Energy in the Cell
... different forms) in living things all the time. – For example, the chemical energy in food is transformed into the movement of your muscles. – Plants take the radiant energy from the sun and turn it into chemical energy when they make food in photosynthesis. ...
... different forms) in living things all the time. – For example, the chemical energy in food is transformed into the movement of your muscles. – Plants take the radiant energy from the sun and turn it into chemical energy when they make food in photosynthesis. ...
CELL PARTS Chapter 4
... (… role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code define homeostasis; ...
... (… role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code define homeostasis; ...
lysosomes - cfonjungosite.com
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION lysosomes are cellular organelles. organelles are a cell that have a specific function. They are usually in a lipid bilayer and a lipid bilayer is fat that has two layers. ...
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION lysosomes are cellular organelles. organelles are a cell that have a specific function. They are usually in a lipid bilayer and a lipid bilayer is fat that has two layers. ...
Domains and Kingdoms
... All protists are eukaryotes. Some reproduce asexually by mitosis while others exchange genetic material during meiosis. ...
... All protists are eukaryotes. Some reproduce asexually by mitosis while others exchange genetic material during meiosis. ...
Unit title: Cells
... and differences between them, and giving at least one example of substance, used or produced by the cell that would be transported by that mechanism: 1. Simple diffusion 2. Facilitated diffusion 3. Active transport 4. Bulk transport 5. Osmosis ...
... and differences between them, and giving at least one example of substance, used or produced by the cell that would be transported by that mechanism: 1. Simple diffusion 2. Facilitated diffusion 3. Active transport 4. Bulk transport 5. Osmosis ...
North Carolina Essential Standards Assessment
... A student observes a typical onion root tip where many of the cells have just successfully completed mitosis. Which statement best explains what must have happened to result in cells that only have half as many chromosomes as all of the other cells in the same section of the tip? a. The parent cell ...
... A student observes a typical onion root tip where many of the cells have just successfully completed mitosis. Which statement best explains what must have happened to result in cells that only have half as many chromosomes as all of the other cells in the same section of the tip? a. The parent cell ...
Case Study 55
... he died. A post mortem examination of the brain revealed several findings. Describe them. ...
... he died. A post mortem examination of the brain revealed several findings. Describe them. ...
6 Kingdoms - Denton ISD
... Protists • Protists include many single celled organisms, like slime molds, protozoa and primitive ...
... Protists • Protists include many single celled organisms, like slime molds, protozoa and primitive ...
Sometimes a cell must force molecules in or out of the cell, and use
... True or False _____ 1. Passive transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move something across its membrane. _____ 2. Active transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move something across its membrane. _____ 3. Carrier proteins move molecules from an area of high concentration to an area conce ...
... True or False _____ 1. Passive transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move something across its membrane. _____ 2. Active transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move something across its membrane. _____ 3. Carrier proteins move molecules from an area of high concentration to an area conce ...
Protista
... A wide variety of protists are photosynthetic. The major photosynthetic groups of protists are distinguished by the pigments they contain and many live symbiotically with animals or other protists. ...
... A wide variety of protists are photosynthetic. The major photosynthetic groups of protists are distinguished by the pigments they contain and many live symbiotically with animals or other protists. ...
Parts of a cell
... -Lysosomes are created when the Endoplasmic Reticulum develops its enzyme proteins, then the Golgi Complex finishes creating its digestive enzymes. -Lysosomes floats in the cytoplasm until they are needed. ...
... -Lysosomes are created when the Endoplasmic Reticulum develops its enzyme proteins, then the Golgi Complex finishes creating its digestive enzymes. -Lysosomes floats in the cytoplasm until they are needed. ...
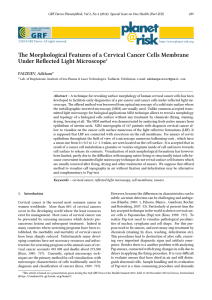
e Morphological Features of a Cervical Cancer Cells Membrane
... a sophisticated testing infrastructure and highly trained professionals to evaluate the cytological test as a result, the vast majority of women in the developing world do not have access to life-saving screening programs (Goldie, 2005: 2158). To reach the main goal of cervical cancer screening we n ...
... a sophisticated testing infrastructure and highly trained professionals to evaluate the cytological test as a result, the vast majority of women in the developing world do not have access to life-saving screening programs (Goldie, 2005: 2158). To reach the main goal of cervical cancer screening we n ...
A1984SS75600001
... tic pathological skin color changes. To delineate pathogenesis and cause of pigmentary disorders, basic knowledge of melanogenesis is essential. “Fortunately, around that time, melanogenesis at the macromolecular level became increasingly clarified. Before that time, melanin was considered to be syn ...
