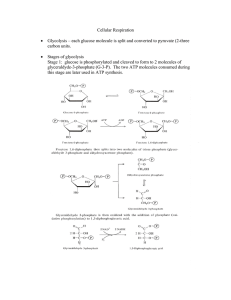
Cellular Respiration - Mayfield City Schools
... 1. Third major pathway that occurs along the inner mitochondrial MEMBRANE (CRISTAE). 2. Produces most of the ATP in cellular respiration; yields 32 to 34 ATP molecules a. Only 4 ATP have been synthesized thus far by substrate level phosphorylation b. A total of 36 -38 can be synthesized from energy ...
... 1. Third major pathway that occurs along the inner mitochondrial MEMBRANE (CRISTAE). 2. Produces most of the ATP in cellular respiration; yields 32 to 34 ATP molecules a. Only 4 ATP have been synthesized thus far by substrate level phosphorylation b. A total of 36 -38 can be synthesized from energy ...
Which of the following is a coenzyme associated with cellular
... group to ADP to form ATP it's referred to as _____. A. photophosphorylation ___ B. substrate-level phosphorylation C. oxidative phosphorylation ...
... group to ADP to form ATP it's referred to as _____. A. photophosphorylation ___ B. substrate-level phosphorylation C. oxidative phosphorylation ...
2nd bio1 exam sample
... Q2. Write true (T) or false (F) 1) A cell lacking oligosaccharides on the external surface of its plasma membrane would likely be inefficient in cell-cell recognition. 2) The most accepted model of plasma membrane structure is the fluid mosaic model. 3) The presence of cholesterol in the plasma memb ...
... Q2. Write true (T) or false (F) 1) A cell lacking oligosaccharides on the external surface of its plasma membrane would likely be inefficient in cell-cell recognition. 2) The most accepted model of plasma membrane structure is the fluid mosaic model. 3) The presence of cholesterol in the plasma memb ...
FERMENTATION: an anaerobic biological reaction process in which
... FERMENTATION: an anaerobic biological reaction process in which a reduced organic compound (like glucose) acts as an electron donor and another organic compound acts as an electron acceptor What are the products of fermentation in yeast? ...
... FERMENTATION: an anaerobic biological reaction process in which a reduced organic compound (like glucose) acts as an electron donor and another organic compound acts as an electron acceptor What are the products of fermentation in yeast? ...
Which of the following is a coenzyme associated with
... The energy released by the electron transport system produces ATP by _____. A. photophosphorylation B. substrate-level phosphorylation C. oxidative phosphorylation ___ ...
... The energy released by the electron transport system produces ATP by _____. A. photophosphorylation B. substrate-level phosphorylation C. oxidative phosphorylation ___ ...
Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
... The carbons eventually leave the cycle as CO2 Some ATP is produced during the citric acid cycle NADH and FADH2 are also produced The Electron Transport Chain Embedded in the inner membrane is a series of electron carriers comprising the electron transport chain As high energy electrons move down the ...
... The carbons eventually leave the cycle as CO2 Some ATP is produced during the citric acid cycle NADH and FADH2 are also produced The Electron Transport Chain Embedded in the inner membrane is a series of electron carriers comprising the electron transport chain As high energy electrons move down the ...
Cellular Respiration
... 3. Citric Acid goes through a cycle where CO2 and electron carriers are formed. 4. The 2 original pyruvic acid molecules are completely broken down into CO2 ...
... 3. Citric Acid goes through a cycle where CO2 and electron carriers are formed. 4. The 2 original pyruvic acid molecules are completely broken down into CO2 ...
HONORS BIOLOGY CHAPTERy 6 STUDY GUIDE
... Label the following diagram: intermembrane space ATP H 2O ...
... Label the following diagram: intermembrane space ATP H 2O ...
cellular respiration - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● Respiration uses an ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN to break the fall of electrons into several energyreleasing steps (instead of one ...
... ● Respiration uses an ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN to break the fall of electrons into several energyreleasing steps (instead of one ...
Cellular Respiration
... Krebs cycle-happens in matrix of mitochondria Electron transport and oxidative phophorylation-cristae ...
