ExamView - 10 A B C Test (PreAP) #1
... b. Cells are one of several basic units of structure and function in living things. c. All cells are produced from other cells. ...
... b. Cells are one of several basic units of structure and function in living things. c. All cells are produced from other cells. ...
MODELING THE CELL RECOGNITION PROCESS
... The recognition process is used by the cell to learn about its environment and is necessary for the viability and motility of singe cells but also tissues. The process is onset by the formation of ligand‐receptor bonds that form adhesion clusters. In the later stages, controlled by active regu ...
... The recognition process is used by the cell to learn about its environment and is necessary for the viability and motility of singe cells but also tissues. The process is onset by the formation of ligand‐receptor bonds that form adhesion clusters. In the later stages, controlled by active regu ...
Test Review Unit 3 Bio
... the way through a cell membrane and stretches both inside and outside the cell. Show the structure of the molecules of the cell membrane and discuss the polarity of the head and tails of these molecules. Think about where water is in relation to the cell. Use the following terms in your description: ...
... the way through a cell membrane and stretches both inside and outside the cell. Show the structure of the molecules of the cell membrane and discuss the polarity of the head and tails of these molecules. Think about where water is in relation to the cell. Use the following terms in your description: ...
A counter-example to Paul`s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as
... A counter-example to Paul’s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as Marquis points out. When a human cancer cell appears in my body, it is a human individual according to the criterion in premise 1: “a life is begun which is neither that of the father nor the mother; it is rather new human life with it ...
... A counter-example to Paul’s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as Marquis points out. When a human cancer cell appears in my body, it is a human individual according to the criterion in premise 1: “a life is begun which is neither that of the father nor the mother; it is rather new human life with it ...
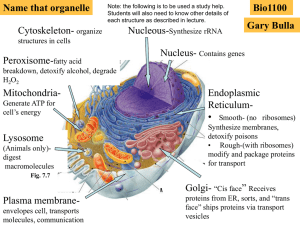
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell
... with intermediate filaments (nuclear lamina) that maintains shape • ER often is an extension of the nuclear membrane • Contain DNA of eukaryotic cells – “brain” of cell A single strand of DNA can be 3 meters long. How does all that DNA fit? ...
... with intermediate filaments (nuclear lamina) that maintains shape • ER often is an extension of the nuclear membrane • Contain DNA of eukaryotic cells – “brain” of cell A single strand of DNA can be 3 meters long. How does all that DNA fit? ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell
... with intermediate filaments (nuclear lamina) that maintains shape • ER often is an extension of the nuclear membrane • Contain DNA of eukaryotic cells – “brain” of cell A single strand of DNA can be 3 meters long. How does all that DNA fit? ...
... with intermediate filaments (nuclear lamina) that maintains shape • ER often is an extension of the nuclear membrane • Contain DNA of eukaryotic cells – “brain” of cell A single strand of DNA can be 3 meters long. How does all that DNA fit? ...
Ch 6: Cells
... Evidence: Chloroplasts and mitochondria each have their own separate DNA and can reproduce on their own ...
... Evidence: Chloroplasts and mitochondria each have their own separate DNA and can reproduce on their own ...
Cell Analogy Rubric
... vacuoles and closets store materials (think of the factory we used in class---You cannot do a factory!!!!). You are required to complete this project independently. The 10 required cell parts are: vacuole mitochondria Golgi apparatus ribosomes ...
... vacuoles and closets store materials (think of the factory we used in class---You cannot do a factory!!!!). You are required to complete this project independently. The 10 required cell parts are: vacuole mitochondria Golgi apparatus ribosomes ...
Genetics Lesson 03
... • The process begins with a diploid (2n) cell called an oogonium. • Oogonia reproduce by mitosis before birth and begin meiosis, but stop at Prophase I. ...
... • The process begins with a diploid (2n) cell called an oogonium. • Oogonia reproduce by mitosis before birth and begin meiosis, but stop at Prophase I. ...
Lecture #12 - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... 1. Cdks generally present throughout cell cycle but are inactive w/o cyclin subunits. ...
... 1. Cdks generally present throughout cell cycle but are inactive w/o cyclin subunits. ...
Cell Membrane
... temporarily stored your clothes. Within a cell, a vacuole fills a similar role as a temporary storage space for the cell. Vacuoles store water, food, pigments, waste or other materials. Vacuoles are large in plant cells and small in animal cells. Vacuoles can also be found in fungi and protists. ...
