Cell Shape and Arrangement
... Gram Staining (and Cell Shape and Arrangement) (WINTER 2014 version) Introduction Gram stain - Most common bacteria are described as being either Gram positive (G+) or Gram negative (G-), based on the structure of their cell walls. Gram positive cell walls consist of many layers of peptidoglycan (cr ...
... Gram Staining (and Cell Shape and Arrangement) (WINTER 2014 version) Introduction Gram stain - Most common bacteria are described as being either Gram positive (G+) or Gram negative (G-), based on the structure of their cell walls. Gram positive cell walls consist of many layers of peptidoglycan (cr ...
Cell Diversity Lab 2 Name __________________________
... bacteria are either round (coccus), rod-shaped (bacillus), or spiral-shaped (spirillum). To view them with the compound microscope, you must use an oil-immersion lens (100x objective). Even then, not much more than their basic shapes will be visible. With the aid of the electron microscope, however, ...
... bacteria are either round (coccus), rod-shaped (bacillus), or spiral-shaped (spirillum). To view them with the compound microscope, you must use an oil-immersion lens (100x objective). Even then, not much more than their basic shapes will be visible. With the aid of the electron microscope, however, ...
Meiosis (11-4)
... Sister chromatids — now individual chromosomes — move toward the opposite poles of the cell. ...
... Sister chromatids — now individual chromosomes — move toward the opposite poles of the cell. ...
Relationships between cellular activity and culturability
... carbon nitrogen stressed NC H. pylori cells maintained at 4°C retained a higher proportion of active cells than similarly maintained V. vulnificus cells [4]. Further image analysis of the succinate-enhanced tetrazolium reactions used in these studies revealed the additional features that are demonst ...
... carbon nitrogen stressed NC H. pylori cells maintained at 4°C retained a higher proportion of active cells than similarly maintained V. vulnificus cells [4]. Further image analysis of the succinate-enhanced tetrazolium reactions used in these studies revealed the additional features that are demonst ...
and Save - Workshops+SJCOE Workshop Management
... Students use the model to describe a causal account for the phenomenon, including how different parts of a cell contribute to how the cell functions as a whole, both separately and together with other structures. Students include how components, separately and together, contribute to: i. Maintaining ...
... Students use the model to describe a causal account for the phenomenon, including how different parts of a cell contribute to how the cell functions as a whole, both separately and together with other structures. Students include how components, separately and together, contribute to: i. Maintaining ...
ATCC® PRIMARY CELL CuLTuRE GuIdE
... relevant data representing living systems. Primary cultures consist of cells that have been freshly derived from a living organism and are maintained for growth in vitro. Primary cells can be categorized according to the genus from which they are isolated, as well as by species or tissue type. Each ...
... relevant data representing living systems. Primary cultures consist of cells that have been freshly derived from a living organism and are maintained for growth in vitro. Primary cells can be categorized according to the genus from which they are isolated, as well as by species or tissue type. Each ...
1 Plant Physiology I: PLS622 2006 Introduction: Cell division
... involved in cellulose synthesis has been isolated. Dubbed korrigan (kor), the mutant plants are dwarfed and exhibit aberrant cell expansion. The hemicellulosic component of plant cell walls is thought to be intimately associated with the cellulose microfibrils, either laying along the microfibrils ...
... involved in cellulose synthesis has been isolated. Dubbed korrigan (kor), the mutant plants are dwarfed and exhibit aberrant cell expansion. The hemicellulosic component of plant cell walls is thought to be intimately associated with the cellulose microfibrils, either laying along the microfibrils ...
A Single-Phase Grid-Connected Fuel Cell System Based on a Boost
... In this paper, the boost-inverter topology is used as a building block for a single-phase gridconnected fuel cell (FC) system offering low cost and compactness. In addition, the proposed system incorporates battery-based energy storage and a dc–dc bidirectional converter to support the slow dynamics ...
... In this paper, the boost-inverter topology is used as a building block for a single-phase gridconnected fuel cell (FC) system offering low cost and compactness. In addition, the proposed system incorporates battery-based energy storage and a dc–dc bidirectional converter to support the slow dynamics ...
Cell!Transport!Concept!Map! - AHS
... Living cells maintain a _________________________ by controlling material that enter and leave. Without this ability, the cell cannot maintain _____________________________ and will die. The cell must regulate ...
... Living cells maintain a _________________________ by controlling material that enter and leave. Without this ability, the cell cannot maintain _____________________________ and will die. The cell must regulate ...
The Nervous System The Nervous System Nervous System
... • slow increase until threshold is reached • voltage-gated Na+ channels open quickly (K+ channels slowly) ...
... • slow increase until threshold is reached • voltage-gated Na+ channels open quickly (K+ channels slowly) ...
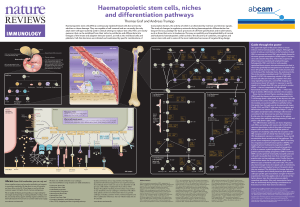
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... granulocyte/macrophage progenitors (GMPs). However, GMPs can also generate eosinophils, basophils and mast cells and it is possible that more than one pathway to granulocytes and macrophages exists. Finally, there are controversies about the developmental origin of the different types of dendritic c ...
