Guide B
... 9. Which typically increases faster as a cell grows, surface area or volume? _______________________________________________________________ 10. For cells to stay the same size from generation to generation, what two things must be coordinated? _______________________________________________________ ...
... 9. Which typically increases faster as a cell grows, surface area or volume? _______________________________________________________________ 10. For cells to stay the same size from generation to generation, what two things must be coordinated? _______________________________________________________ ...
Cell Wall Cell Membrane Flagella Cell Structure Comparison Activity
... Block Number:_________ What other organelles can it be grouped with and why? Rough ER, Smooth ER, Golgi work with the nucleus. What and how does it work? ...
... Block Number:_________ What other organelles can it be grouped with and why? Rough ER, Smooth ER, Golgi work with the nucleus. What and how does it work? ...
Flow of Matter_04_Sample Quiz Questions
... Using your model of how matter flows from our food cells to our own cells, answer the following questions: Breakout session #2 Question #1: Athletes preparing for a competition will often “carbo load” or eat a meal high in carbohydrates the night before. If glycogen is an important source of energ ...
... Using your model of how matter flows from our food cells to our own cells, answer the following questions: Breakout session #2 Question #1: Athletes preparing for a competition will often “carbo load” or eat a meal high in carbohydrates the night before. If glycogen is an important source of energ ...
Stage 2 - Mitosis
... Prophase is the first step of mitosis. In this step, the DNA gathers together and forms chromosomes in order to get ready to divide. Tiny “threads” of DNA coil up to form chromatids that join to form chromosomes. The nuclear membrane dissolves, and two points (called centrioles) form at the opposite ...
... Prophase is the first step of mitosis. In this step, the DNA gathers together and forms chromosomes in order to get ready to divide. Tiny “threads” of DNA coil up to form chromatids that join to form chromosomes. The nuclear membrane dissolves, and two points (called centrioles) form at the opposite ...
Select this.
... with microtubules are associated special proteins called motor proteins (take participation in transporting processes in cells with utilization of ATP) ...
... with microtubules are associated special proteins called motor proteins (take participation in transporting processes in cells with utilization of ATP) ...
Name - gcisd
... b. SISTER CHROMATIDS ARE PULLED BY CONTRACTION OF SPINDLE FIBERS 25. What is the last stage of mitosis? TELOPHASE ...
... b. SISTER CHROMATIDS ARE PULLED BY CONTRACTION OF SPINDLE FIBERS 25. What is the last stage of mitosis? TELOPHASE ...
CHAPTER 8 Mitosis - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Getting ready to split • Cell cycle has two parts: –growth and preparation (interphase) –cell division • mitosis (nuclear division) • cytokinesis (cytoplasm division) ...
... Getting ready to split • Cell cycle has two parts: –growth and preparation (interphase) –cell division • mitosis (nuclear division) • cytokinesis (cytoplasm division) ...
File - wedgwood science
... How do daughter cells split apart after mitosis? Cytokinesis completes the process of cell division – it splits one cell into two. ...
... How do daughter cells split apart after mitosis? Cytokinesis completes the process of cell division – it splits one cell into two. ...
Plant cells Structure of the plant cells :
... made of outer membrane and inner membrane which are different in lipid composition and enzyme activity . ...
... made of outer membrane and inner membrane which are different in lipid composition and enzyme activity . ...
Chapter 2 – Chromosomes and Sexual
... • Division of cytoplasm – Animal cells – cleavage furrow – Plant cells – cell plate ...
... • Division of cytoplasm – Animal cells – cleavage furrow – Plant cells – cell plate ...
Chapter 3 Lesson 2
... Tissues are groups of similar types of cells in multicellular organisms that work together to carry out specific tasks. ...
... Tissues are groups of similar types of cells in multicellular organisms that work together to carry out specific tasks. ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide - Conackamack Middle School
... i. Definitions of each ii. Differences between the two b. Organelles of the plant and animal cells i. Structure of each ii. Function of each c. Similarities/Differences of plant and animal cells d. Vocabulary to include – organelle, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, ...
... i. Definitions of each ii. Differences between the two b. Organelles of the plant and animal cells i. Structure of each ii. Function of each c. Similarities/Differences of plant and animal cells d. Vocabulary to include – organelle, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, ...
Name
... school (just like we did with a city analogy on our index cards.) Just as all of the organelles are found inside of a cell, all of your comparisons should include things are found inside a school, so no school buses, playgrounds, etc. will be accepted. Use a computer to copy and paste Google images ...
... school (just like we did with a city analogy on our index cards.) Just as all of the organelles are found inside of a cell, all of your comparisons should include things are found inside a school, so no school buses, playgrounds, etc. will be accepted. Use a computer to copy and paste Google images ...
Cells Homework 1
... walls of a growing plant are built up from at least six different sugars; at least two structural proteins; about twenty different enzymes and small quantities of many other substances. Cell walls are complex structures and this complexity must be important to plant life. Cell walls, therefore, must ...
... walls of a growing plant are built up from at least six different sugars; at least two structural proteins; about twenty different enzymes and small quantities of many other substances. Cell walls are complex structures and this complexity must be important to plant life. Cell walls, therefore, must ...
The Cell Cycle
... • This results in two identical cells that are also identical to the original cell from which they were formed. • After cytokenesis, the cell cycle is complete and they will begin the cell cycle again. ...
... • This results in two identical cells that are also identical to the original cell from which they were formed. • After cytokenesis, the cell cycle is complete and they will begin the cell cycle again. ...
Organelles Day 3 - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... purpose that allows the cell to function. To be inducted into the biology club, you need to know all the organelles. ...
... purpose that allows the cell to function. To be inducted into the biology club, you need to know all the organelles. ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.