... temporarily stored your clothes. Within a cell, a vacuole fills a similar role as a temporary storage space for the cell. Vacuoles store water, food, pigments, waste or other materials. Vacuoles are large in plant cells and small in animal cells. Vacuoles can also be found in fungi and protists. ...
CELL- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS a. Unicellular organisms have one celled body. True
... Prokaryotes: Those organisms whose cells do not have well organized nucleus are called prokaryotes. The nuclear membrane is absent. Examples: Bacteria and Blue Green algae. Eukaryotes: Those organisms whose cells have well organized nucleus with nuclear membrane are called eukaryotes. The eukaryotic ...
... Prokaryotes: Those organisms whose cells do not have well organized nucleus are called prokaryotes. The nuclear membrane is absent. Examples: Bacteria and Blue Green algae. Eukaryotes: Those organisms whose cells have well organized nucleus with nuclear membrane are called eukaryotes. The eukaryotic ...
cell - Hicksville Public Schools
... Used to view extremely small structures inside cells & viruses Utilizes an electron beam instead of a light beam Can magnify up to a million times Subject must be dead and dry ...
... Used to view extremely small structures inside cells & viruses Utilizes an electron beam instead of a light beam Can magnify up to a million times Subject must be dead and dry ...
CELL THEORY GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS of all CELLS
... DOCTOR STUDIED BACTERIA CELLS DIVIDING AND HYPOTHESIZED THAT ALL “CELLS COME FROM OTHER CELLS” BECAME KNOWN AS BIOGENESIS, REPLACED THE WIDELY HELD IDEA OF SPONTANEOUS GENERATION, NOTION THAT NON-LIVING THINGS COULD GIVE RISE TO LIVING ORGANISMS ...
... DOCTOR STUDIED BACTERIA CELLS DIVIDING AND HYPOTHESIZED THAT ALL “CELLS COME FROM OTHER CELLS” BECAME KNOWN AS BIOGENESIS, REPLACED THE WIDELY HELD IDEA OF SPONTANEOUS GENERATION, NOTION THAT NON-LIVING THINGS COULD GIVE RISE TO LIVING ORGANISMS ...
Ch 6 Homework Questions
... 7. When the cytoskeleton was first discovered, scientists thought what they were seeing were artifacts of the TEM. Discuss why shouldn’t they have been surprised to find the cytoskeleton. (e.g. why is a cytoskeleton necessary for cells). 8. Explain how are the cell walls of plants and bacteria simil ...
... 7. When the cytoskeleton was first discovered, scientists thought what they were seeing were artifacts of the TEM. Discuss why shouldn’t they have been surprised to find the cytoskeleton. (e.g. why is a cytoskeleton necessary for cells). 8. Explain how are the cell walls of plants and bacteria simil ...
Diversity of Life: a little background Bacteria Archaea Eukarya
... Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells ...
... Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells ...
Cell Membrane, Photosynthesis and Respiration Name Date Word
... water, and carbon dioxide to make food. through a cell membrane into the cytoplasm. b. Green plants use energy from sunlight to unite water and carbon dioxide, thus forming sugar. _________________ _________________ 9. "to exit," "out" _________________ ...
... water, and carbon dioxide to make food. through a cell membrane into the cytoplasm. b. Green plants use energy from sunlight to unite water and carbon dioxide, thus forming sugar. _________________ _________________ 9. "to exit," "out" _________________ ...
Cell Structure Notes
... The Importance of Compartmental Organization a. Eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a ______________________________ ______________________________ and are partitioned into various compartments by a complex system of membranes which provide correct environments for specific metabolic processes. b. ...
... The Importance of Compartmental Organization a. Eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a ______________________________ ______________________________ and are partitioned into various compartments by a complex system of membranes which provide correct environments for specific metabolic processes. b. ...
The 7 Characteristics of Life
... 3. Living Things Use Energy: Living things take in energy and use it for maintenance and growth. 4. Living Things Respond To Their Environment: Living things will make changes in response to a stimulus in their environment. A behavior is a complex set of responses. 5. Living Things Grow: Cel ...
... 3. Living Things Use Energy: Living things take in energy and use it for maintenance and growth. 4. Living Things Respond To Their Environment: Living things will make changes in response to a stimulus in their environment. A behavior is a complex set of responses. 5. Living Things Grow: Cel ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.