... granulocyte/macrophage progenitors (GMPs). However, GMPs can also generate eosinophils, basophils and mast cells and it is possible that more than one pathway to granulocytes and macrophages exists. Finally, there are controversies about the developmental origin of the different types of dendritic c ...
Lab 02- Cell Diversity
... small, with specialized structures that allow for a diversity of functions. All eukaryotic cells have their genetic material enclosed by a nuclear membrane, the nuclear envelope. In addition, a variety of subcellular membrane-bound organelles are present. These include plastids, mitochondria, lysoso ...
... small, with specialized structures that allow for a diversity of functions. All eukaryotic cells have their genetic material enclosed by a nuclear membrane, the nuclear envelope. In addition, a variety of subcellular membrane-bound organelles are present. These include plastids, mitochondria, lysoso ...
The septins: roles in cytokinesis and other processes Mark S
... also been seen at the mother-bud neck and near the bases of hyphae in the dimorphie yeast C. a/b/cans [22], and it is likely, although not yet demonstrated, that these filaments contain the C. albicans septins [10]. However, C. albicans is morphologically similar and relatively close phylogeneticall ...
... also been seen at the mother-bud neck and near the bases of hyphae in the dimorphie yeast C. a/b/cans [22], and it is likely, although not yet demonstrated, that these filaments contain the C. albicans septins [10]. However, C. albicans is morphologically similar and relatively close phylogeneticall ...
U2_Obj13
... Describe how living cells with and without cell walls regulate water balance. Explain how transport proteins facilitate diffusion. Distinguish among osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Describe the two forces that combine to produce an electrochemical gradient. Explain how an elect ...
... Describe how living cells with and without cell walls regulate water balance. Explain how transport proteins facilitate diffusion. Distinguish among osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Describe the two forces that combine to produce an electrochemical gradient. Explain how an elect ...
Unit 2 Objectives
... Describe how living cells with and without cell walls regulate water balance. Explain how transport proteins facilitate diffusion. Distinguish among osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Describe the two forces that combine to produce an electrochemical gradient. Explain how an elect ...
... Describe how living cells with and without cell walls regulate water balance. Explain how transport proteins facilitate diffusion. Distinguish among osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Describe the two forces that combine to produce an electrochemical gradient. Explain how an elect ...
Doxorubicin major clinical activity
... Alkylating agents exert cytotoxic effects via transfer of their alkyl groups to various cellular constituents. Alkylations of DNA within the nucleus probably represent the major interactions that lead to cell death. ...
... Alkylating agents exert cytotoxic effects via transfer of their alkyl groups to various cellular constituents. Alkylations of DNA within the nucleus probably represent the major interactions that lead to cell death. ...
The Cytoplasm of a Cell and the Courtyard of a Siheyuan
... cytoplasm gives the cell some advantages that keep this type of organisms in the evolutionary history. First, by being the medium that hold all its suspension together, the cytoplasm supports the interior cell structure and maintains the basic shape of the cell. Without this cushioning liquid, the c ...
... cytoplasm gives the cell some advantages that keep this type of organisms in the evolutionary history. First, by being the medium that hold all its suspension together, the cytoplasm supports the interior cell structure and maintains the basic shape of the cell. Without this cushioning liquid, the c ...
Bones and ligaments
... Skeletal cont… • Structure: MuscleFasicle Myofiber (cell) Myofibril (with many sarcomeres)Myofilaments • Many myofibers connected lengthwise through entire fiber • Many mitochondria • Many nuclei (why? The multiple nuclei arise from the fact that each muscle fiber develops from the fusion of ma ...
... Skeletal cont… • Structure: MuscleFasicle Myofiber (cell) Myofibril (with many sarcomeres)Myofilaments • Many myofibers connected lengthwise through entire fiber • Many mitochondria • Many nuclei (why? The multiple nuclei arise from the fact that each muscle fiber develops from the fusion of ma ...
Evening Session- Cytopathology USCAP Annual Meeting 2016 Dr
... Most studies investigating this antibody have used strong cytoplasmic staining as a positive result.[10] Although it has been shown to be sensitive and specific, there can be heterogeneity in the staining pattern, and thus, the results should be confirmed with molecular testing.[3,9,10] The immun ...
... Most studies investigating this antibody have used strong cytoplasmic staining as a positive result.[10] Although it has been shown to be sensitive and specific, there can be heterogeneity in the staining pattern, and thus, the results should be confirmed with molecular testing.[3,9,10] The immun ...
Glencoe Biology
... At what stage of interphase does the cell take inventory and make sure it is ready for the division of its nucleus? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M ...
... At what stage of interphase does the cell take inventory and make sure it is ready for the division of its nucleus? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M ...
Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell Lines and Cell Culture
... diacetate succinimidyl ester; Life Technologies) according to manufacturers protocol. ...
... diacetate succinimidyl ester; Life Technologies) according to manufacturers protocol. ...
Chapter 9 Lecture
... At what stage of interphase does the cell take inventory and make sure it is ready for the division of its nucleus? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M ...
... At what stage of interphase does the cell take inventory and make sure it is ready for the division of its nucleus? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.