Red Tide Activity 2 - Tampa Bay Water Atlas
... Read to students or have them read the magazine article on plankton. Students should have a basic understanding of the typical parts of a cell in order to complete this activity. Give each student a copy of the "Typical Dinoflagellate" worksheet. Have the students complete it independently or as a g ...
... Read to students or have them read the magazine article on plankton. Students should have a basic understanding of the typical parts of a cell in order to complete this activity. Give each student a copy of the "Typical Dinoflagellate" worksheet. Have the students complete it independently or as a g ...
The NUCLEUS (“mayor of city hall”)
... blueprint (like the blueprints of a city) the nucleus directs the production of proteins. You will learn about this process in the DNA Transcription and Translation lab. ...
... blueprint (like the blueprints of a city) the nucleus directs the production of proteins. You will learn about this process in the DNA Transcription and Translation lab. ...
009 Chapter 9 The Continuity of Life
... A. that meiosis reduces the chromosome number in half. B. that synapsis must occur for crossing over to take place. C. that parthenogenesis does not increase genetic variability. D. that evolution is due to mutations, not crossing over. E. that once harmful mutations arise, asexual populations have ...
... A. that meiosis reduces the chromosome number in half. B. that synapsis must occur for crossing over to take place. C. that parthenogenesis does not increase genetic variability. D. that evolution is due to mutations, not crossing over. E. that once harmful mutations arise, asexual populations have ...
CELLS
... Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external environment; it gives support and protection to the cell Composed of a double layer of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer; it also has proteins embedded in it The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and lea ...
... Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external environment; it gives support and protection to the cell Composed of a double layer of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer; it also has proteins embedded in it The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and lea ...
Cells Compared to Manhattan Beach, CA
... and even Manhattan Beach, CA. These cells are busy building and breaking down macromolecules. They are at work releasing energy from foods, and then using that energy to make needed cell parts. Together your cells function to make your body operate like Manhattan Beach, CA. Procedure: 1. Use your no ...
... and even Manhattan Beach, CA. These cells are busy building and breaking down macromolecules. They are at work releasing energy from foods, and then using that energy to make needed cell parts. Together your cells function to make your body operate like Manhattan Beach, CA. Procedure: 1. Use your no ...
Cell cycle - Instructure
... commit to S phase and mitosis, mate (haploids), sporulate (diploids), arrest (starvation) These choices and the ability of cdc28 mutants to block all early cell cycle events define Start If cells grow in size exponentially, the time it take to double in mass is independent of birth mass Start is del ...
... commit to S phase and mitosis, mate (haploids), sporulate (diploids), arrest (starvation) These choices and the ability of cdc28 mutants to block all early cell cycle events define Start If cells grow in size exponentially, the time it take to double in mass is independent of birth mass Start is del ...
Tour Of The Cell - BronxPrepAPBiology
... • Envelope = double layered membrane that has pores for molecular transport. • Chromatin = DNA + protein complex of threadlike fibers that make up the eukaryotic chromosome. • Chromosome = Chromatin fibers condense into visible chromosomes during cell division. ...
... • Envelope = double layered membrane that has pores for molecular transport. • Chromatin = DNA + protein complex of threadlike fibers that make up the eukaryotic chromosome. • Chromosome = Chromatin fibers condense into visible chromosomes during cell division. ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Answer the following questions on your
... Eukaryotic Cell Structure Answer the following questions on your own paper. (25 points) Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) ...
... Eukaryotic Cell Structure Answer the following questions on your own paper. (25 points) Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) ...
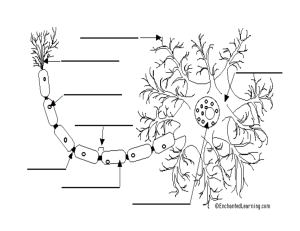
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
Looking Inside Cells
... write two questions that you have about the illustrations in a graphic organizer like the one below. As you read, answer your questions. Plant and Animal Cells Q. How are animal cells different from plant cells? ...
... write two questions that you have about the illustrations in a graphic organizer like the one below. As you read, answer your questions. Plant and Animal Cells Q. How are animal cells different from plant cells? ...
Cancer Cells - Answers - Iowa State University
... These cells were deemed ‘immortal’ because they never died - they just kept dividing and dividing. Almost all original caner testing and research were done on her cells because they lived on for so long. ...