... Krebs cycle-happens in matrix of mitochondria Electron transport and oxidative phophorylation-cristae ...
this lecture as PDF here
... • Ex. 1: Nitrosomonas: 2 NH3 (ammonia) + 3 O2 -----> 2 HNO2 (nitrite) + 2 H2O • Ex. 2: Nitrobacter: 2 HNO2 (nitrite) + 2 O2 -----> 2 HNO3 (nitrate) • Note potential problem: redox potential for nitrite as electron donor is + 0.42 v., so can easily pass electrons down to oxygen at + 0.82 v., reaction ...
... • Ex. 1: Nitrosomonas: 2 NH3 (ammonia) + 3 O2 -----> 2 HNO2 (nitrite) + 2 H2O • Ex. 2: Nitrobacter: 2 HNO2 (nitrite) + 2 O2 -----> 2 HNO3 (nitrate) • Note potential problem: redox potential for nitrite as electron donor is + 0.42 v., so can easily pass electrons down to oxygen at + 0.82 v., reaction ...
notes for cell resp - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 1. Pyruvate looses 2 hydrogen atoms (oxidized) and a carboxyl group that yields a two carbon acetyl group. Carbon dioxide is released 2. The acetyl group is linked to a coenzyme called coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA. 3. Part of the energy from the oxidation is saved by the reduction of NAD+ to ...
... 1. Pyruvate looses 2 hydrogen atoms (oxidized) and a carboxyl group that yields a two carbon acetyl group. Carbon dioxide is released 2. The acetyl group is linked to a coenzyme called coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA. 3. Part of the energy from the oxidation is saved by the reduction of NAD+ to ...
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages
... 3. The Electron Transport Chain (also known as oxidative phosphorylation) produces the energy that drives the synthesis of ATP in oxidative phosphorylation it consists of molecules (mostly proteins) that are embedded in the inner mitochondria Sitting atop these proteins are molecules that are ...
... 3. The Electron Transport Chain (also known as oxidative phosphorylation) produces the energy that drives the synthesis of ATP in oxidative phosphorylation it consists of molecules (mostly proteins) that are embedded in the inner mitochondria Sitting atop these proteins are molecules that are ...
Exam #2
... down processes, called catabolism, which usually result in energy release. 21. __________ About two thirds of the energy generated by a cell is spent on motility. 22. __________ Enzymes lower the activation energy required for a chemical reaction. 23. __________ Coenzyme A is involved with electron ...
... down processes, called catabolism, which usually result in energy release. 21. __________ About two thirds of the energy generated by a cell is spent on motility. 22. __________ Enzymes lower the activation energy required for a chemical reaction. 23. __________ Coenzyme A is involved with electron ...
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
... abbreviated as NAD+, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. • This is an oxidation reaction where 2 hydrogen atoms (or 2 hydrogen ions and 2 electrons) are removed from the organic metabolite. When electrons are transferred from a metabolite by NAD+, NAD+ additionally removes two protons, hydrogen ions, ...
... abbreviated as NAD+, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. • This is an oxidation reaction where 2 hydrogen atoms (or 2 hydrogen ions and 2 electrons) are removed from the organic metabolite. When electrons are transferred from a metabolite by NAD+, NAD+ additionally removes two protons, hydrogen ions, ...
Biological Oxidation
... Two molecules of the reduced form of cytochrome c pass their electrons to a copper-heme a complex and then to a copper-heme a3 group. This last group is responsible for the reduction of oxygen to produce water in a multi-step reaction which uses four electrons and four protons for each molecule of o ...
... Two molecules of the reduced form of cytochrome c pass their electrons to a copper-heme a complex and then to a copper-heme a3 group. This last group is responsible for the reduction of oxygen to produce water in a multi-step reaction which uses four electrons and four protons for each molecule of o ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. Define Gibb's free energy. 5. What are ketone bodies? 6. Give the energy value of one ATP molecule. 7. What is meant by β - oxidation? 8. What are porphyrins? 9. Mention the role of glutamate dehydrogenase. 10. What are primary metabolites? Part - B (8 x 5 = 40) Answer any five of the following q ...
