The Cell and Its Environment POWER POINT
... What is the function of a cell? For an organism to live, grow and reproduce an organism must perform processes that allow them to do so. An organism must be able to use energy to live. All living things use energy and different types of organisms obtain energy different ways through the proce ...
... What is the function of a cell? For an organism to live, grow and reproduce an organism must perform processes that allow them to do so. An organism must be able to use energy to live. All living things use energy and different types of organisms obtain energy different ways through the proce ...
cells - TeacherWeb
... of microscopic structures called cells. There are many types of cells, including plant cells and animal cells. Cells consist of smaller pieces, called organelles. Organelles are like the "organs" of a cell; they are groups of complex molecules that help cells survive. Different cells can have ...
... of microscopic structures called cells. There are many types of cells, including plant cells and animal cells. Cells consist of smaller pieces, called organelles. Organelles are like the "organs" of a cell; they are groups of complex molecules that help cells survive. Different cells can have ...
Cell Structure
... A. Prokaryotes have little or no internal membrane structure. 1. They have a rigid cell wall surrounded by a slime capsule. 2. Cytoplasm is the location of most metabolic activity. 3. DNA makes RNA, which makes protein. B. Prokaryotes divide into Bacteria and Archaea. 1. Bacteria and Archaea share s ...
... A. Prokaryotes have little or no internal membrane structure. 1. They have a rigid cell wall surrounded by a slime capsule. 2. Cytoplasm is the location of most metabolic activity. 3. DNA makes RNA, which makes protein. B. Prokaryotes divide into Bacteria and Archaea. 1. Bacteria and Archaea share s ...
Classification Taxonomy Powerpoint
... An organism that automatically feeds itself. It makes its own food by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. ...
... An organism that automatically feeds itself. It makes its own food by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. ...
Cell-Pre-test
... atoms from a high concentration to a low. They are different because in osmosis there is a membrane and only water is moving. Diffusion can be the movement of any type of molecule and no membrane is present. 2. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts and animal cells don’t. Both plant and anima ...
... atoms from a high concentration to a low. They are different because in osmosis there is a membrane and only water is moving. Diffusion can be the movement of any type of molecule and no membrane is present. 2. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts and animal cells don’t. Both plant and anima ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for t ...
... Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for t ...
Cell Structure & Function
... Very small size Can only be observed under a microscope Have specific functions Found throughout cytoplasm ...
... Very small size Can only be observed under a microscope Have specific functions Found throughout cytoplasm ...
H 3 - Absorption of digested foods - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... pinocytotic vesicles – these are the site of pinocytosis by which fluid is taken up or released in tiny vesicles, across the plasma membrane of a cell tight junctions – these bind together the individual epithelial cells, so that the only way into the tissues of the body is through the epitheliu ...
... pinocytotic vesicles – these are the site of pinocytosis by which fluid is taken up or released in tiny vesicles, across the plasma membrane of a cell tight junctions – these bind together the individual epithelial cells, so that the only way into the tissues of the body is through the epitheliu ...
Flow of Matter Model Checklist
... In this model you will concentrate on telling a story of the flow of matter from our food cells to a typical human animal cell. A story flows from a beginning, a middle, and an end. This story will be mostly a picture book story supported by words when necessary to help explain your point. The objec ...
... In this model you will concentrate on telling a story of the flow of matter from our food cells to a typical human animal cell. A story flows from a beginning, a middle, and an end. This story will be mostly a picture book story supported by words when necessary to help explain your point. The objec ...
Name
... 2. __________________________ this holds the two parts of the chromosome together 3. __________________________ only animal cells have these to help with chromosome movement 4. __________________________ phase where chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends 5. __________________________ phase w ...
... 2. __________________________ this holds the two parts of the chromosome together 3. __________________________ only animal cells have these to help with chromosome movement 4. __________________________ phase where chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends 5. __________________________ phase w ...
1. The transport method of neurotransmitters between nerve cells is
... b. Occurs in protozoans and algae but not in more complex organisms c. Involves the specific binding of molecules to receptors on the cell surface d. Is the nonspecific uptake of fluids by pinching inward of the plasma membrane e. Is movement of molecules against the concentration gradient through a ...
... b. Occurs in protozoans and algae but not in more complex organisms c. Involves the specific binding of molecules to receptors on the cell surface d. Is the nonspecific uptake of fluids by pinching inward of the plasma membrane e. Is movement of molecules against the concentration gradient through a ...
Cell Membrane
... Living part of the cell-legitimate cell organelle Separates living from the nonliving world Semipermeable-regulates what enters and exits the cell Partitions the cell into different regions where different functions take place Participates in chemical reactions Transmits signals between outside of c ...