... tic pathological skin color changes. To delineate pathogenesis and cause of pigmentary disorders, basic knowledge of melanogenesis is essential. “Fortunately, around that time, melanogenesis at the macromolecular level became increasingly clarified. Before that time, melanin was considered to be syn ...
Dictyostelium discoideum, model organism, social amoeba: facts
... myxamoeba stage; free-living amoebae; unicellular form; vegetative growth by mitotic division ...
... myxamoeba stage; free-living amoebae; unicellular form; vegetative growth by mitotic division ...
Herpes Virus - mbbsclub.com
... Structure of Cell Wall • Some bacteria have surface features, external to cell wall like capsule, flagella and pili. • Cell wall is a multi-layered structure, located external to cell membrane. • It is composed of inner layer, peptidoglycan and outer layer which is of variable thickness. • Peptidog ...
... Structure of Cell Wall • Some bacteria have surface features, external to cell wall like capsule, flagella and pili. • Cell wall is a multi-layered structure, located external to cell membrane. • It is composed of inner layer, peptidoglycan and outer layer which is of variable thickness. • Peptidog ...
Chapter 3-Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis
... What is osmosis? How is osmosis different that diffusion? If a solution is hypotonic to a cell, in which direction will water move (in or out of the cell)? If a solution is isotonic to a cell, is there movement of water? What can happen to a cell if it is placed in a hypertonic solution? How does th ...
... What is osmosis? How is osmosis different that diffusion? If a solution is hypotonic to a cell, in which direction will water move (in or out of the cell)? If a solution is isotonic to a cell, is there movement of water? What can happen to a cell if it is placed in a hypertonic solution? How does th ...
Running List For Exam 1
... lateral inhibition] Mach bands and intensity step function and lateral inhibition simultaneous contrast in general explained by lateral inhibition two problems (or problem cases) for lateral inhibition as explanation Benary cross is one Craik-O’Brien-Cornsweet illusion, Corregated plaid, Koffka ring ...
... lateral inhibition] Mach bands and intensity step function and lateral inhibition simultaneous contrast in general explained by lateral inhibition two problems (or problem cases) for lateral inhibition as explanation Benary cross is one Craik-O’Brien-Cornsweet illusion, Corregated plaid, Koffka ring ...
cell growth and division
... • Chromatid – each strand of a duplicated chromosome • Centromere – the area where each pair of chromatids is joined • Centrioles – tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells that help organize the spindle • Spindle – a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromatids ...
... • Chromatid – each strand of a duplicated chromosome • Centromere – the area where each pair of chromatids is joined • Centrioles – tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells that help organize the spindle • Spindle – a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromatids ...
EMBO Workshop on Cell Size Regulation
... Ariel Amir – Simultaneous regulation of size and DNA replication in bacteria: is cell size driver or passenger? Short talk - Marco Cosentino – Stochasticity and key steps of cell cycle homeostasis Short talk – Carolina Gallo - Bacterial growth factors: Mycoplasma pneumoniae as a model organism ...
... Ariel Amir – Simultaneous regulation of size and DNA replication in bacteria: is cell size driver or passenger? Short talk - Marco Cosentino – Stochasticity and key steps of cell cycle homeostasis Short talk – Carolina Gallo - Bacterial growth factors: Mycoplasma pneumoniae as a model organism ...
Click here
... down a concentration gradient, active transport pumps molecules and ions against a concentration gradient. Sometimes an organism needs to transport something against a concentration gradient. The only way this can be done is through active transport, which uses energy that is produced by respiration ...
... down a concentration gradient, active transport pumps molecules and ions against a concentration gradient. Sometimes an organism needs to transport something against a concentration gradient. The only way this can be done is through active transport, which uses energy that is produced by respiration ...
Mechanical Properties of the Middle Lamella of an Epidermal Cell Wall
... Mechanical Properties of the Middle Lamella of an Epidermal Cell Wall Scientific Achievement The middle lamella (ML) is a pectin-rich adhesive layer between two adjacent cells. Despite the absence of cellulose, the ML is as strong as the cell wall proper. ...
... Mechanical Properties of the Middle Lamella of an Epidermal Cell Wall Scientific Achievement The middle lamella (ML) is a pectin-rich adhesive layer between two adjacent cells. Despite the absence of cellulose, the ML is as strong as the cell wall proper. ...
MMP - OpenWetWare
... • Intravital videomicroscopy shows TIMP1overexpressing cancer cells exiting vasculature at the same rate as their parental counterparts, but these cells yield fewer and smaller metastases ...
... • Intravital videomicroscopy shows TIMP1overexpressing cancer cells exiting vasculature at the same rate as their parental counterparts, but these cells yield fewer and smaller metastases ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.