Power Point Notes
... Mitosis - The process by which the cell’s nucleus divides into two nuclei. ...
... Mitosis - The process by which the cell’s nucleus divides into two nuclei. ...
Biology -Cellular Processes OEQs
... List and describe three processes used by cells to control the movement of substances across the cell membrane. What could/would happen to a cell if the cell membrane was damaged? Stem cell research is a current ethical issue in science. Describe how stem cells are being used today. Give speci ...
... List and describe three processes used by cells to control the movement of substances across the cell membrane. What could/would happen to a cell if the cell membrane was damaged? Stem cell research is a current ethical issue in science. Describe how stem cells are being used today. Give speci ...
Starter Activity
... 1. Shape (plant cells are rectangular and animal cells are generally round) 2. Plant cells have a large vacuole 3. Plant cells have a cell wall (to provide extra structure) 4. Plant cells have chroloplasts (where photosynthesis takes place) ...
... 1. Shape (plant cells are rectangular and animal cells are generally round) 2. Plant cells have a large vacuole 3. Plant cells have a cell wall (to provide extra structure) 4. Plant cells have chroloplasts (where photosynthesis takes place) ...
Onion Mitosis Worksheet
... For the following questions, you may look back through your notes, open power points we have used or use the digital lesson. You should be able to answer them based on what we have learned in class. ...
... For the following questions, you may look back through your notes, open power points we have used or use the digital lesson. You should be able to answer them based on what we have learned in class. ...
Intro (MITOSIS)(Asexual Reproduction).
... • MITOSIS: a process by which the nucleus of a cell divides while maintaining the chromosome number One cell two cells New cells have identical genetic material (DNA) of the parent cell • Four stages of division (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase - PMAT) plus a period of growth and m ...
... • MITOSIS: a process by which the nucleus of a cell divides while maintaining the chromosome number One cell two cells New cells have identical genetic material (DNA) of the parent cell • Four stages of division (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase - PMAT) plus a period of growth and m ...
II. Process of Meiosis (6.2) A. Cells go through in meiosis 1. Meiosis
... 1). _______________________ _______________________ 2). _______________________ _______________________ C. Meiosis I (first of two phases) 1. Occurs _____________________________________________ 2. Divides _______________________ in four phases D. Meiosis II (second of two phases) 1. Divides _______ ...
... 1). _______________________ _______________________ 2). _______________________ _______________________ C. Meiosis I (first of two phases) 1. Occurs _____________________________________________ 2. Divides _______________________ in four phases D. Meiosis II (second of two phases) 1. Divides _______ ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Introduction to Cells
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
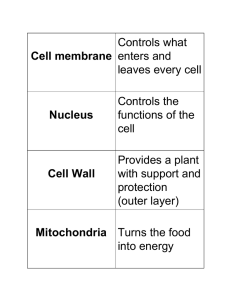
Cell membrane
... The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus ...
... The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus ...
Microbiology Slides - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
Cell Organelle Summarizer Match the organelles below to their
... Label the following organelles on the diagram below: Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Chromosomes, Chloroplast, Mitochondrion, Cytoplasm. ...
... Label the following organelles on the diagram below: Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Chromosomes, Chloroplast, Mitochondrion, Cytoplasm. ...
Chapter 6 1. ______ ______: all organisms are made up of cells. 2
... 11. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): __________________ and ________________ are the two regions of the ER. SER is in charge of _____________ production, metabolism of _______________, drug detoxification, and making sex hormones. RER synthesizes and packages _____________ in ___________ to move to the g ...
... 11. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): __________________ and ________________ are the two regions of the ER. SER is in charge of _____________ production, metabolism of _______________, drug detoxification, and making sex hormones. RER synthesizes and packages _____________ in ___________ to move to the g ...
cells
... Other Cell Structures • Microbodies – Peroxisomes: enzymes that help neutralize peroxide and other acids and bases (ex. Catalase) Found mostly in liver, spleen, and kidney – Glyoxysomes – help produce the seed coat ...
... Other Cell Structures • Microbodies – Peroxisomes: enzymes that help neutralize peroxide and other acids and bases (ex. Catalase) Found mostly in liver, spleen, and kidney – Glyoxysomes – help produce the seed coat ...
name date ______ period
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the correct answer for each question that follows. The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm B. nuclear envelope C. DNA D. nucleolus E. chromatin Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many ___________ ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the correct answer for each question that follows. The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm B. nuclear envelope C. DNA D. nucleolus E. chromatin Cells like muscle cells which require lots of energy would probably have many ___________ ...
View this PowerPoint here.
... • Describe the phases of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in plants and animals. • What is the importance of checkpoints in control of the cell cycle? • What is the relationship between cancer and cell ...
... • Describe the phases of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in plants and animals. • What is the importance of checkpoints in control of the cell cycle? • What is the relationship between cancer and cell ...
08.1 Cell Continuity
... If this continued to happen eventually the cell would be filled by a nucleus. To prevent this happening, special cells are produced which contain only half of the diploid number of chromosomes. These cells are called gametes and are haploid (n) i.e. they contain only one set of chromosomes. ...
... If this continued to happen eventually the cell would be filled by a nucleus. To prevent this happening, special cells are produced which contain only half of the diploid number of chromosomes. These cells are called gametes and are haploid (n) i.e. they contain only one set of chromosomes. ...
Organism of the Day: Cheetah
... and kept them as pets. Cheetahs can reach speeds of 70 to 75 mph, making it the fastest land animal. Cheetahs can accelerate from 0 to 63 mph in 3 ...
... and kept them as pets. Cheetahs can reach speeds of 70 to 75 mph, making it the fastest land animal. Cheetahs can accelerate from 0 to 63 mph in 3 ...
Plant and Animal Cells www
... diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
... diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
Cells Glossary
... Organelle - small structure inside a cell, performs specific function to meet cell’s basic needs (survive & reproduce) Osmosis - diffusion in which a fluid (usually H2O) moves through a selectively permeable membrane Permeable - that can be easily permeated or penetrated (by air of water, for examp ...
... Organelle - small structure inside a cell, performs specific function to meet cell’s basic needs (survive & reproduce) Osmosis - diffusion in which a fluid (usually H2O) moves through a selectively permeable membrane Permeable - that can be easily permeated or penetrated (by air of water, for examp ...
Plant and Animal Cells www
... diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
... diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
Cell Cycle
... Nuclear envelope and nucleus break up, disperse, and are no longer visible. Spindle shaped array of microtubules forms between the centrioles as they move apart. ...
... Nuclear envelope and nucleus break up, disperse, and are no longer visible. Spindle shaped array of microtubules forms between the centrioles as they move apart. ...
Chapter 8A
... – Mitosis: two genetically identical cells, with the same chromosome number as the original cell – Meiosis: four genetically different cells, with half the chromosome number of the original cell ...
... – Mitosis: two genetically identical cells, with the same chromosome number as the original cell – Meiosis: four genetically different cells, with half the chromosome number of the original cell ...
Science Benchmark # 1 STUDY GUIDE!!!!!!
... 3. Which type of cell does NOT have a nucleus? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic 4. A cell membrane is selectively _permeable_; it lets some things in or out but not others, it shows direction of flow, the final net movement, and the rate of movement of molecules. 5. The plant’s _leaves contain the most chl ...
... 3. Which type of cell does NOT have a nucleus? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic 4. A cell membrane is selectively _permeable_; it lets some things in or out but not others, it shows direction of flow, the final net movement, and the rate of movement of molecules. 5. The plant’s _leaves contain the most chl ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.