File
... 1. Why must some multicellular organisms breathe and eat? 2. Why do cells interact with their environment? 3. What structure do molecules pass through when entering or leaving the cell? 4. What type of transport requires no energy and includes diffusion and osmosis? 5. What is a concentration gradie ...
... 1. Why must some multicellular organisms breathe and eat? 2. Why do cells interact with their environment? 3. What structure do molecules pass through when entering or leaving the cell? 4. What type of transport requires no energy and includes diffusion and osmosis? 5. What is a concentration gradie ...
Inflammatory changes in Pap smears
... •Their name means “big eating cells”, being their task to swallow up foreign bodies (i.e. bacteria) or cellular debris from erosive processes. •They are more or less large than a intermediate or superficial squamous cells, with central round or cleaved nucleus, with one or two nucleoli, and eosinoph ...
... •Their name means “big eating cells”, being their task to swallow up foreign bodies (i.e. bacteria) or cellular debris from erosive processes. •They are more or less large than a intermediate or superficial squamous cells, with central round or cleaved nucleus, with one or two nucleoli, and eosinoph ...
Cell Discovery and Cell Theory
... 1. What is the most important PRODUCT of cells and lies at the center of all cellular activity? 2. What is cytology? ...
... 1. What is the most important PRODUCT of cells and lies at the center of all cellular activity? 2. What is cytology? ...
Chapter 15 Regulation of Cell Number Normal and Cancer Cells
... The engines that drive progression from one step of the cell cycle to the next are a series of protein complexes composed of two subunits: a cyclin and a cyclin-dependent protein kinase (abbreviated CDK). In every eukaryote, there is a family of structurally and functionally related cyclin proteins. ...
... The engines that drive progression from one step of the cell cycle to the next are a series of protein complexes composed of two subunits: a cyclin and a cyclin-dependent protein kinase (abbreviated CDK). In every eukaryote, there is a family of structurally and functionally related cyclin proteins. ...
Plant Cell
... Where energy is released. Rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane Membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae) In Both Plant and Animal Cell ...
... Where energy is released. Rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane Membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae) In Both Plant and Animal Cell ...
bsaa processes in plant cells worksheet
... The nucleus is important because it stores the genetic information that directs cell function. It also expresses the heredity of the plant. Each cell contains a complete copy of that organism’s genetic code. The function of the nucleus is regulated by its simple structure. The nucleus is a porous me ...
... The nucleus is important because it stores the genetic information that directs cell function. It also expresses the heredity of the plant. Each cell contains a complete copy of that organism’s genetic code. The function of the nucleus is regulated by its simple structure. The nucleus is a porous me ...
10–2 Cell Division
... •Before cell division, each chromosomes replicates, creating 2 identical sister chromatids. •Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the centromere which is usually located in the center. •When a cell divides, the sister chromatids separate and each new cell receives one of the sister ...
... •Before cell division, each chromosomes replicates, creating 2 identical sister chromatids. •Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the centromere which is usually located in the center. •When a cell divides, the sister chromatids separate and each new cell receives one of the sister ...
news and views Cell cycle micromanagement in
... Embryonic stem (ES) cells are derived from the inner cell mass of an early-stage embryo known as a blastocyst. ES cells can differentiate into all cell types of the adult body and, in the absence of stimuli, can infinitely divide without losing the capacity of self-renewal. Because of these capaciti ...
... Embryonic stem (ES) cells are derived from the inner cell mass of an early-stage embryo known as a blastocyst. ES cells can differentiate into all cell types of the adult body and, in the absence of stimuli, can infinitely divide without losing the capacity of self-renewal. Because of these capaciti ...
PPT - Yavapai College
... • Eukaryotic cells evolved from fusion or integration of prokaryotic cells • Best evidence is in bacterial or prokaryotic appearance of mitochondria and chloroplasts • These organelles are like little bacterial cells within our cells, now fully functionally integrated • They perform fundamental cell ...
... • Eukaryotic cells evolved from fusion or integration of prokaryotic cells • Best evidence is in bacterial or prokaryotic appearance of mitochondria and chloroplasts • These organelles are like little bacterial cells within our cells, now fully functionally integrated • They perform fundamental cell ...
Phylum Apicomplexa
... • some ciliates possess an oral groove • cilia sweep food particles down this groove toward the cytopharynx where a food vacuole forms ...
... • some ciliates possess an oral groove • cilia sweep food particles down this groove toward the cytopharynx where a food vacuole forms ...
1 - What a Year!
... Dr. Perrin and Dr. Chuenkova compared cells that contained PDNF and the T. cruzi parasite to control cells when they were exposed to hydrogen peroxide, a toxin that would kill the cell under normal circumstances. They found that the control cells died from exposure to the toxin, but the cells with P ...
... Dr. Perrin and Dr. Chuenkova compared cells that contained PDNF and the T. cruzi parasite to control cells when they were exposed to hydrogen peroxide, a toxin that would kill the cell under normal circumstances. They found that the control cells died from exposure to the toxin, but the cells with P ...