... 4. Define Gibb's free energy. 5. What are ketone bodies? 6. Give the energy value of one ATP molecule. 7. What is meant by β - oxidation? 8. What are porphyrins? 9. Mention the role of glutamate dehydrogenase. 10. What are primary metabolites? Part - B (8 x 5 = 40) Answer any five of the following q ...
CHAPTER 3: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... mitochondria. It oxidizes acetyl groups to carbon dioxide, making ATP by substratelevel ATP synthesis, and producing NADH + H+ and FADH2. Electron Transport Chain The electron transport chain is located in the cristae of the mitochondria. It is a series of carriers that pass electrons from one to th ...
... mitochondria. It oxidizes acetyl groups to carbon dioxide, making ATP by substratelevel ATP synthesis, and producing NADH + H+ and FADH2. Electron Transport Chain The electron transport chain is located in the cristae of the mitochondria. It is a series of carriers that pass electrons from one to th ...
aerobic respiration
... • Cells break down glucose and other organic fuels to yield chemical energy in the form of ATP. Fermentation is a partial degradation of glucose without the use of oxygen. • Cellular respiration is a more complete breakdown of glucose; in aerobic respiration, oxygen is used as a reactant. ...
... • Cells break down glucose and other organic fuels to yield chemical energy in the form of ATP. Fermentation is a partial degradation of glucose without the use of oxygen. • Cellular respiration is a more complete breakdown of glucose; in aerobic respiration, oxygen is used as a reactant. ...
Matrix: Citric Acid Cycle and Pyruvate Oxidation Mitochondrion A
... • Production of ATP as a result of electron transfer through carriers in the Electron Transport Chain – Electrons pass through a set of membrane-associated carriers by a series of redox reactions – Energy from electron transport powers the active transport of H+ to the intermembrane compartment of t ...
... • Production of ATP as a result of electron transfer through carriers in the Electron Transport Chain – Electrons pass through a set of membrane-associated carriers by a series of redox reactions – Energy from electron transport powers the active transport of H+ to the intermembrane compartment of t ...
Plant Respiration
... O2 resulting in the formation of H 2O. The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another, is called the electron transport system (ETS) and it is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Electrons from NADH produced in the mitochondrial matrix during citric acid ...
... O2 resulting in the formation of H 2O. The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another, is called the electron transport system (ETS) and it is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Electrons from NADH produced in the mitochondrial matrix during citric acid ...
Chapter 11
... become OH- (H, Fig XI-12) At which point the two water species are released is unclear though each must capture an additional protons as they leave the enzyme as H2O (O, p XI-12).. These 4 protons are called the scalar protons because they are required by the balanced chemical reaction. I prefer to ...
... become OH- (H, Fig XI-12) At which point the two water species are released is unclear though each must capture an additional protons as they leave the enzyme as H2O (O, p XI-12).. These 4 protons are called the scalar protons because they are required by the balanced chemical reaction. I prefer to ...
2.2 cellular respiration: the details
... intermembrane space. NADH gives up the two electrons it carries to NADH hydrogenase. Electron carriers, ubiquinone and cytochrome c, shuttle electrons from NADH hydrogenase to cytochrone b-c1 complex to cytochrome oxidase complex. Free energy is lost from the electrons during each step in this proce ...
... intermembrane space. NADH gives up the two electrons it carries to NADH hydrogenase. Electron carriers, ubiquinone and cytochrome c, shuttle electrons from NADH hydrogenase to cytochrone b-c1 complex to cytochrome oxidase complex. Free energy is lost from the electrons during each step in this proce ...
Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration
... mitochondrial membrane. The number of protons pumped out as electrons drop from NADH through the respiratory chain to oxygen is theoretically large enough to generate, as they return through ATP synthase, 3 ATPs per electron pair (but only 2 ATPs for each pair donated by FADH2). With 12 pairs of el ...
... mitochondrial membrane. The number of protons pumped out as electrons drop from NADH through the respiratory chain to oxygen is theoretically large enough to generate, as they return through ATP synthase, 3 ATPs per electron pair (but only 2 ATPs for each pair donated by FADH2). With 12 pairs of el ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.