The Cell Cycle
... Plant cells At the time of telophase, small membraneous vesicles forms a double membrane, which is called the __________ ____________. It forms across the midline of the plant cell from the inside out where the equatorial plane was located. ...
... Plant cells At the time of telophase, small membraneous vesicles forms a double membrane, which is called the __________ ____________. It forms across the midline of the plant cell from the inside out where the equatorial plane was located. ...
THE CELL CYCLE AND MITOSIS UNIT 3 ORGANIZATION AND
... • The chromosomes move centromere first. • The cell elongates as the other microtubules lengthen. • By the end of anaphase, the two ends of the cell have equivalent—and complete—collections of chromosomes. ...
... • The chromosomes move centromere first. • The cell elongates as the other microtubules lengthen. • By the end of anaphase, the two ends of the cell have equivalent—and complete—collections of chromosomes. ...
The Cell
... Modify (address) proteins & lipids and send them in packages (vessicles) throughout (or out of) the cell. ...
... Modify (address) proteins & lipids and send them in packages (vessicles) throughout (or out of) the cell. ...
Parts of the Cell
... iii. Fluid Mosaic Model: Lipid bilayers behaves more like a fluid than a solid. Organelles: internal structures that form special functions for the cell. a. Cytoplasm: material between cell membrane and nucleus that contains the organelles. b. Mitochondria: “Powerhouse” of the cell. Produce ATP whic ...
... iii. Fluid Mosaic Model: Lipid bilayers behaves more like a fluid than a solid. Organelles: internal structures that form special functions for the cell. a. Cytoplasm: material between cell membrane and nucleus that contains the organelles. b. Mitochondria: “Powerhouse” of the cell. Produce ATP whic ...
The Cell - Biology Junction
... Modify (address) proteins & lipids and send them in packages (vessicles) throughout (or out of) the cell. ...
... Modify (address) proteins & lipids and send them in packages (vessicles) throughout (or out of) the cell. ...
Cell Biology
... This is a one semester college transfer-level course designed to meet the needs of science majors. This course is an elective course for science majors in their second year of college study following completion of BIO 101 and 102 - “General Biology I & II”. This course would also benefit the student ...
... This is a one semester college transfer-level course designed to meet the needs of science majors. This course is an elective course for science majors in their second year of college study following completion of BIO 101 and 102 - “General Biology I & II”. This course would also benefit the student ...
The Eukaryotic Cell
... Maine power source Sugar is broken down to produce energy Have their own DNA and can divide within cell ...
... Maine power source Sugar is broken down to produce energy Have their own DNA and can divide within cell ...
Study Guide for AP Biology Mid-term Biochemistry What is
... Cell Unit 1. What type of cell contains only circular chromosomes? 2. What environmental conditions can decrease photosynthetic yield? 3. The most ATP is made during which part of aerobic respiration? 4. Why would club soda cause a plant to grow bigger? 5. Metabolic process common in aerobic respira ...
... Cell Unit 1. What type of cell contains only circular chromosomes? 2. What environmental conditions can decrease photosynthetic yield? 3. The most ATP is made during which part of aerobic respiration? 4. Why would club soda cause a plant to grow bigger? 5. Metabolic process common in aerobic respira ...
Honors Bio SFO Ch 07
... a. Identify the main functions of the cell membrane and the cell wall. b. Describe what happens during diffusion. c. Explain the processes of osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. ...
... a. Identify the main functions of the cell membrane and the cell wall. b. Describe what happens during diffusion. c. Explain the processes of osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. ...
Slide 1
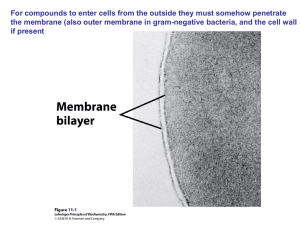
... are not like a concrete wall and also not like the thin membrane in a soap-bubble. It is a much more complex barrier that lets certain selected compounds through in a strictly controlled manner. •Macromolecules and charged smaller molecules do not generally pass through membranes passively (by diffu ...
... are not like a concrete wall and also not like the thin membrane in a soap-bubble. It is a much more complex barrier that lets certain selected compounds through in a strictly controlled manner. •Macromolecules and charged smaller molecules do not generally pass through membranes passively (by diffu ...
Extra Credit Ch.10
... 3. During cell division in a eukaryotic cell, the movement of chromosomes is aided by an organelle called the ______________________. 4. Three checkpoints help ensure that a cell does not divide unless it is ready to go on to the next phase of the ______________________ ______________________. If co ...