8_SEMIPERMEABLEMemb
... concentration.The dashed line is intended to indicate a membrane that is permeable to the molecules or ions illustrated as red dots. Initially all of the red dots are within the membrane. As time passes, there is net diffusion of the red dots out of the membrane, following their concentration gradie ...
... concentration.The dashed line is intended to indicate a membrane that is permeable to the molecules or ions illustrated as red dots. Initially all of the red dots are within the membrane. As time passes, there is net diffusion of the red dots out of the membrane, following their concentration gradie ...
Student Learning Objectives
... A cell contains special structures called organelles which have specific functions for maintaining the health of the cell. These functions include taking in food and breaking it apart into simple molecules, releasing energy from food, building and repairing cell parts, getting rid of harmful wastes, ...
... A cell contains special structures called organelles which have specific functions for maintaining the health of the cell. These functions include taking in food and breaking it apart into simple molecules, releasing energy from food, building and repairing cell parts, getting rid of harmful wastes, ...
Lesson Plan - Colorado FFA
... A cell contains special structures called organelles which have specific functions for maintaining the health of the cell. These functions include taking in food and breaking it apart into simple molecules, releasing energy from food, building and repairing cell parts, getting rid of harmful wastes, ...
... A cell contains special structures called organelles which have specific functions for maintaining the health of the cell. These functions include taking in food and breaking it apart into simple molecules, releasing energy from food, building and repairing cell parts, getting rid of harmful wastes, ...
LECTURE 1 - Portal UniMAP
... obtain after one week, the formation of amino acids and small organic molecules The molecules that make up living organisms are referred ...
... obtain after one week, the formation of amino acids and small organic molecules The molecules that make up living organisms are referred ...
Outline - Science in the News
... The sperm and eggs are combined in a dish in a laboratory to ensure that the maximum number of eggs is fertilized. A few fertilized eggs (embryos) are implanted into the woman, and any remaining embryos are frozen, discarded, or donated; a decision made by the parent(s). Blastocyst: A very early sta ...
... The sperm and eggs are combined in a dish in a laboratory to ensure that the maximum number of eggs is fertilized. A few fertilized eggs (embryos) are implanted into the woman, and any remaining embryos are frozen, discarded, or donated; a decision made by the parent(s). Blastocyst: A very early sta ...
Lecture02_Su2010_A Tour of the Cell
... Function: Protein synthesis Ribosome parts are made in nucleus by nucleolus Parts travel out of nucleus, into cytoplasm Two types: Bound ribosome ...
... Function: Protein synthesis Ribosome parts are made in nucleus by nucleolus Parts travel out of nucleus, into cytoplasm Two types: Bound ribosome ...
D Chlamydomonas
... Among the following, which is not a correct step in handling a microscope? A Place the microscope on a level surface B Adjust the microscope so that sufficient light enters the microscope C Adjust the coarse focus knob first before the fine focus knob D Adjust the fine focus knob first before the co ...
... Among the following, which is not a correct step in handling a microscope? A Place the microscope on a level surface B Adjust the microscope so that sufficient light enters the microscope C Adjust the coarse focus knob first before the fine focus knob D Adjust the fine focus knob first before the co ...
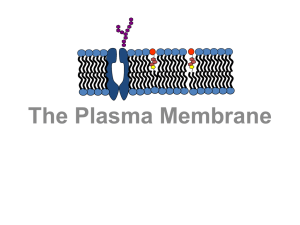
Notes Cell membrane and its Environment
... Active transport – is the movement of any substance across a cell membrane with the use of chemical energy. Materials will cross the cell membrane by either passive or active transport, depending on the size and chemical makeup of the material. The structure of the cell membrane also plays an import ...
... Active transport – is the movement of any substance across a cell membrane with the use of chemical energy. Materials will cross the cell membrane by either passive or active transport, depending on the size and chemical makeup of the material. The structure of the cell membrane also plays an import ...
16792_cell-structure-handout
... (Prokaryotes have no nucleus, having a nuclear body or a nucleoid instead). 2. The nucleus contains the cell’s chromosomes (human, 46, fruit fly 6, fern 1260) which are normally uncoiled to form a chromatin network, which contain both linear DNA and proteins, known as histones. These proteins coil u ...
... (Prokaryotes have no nucleus, having a nuclear body or a nucleoid instead). 2. The nucleus contains the cell’s chromosomes (human, 46, fruit fly 6, fern 1260) which are normally uncoiled to form a chromatin network, which contain both linear DNA and proteins, known as histones. These proteins coil u ...
File
... 3. FACILITATED TRANSPORT- requires transport proteins in the cell membrane to move materials into and out of the cell either because the molecules that are transported are too big or they are polar (act against the nonpolar fatty acid tail of the lipid bilayer) ...
... 3. FACILITATED TRANSPORT- requires transport proteins in the cell membrane to move materials into and out of the cell either because the molecules that are transported are too big or they are polar (act against the nonpolar fatty acid tail of the lipid bilayer) ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.