Characterizing Individual Tissue-Infiltrating T Cell
... autoimmunity and potentially to the identification of novel targets for future drug development. Herein, we will take advantage of a novel application that, for the first time, will allow for a highly focused dissection of the pathogenic T cell repertoire. To date, most studies have focused on chara ...
... autoimmunity and potentially to the identification of novel targets for future drug development. Herein, we will take advantage of a novel application that, for the first time, will allow for a highly focused dissection of the pathogenic T cell repertoire. To date, most studies have focused on chara ...
Slide 1
... Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis, made up of rRNA Golgi apparatus – folded membranes that store and transports enzymes and hormones, also produces the cell wall in plants Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Sit ...
... Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis, made up of rRNA Golgi apparatus – folded membranes that store and transports enzymes and hormones, also produces the cell wall in plants Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Sit ...
Cells - Midway ISD
... a. all living things are composed of cells b. cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things c. new cells are produced from existing cells ...
... a. all living things are composed of cells b. cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things c. new cells are produced from existing cells ...
Theoretical immunology/Microbiology Dept./Vet.Med. 2015--
... Inhibition of B cell activation:Plasma cells die shortly, they have a life span of few days only and the Abs production is stopped .There is a negative feedback mechanisms that regulate the Abs production. The inhibition of B cell activation is probably mediated by the binding of Ag Abs complex to ...
... Inhibition of B cell activation:Plasma cells die shortly, they have a life span of few days only and the Abs production is stopped .There is a negative feedback mechanisms that regulate the Abs production. The inhibition of B cell activation is probably mediated by the binding of Ag Abs complex to ...
Cells - bollendorfscience
... Nucleus is like the “brain” of the cell. It contains chromosomal information on chromatin. Chromatin is composed of long, thin strands of DNA which contains “instructions” that control cell metabolism and heredity. Ribosomes are small grain-like bodies that produce proteins. Mitochondria take ...
... Nucleus is like the “brain” of the cell. It contains chromosomal information on chromatin. Chromatin is composed of long, thin strands of DNA which contains “instructions” that control cell metabolism and heredity. Ribosomes are small grain-like bodies that produce proteins. Mitochondria take ...
cell division - WordPress.com
... number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus • Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells) have two sets of chromosomes • Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs) have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells ...
... number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus • Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells) have two sets of chromosomes • Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs) have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells ...
cells. - Effingham County Schools
... b. Most living organisms are made up of many cells (multicellular). These are the organisms that you can see. Both multicellular organisms and unicellular organisms share all the characteristics of life. ...
... b. Most living organisms are made up of many cells (multicellular). These are the organisms that you can see. Both multicellular organisms and unicellular organisms share all the characteristics of life. ...
Cell Division – An Introduction
... Amoeba and budding in yeast. You are also aware about the fact that higher plants and animals cannot divide by binary fission and budding. Cell division is the key phenomenon for both growth and reproduction. Cell division in higher organisms is mainly of two types: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is a ...
... Amoeba and budding in yeast. You are also aware about the fact that higher plants and animals cannot divide by binary fission and budding. Cell division is the key phenomenon for both growth and reproduction. Cell division in higher organisms is mainly of two types: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is a ...
7.3 ANIMAL and PLANT CELL STRUCTURE HO
... Animal and Plant Cells: Organelles All living things are made up of cells and these cells are made up of different parts. The parts are called organelles. Organelles are structures that are scattered throughout the cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant an ...
... Animal and Plant Cells: Organelles All living things are made up of cells and these cells are made up of different parts. The parts are called organelles. Organelles are structures that are scattered throughout the cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant an ...
Cell Specialization notes FIB
... Well, ______________ cells are the ones able to differentiate. Stem cells are ____________________ cells. They have several abilities: 1. The can ________________ and renew themselves for______________ periods of time. 2. They can __________________ undifferentiated in form. 3. They can develo ...
... Well, ______________ cells are the ones able to differentiate. Stem cells are ____________________ cells. They have several abilities: 1. The can ________________ and renew themselves for______________ periods of time. 2. They can __________________ undifferentiated in form. 3. They can develo ...
Biomedica EZ4U - Oxford Biosystems
... coloured formazan derivates. This water soluble formazan is secreted into the culture medium and can be measured with a standard colorimetric reader. ...
... coloured formazan derivates. This water soluble formazan is secreted into the culture medium and can be measured with a standard colorimetric reader. ...
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
... The Cell Cycle: Interphase and Mitosis 1. 1. Interphase: All DNA is duplicated and cell parts are made. 3 stages: •G (gap)1: normal cell growth •S (synthesis): all DNA is copied (new set of chromatin is synthesized) ...
... The Cell Cycle: Interphase and Mitosis 1. 1. Interphase: All DNA is duplicated and cell parts are made. 3 stages: •G (gap)1: normal cell growth •S (synthesis): all DNA is copied (new set of chromatin is synthesized) ...
Cytology R
... The fluid inside a cell, but outside the nucleus “Holds” organelles in place Site of cellular chemical reactions ...
... The fluid inside a cell, but outside the nucleus “Holds” organelles in place Site of cellular chemical reactions ...
08. Cell Organelle II
... for photosynthesis - internal organization: elliptical shape with internal stroma; pigment photosystems are highly ordered and arrayed on thylakoids (membranes with granal & intergranal regions) ...
... for photosynthesis - internal organization: elliptical shape with internal stroma; pigment photosystems are highly ordered and arrayed on thylakoids (membranes with granal & intergranal regions) ...
SG From a Cell to an Organism
... Until the sister chromatids in each duplicated chromosome separate during mitosis, they are held together by a special structure. A chromosome is made up of two identical coiled strands of DNA. Following mitosis, the division of the cell’s cytoplasm occurs. Most cells go through a cyclical process o ...
... Until the sister chromatids in each duplicated chromosome separate during mitosis, they are held together by a special structure. A chromosome is made up of two identical coiled strands of DNA. Following mitosis, the division of the cell’s cytoplasm occurs. Most cells go through a cyclical process o ...
Name
... It’s long been known that cells accumulate flotsam from the wear and tear of everyday living. Broken or misshapen proteins, shreds of cellular membranes, invasive viruses or bacteria, and worn-out, broken-down cellular components, like aged mitochondria, the tiny organelles within cells that produce ...
... It’s long been known that cells accumulate flotsam from the wear and tear of everyday living. Broken or misshapen proteins, shreds of cellular membranes, invasive viruses or bacteria, and worn-out, broken-down cellular components, like aged mitochondria, the tiny organelles within cells that produce ...
Cells need to produce new cells in order to
... 9. What gas is released during cellular respiration? a. Carbon dioxide b. Nitrogen c. Oxygen ...
... 9. What gas is released during cellular respiration? a. Carbon dioxide b. Nitrogen c. Oxygen ...
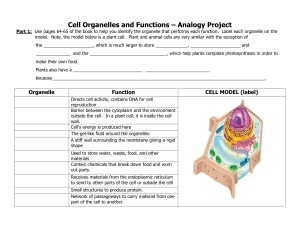
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store _____________, ____________________ and ______________ and the _______________________________, which help plants complete photosynthesi ...
... model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store _____________, ____________________ and ______________ and the _______________________________, which help plants complete photosynthesi ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.