... 3. During cell division in a eukaryotic cell, the movement of chromosomes is aided by an organelle called the ______________________. 4. Three checkpoints help ensure that a cell does not divide unless it is ready to go on to the next phase of the ______________________ ______________________. If co ...
Cells
... features to help a cell carry out its functions. Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell and controls movement of substances in and out. Nucleus: Contains genetic material (DNA) which controls the cell's activities. Vacuole: Area in a cell that contains liquid, and can be used by plants to keep the cell r ...
... features to help a cell carry out its functions. Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell and controls movement of substances in and out. Nucleus: Contains genetic material (DNA) which controls the cell's activities. Vacuole: Area in a cell that contains liquid, and can be used by plants to keep the cell r ...
1 - The main principle of cell theory are 2
... 2. Leucoplasts: These are colourless plastids which store food materials. Ex: Amyloplasts: Store starch Aleuronoplasts: Store proteins Elaeioplasts: Store lipids 3. Cholorplasts: These are green coloured plastids containing chlorophylls and carotenoids (carotenes & xanthophylls). ...
... 2. Leucoplasts: These are colourless plastids which store food materials. Ex: Amyloplasts: Store starch Aleuronoplasts: Store proteins Elaeioplasts: Store lipids 3. Cholorplasts: These are green coloured plastids containing chlorophylls and carotenoids (carotenes & xanthophylls). ...
View PDF
... 18. Make a table to show what happens to plant and animal cells that are placed in the following types of solutions: hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic. ...
... 18. Make a table to show what happens to plant and animal cells that are placed in the following types of solutions: hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic. ...
CELLS
... environment; it gives support and protection to the cell Composed of a double layer of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer; it also has proteins embedded in it The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
... environment; it gives support and protection to the cell Composed of a double layer of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer; it also has proteins embedded in it The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
five unit: “the cell and the smallest living being”
... nucleus and cytoplasm.-Cell membrane controls the passage of chemicals into and out of the cell. Nucleus contains the genetic information of the cell and controls all chemical activity.-Cytoplasm contains water and others substances and all of the organelles like mitochondrion, vacuoles,….-Mitochond ...
... nucleus and cytoplasm.-Cell membrane controls the passage of chemicals into and out of the cell. Nucleus contains the genetic information of the cell and controls all chemical activity.-Cytoplasm contains water and others substances and all of the organelles like mitochondrion, vacuoles,….-Mitochond ...
THE CELL
... A. Cell Wall Cell walls are the outermost boundary in bacteria plants fungi __________, _______, and ___________. animal cells They are not found in _____________________. The primary function of the cell wall is to provide ___________________________. The cell wall structure and support does not re ...
... A. Cell Wall Cell walls are the outermost boundary in bacteria plants fungi __________, _______, and ___________. animal cells They are not found in _____________________. The primary function of the cell wall is to provide ___________________________. The cell wall structure and support does not re ...
Cells A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living
... The organelles in a cell have specific jobs, and their activities are coordinated to maintain homeostasis. Not all cells have all the same organelles. Example: Chloroplasts ...
... The organelles in a cell have specific jobs, and their activities are coordinated to maintain homeostasis. Not all cells have all the same organelles. Example: Chloroplasts ...
Cell Cycle - Dallas Independent School District
... new cell wall will form. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow pinches the cell in two. Nucleus ...
... new cell wall will form. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow pinches the cell in two. Nucleus ...
20 Questions: Mitosis Answers
... Dividing the nucleus Replicating the DNA Split the parent cell into two daughter cells Makes the cell bigger. ...
... Dividing the nucleus Replicating the DNA Split the parent cell into two daughter cells Makes the cell bigger. ...
Notes Sheet
... 3. Cell Division in Prokaryotes is called ______________________ ________________ Prokaryotic cells are bacteria … small ( ~ ____ micron) unicellular no nucleus or other organelles such as m___________________ v______________________ or c___________________________ 3. Cell Division in Eukaryot ...
... 3. Cell Division in Prokaryotes is called ______________________ ________________ Prokaryotic cells are bacteria … small ( ~ ____ micron) unicellular no nucleus or other organelles such as m___________________ v______________________ or c___________________________ 3. Cell Division in Eukaryot ...
General comparisons between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells:
... Cytokinesis occurs: cytoplasm constricts at the metaphase plate forming a cleavage furrow that pinches the cells apart ...
... Cytokinesis occurs: cytoplasm constricts at the metaphase plate forming a cleavage furrow that pinches the cells apart ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... The flexible boundary of a cell that acts as a selectively permeable membrane. ...
... The flexible boundary of a cell that acts as a selectively permeable membrane. ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.