... Living part of the cell-legitimate cell organelle Separates living from the nonliving world Semipermeable-regulates what enters and exits the cell Partitions the cell into different regions where different functions take place Participates in chemical reactions Transmits signals between outside of c ...
If Conwell was a cell
... conwell would be the main office. It is our control center. Our Nucleolus is Mr. Hoffman’s office. He makes our ribosomes. ...
... conwell would be the main office. It is our control center. Our Nucleolus is Mr. Hoffman’s office. He makes our ribosomes. ...
Unit 2 Kind`a nice to know
... • Know hyper’, hypo’, isotonic with regard to cells • Know endocytosis and exocytosis • Know pinocytosis and phagocytosis ...
... • Know hyper’, hypo’, isotonic with regard to cells • Know endocytosis and exocytosis • Know pinocytosis and phagocytosis ...
PSI - Eukaryotes Multiple Choice Review
... a. They include stacks of membranes that absorb light. b. They include compartments where hydrogen ions are concentrated. c. They produce sugars using energy harvested in the cytoplasm. d. They break down sugar to produce ATP. 24. In cell membranes, the fatty acids of the phospholipids a. Face the o ...
... a. They include stacks of membranes that absorb light. b. They include compartments where hydrogen ions are concentrated. c. They produce sugars using energy harvested in the cytoplasm. d. They break down sugar to produce ATP. 24. In cell membranes, the fatty acids of the phospholipids a. Face the o ...
Cellular Transport Vocabulary
... 3. Fluid mosaic model—describes the cell membrane as being made of similar molecules (lipids) which freely move within the membrane 4. Selectively permeable (semi-permeable)—controls what enters and exits the cell 5. Protein markers—allow the cell to communicate with other cells 6. Transport protein ...
... 3. Fluid mosaic model—describes the cell membrane as being made of similar molecules (lipids) which freely move within the membrane 4. Selectively permeable (semi-permeable)—controls what enters and exits the cell 5. Protein markers—allow the cell to communicate with other cells 6. Transport protein ...
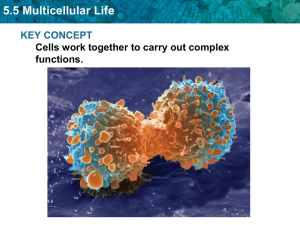
5:5
... 5.5 Multicellular Life Specialized cells perform specific functions. • Cells develop into their mature forms through the process of cell differentiation. • Cells differ because different combinations of genes are expressed. • A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. ...
... 5.5 Multicellular Life Specialized cells perform specific functions. • Cells develop into their mature forms through the process of cell differentiation. • Cells differ because different combinations of genes are expressed. • A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. ...
HONORS BIOLOGY PLASMOLYSIS LAB INTRODUCTION:
... Your favorite potted plant used to be the envy of the neighborhood. It was lush and green. Lately, however, it has begun to look pathetic (not lush and not green). You have been doing what you have always done. You watered it from the hose and added fertilizer according to the directions. Why is it, ...
... Your favorite potted plant used to be the envy of the neighborhood. It was lush and green. Lately, however, it has begun to look pathetic (not lush and not green). You have been doing what you have always done. You watered it from the hose and added fertilizer according to the directions. Why is it, ...
EXPLORE LEARNING: CELL STRUCTURE
... 2. Examine the remaining structures of the plant cell and compare the structure and function of each with their counterparts in the animal cell. 1. Compare the vacuoles in plant cells with those of animal cells. Does the large vacuole of the plant cell fulfill any additional roles beyond those it fu ...
... 2. Examine the remaining structures of the plant cell and compare the structure and function of each with their counterparts in the animal cell. 1. Compare the vacuoles in plant cells with those of animal cells. Does the large vacuole of the plant cell fulfill any additional roles beyond those it fu ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 09-07
... Weak hydrogen bonds holding the two chains together can be easily broke to ‘unzip’ the spiral and expose bases on each strand. The Cell Cycle For most of a cell’s life, when the cell is in G0 and G1 stages, the DNA is in chromatin form. These are times of protein synthesis, making different prot ...
... Weak hydrogen bonds holding the two chains together can be easily broke to ‘unzip’ the spiral and expose bases on each strand. The Cell Cycle For most of a cell’s life, when the cell is in G0 and G1 stages, the DNA is in chromatin form. These are times of protein synthesis, making different prot ...
Irish potato farmers did not allow their plants to undergo sexual
... “Bob” can roll his tongue (Rr), but his wife “Mary” cannot (rr). Predict the chances that any offspring could also roll their tongue. ...
... “Bob” can roll his tongue (Rr), but his wife “Mary” cannot (rr). Predict the chances that any offspring could also roll their tongue. ...
LAB: Observing Plant and Animal Cells
... scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny boxlike structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted th ...
... scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny boxlike structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted th ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.