... These cells were deemed ‘immortal’ because they never died - they just kept dividing and dividing. Almost all original caner testing and research were done on her cells because they lived on for so long. ...
Cells
... Robert Hooke Robert Hooke1st person to view a cell under a microscope, given credit for naming cells. ...
... Robert Hooke Robert Hooke1st person to view a cell under a microscope, given credit for naming cells. ...
Slide () - Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research
... From: Biotechnology in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Foundations and Future of Hair Cell Regeneration J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2011;54(6):1709-1731. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0149) ...
... From: Biotechnology in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Foundations and Future of Hair Cell Regeneration J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2011;54(6):1709-1731. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0149) ...
Cells
... All living organisms are made up of one or more cells and their products The cell is the simplest unit that carries out all life processes All cells come from other living cells (first cell ~ 4 billion years ago) ...
... All living organisms are made up of one or more cells and their products The cell is the simplest unit that carries out all life processes All cells come from other living cells (first cell ~ 4 billion years ago) ...
Cellular Reproduction PowerPoint
... growing & doing its job (i.e. making proteins) S (synthesis) = cell is continuing to grow & duplicates its DNA (i.e. chromosomes) in preparation for making duplicate cells during mitosis G2 (2nd gap) = cell keeps growing & doing its job (i.e. making proteins); it grows too big…solution = divide ...
... growing & doing its job (i.e. making proteins) S (synthesis) = cell is continuing to grow & duplicates its DNA (i.e. chromosomes) in preparation for making duplicate cells during mitosis G2 (2nd gap) = cell keeps growing & doing its job (i.e. making proteins); it grows too big…solution = divide ...
Cell organelle card sort vacuole Where proteins are synthesised
... The activity could be differentiated by giving the students the answer table with some of the names and/or descriptions missing. The missing sections could be given to them on cards to fill in the table. For more able students simply give them the answer table with just one section filled in for eac ...
... The activity could be differentiated by giving the students the answer table with some of the names and/or descriptions missing. The missing sections could be given to them on cards to fill in the table. For more able students simply give them the answer table with just one section filled in for eac ...
: . Mitosis: Chromosome Replication and Division
... 4. Be able to define and correctly use the following terms: allele, anaphase, centriole, centromere, chromosome replication, cytokinesis, diploid, DNA synthesis, Gene, homologous chromosomes, interphase, life cycle, metaphase, mitosis, prometaphase, prophase, replicated chromosomes, sister chromatid ...
... 4. Be able to define and correctly use the following terms: allele, anaphase, centriole, centromere, chromosome replication, cytokinesis, diploid, DNA synthesis, Gene, homologous chromosomes, interphase, life cycle, metaphase, mitosis, prometaphase, prophase, replicated chromosomes, sister chromatid ...
A View of the Cell
... Eukaryotes is such an important distinction that they are placed in separate Kingdoms. ...
... Eukaryotes is such an important distinction that they are placed in separate Kingdoms. ...
Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials Selectively Permeable
... Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials ...
... Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials ...
File
... Organisms made up of more than one cell are called ________Multicellular____ The smallest unit able to perform the activities of life is called ____Cell______ Cells without a nucleus are called _Prokaryotic___________ Cells with a nucleus are called __Eukaryotic________ The three parts of cell theor ...
... Organisms made up of more than one cell are called ________Multicellular____ The smallest unit able to perform the activities of life is called ____Cell______ Cells without a nucleus are called _Prokaryotic___________ Cells with a nucleus are called __Eukaryotic________ The three parts of cell theor ...
Cell Biology Study Guide
... 13. What is the proper arrangement of the phospholipids in the cell membrane? 14. Draw a phospholipid. Label the parts that are: Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Polar, Nonpolar, Phosphate Group, Fatty Acids, Heads and Tails. 15. What is the difference between peripheral and integral proteins? 16. Beside p ...
... 13. What is the proper arrangement of the phospholipids in the cell membrane? 14. Draw a phospholipid. Label the parts that are: Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Polar, Nonpolar, Phosphate Group, Fatty Acids, Heads and Tails. 15. What is the difference between peripheral and integral proteins? 16. Beside p ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.