Theory of Evolution Notes
... Biochemistry: ____________ with more similar sequences suggest species are ________________ closely _________________________. o EX: ______________________ and _______________________________ share more than _______________ of ________________________ DNA sequences. ...
... Biochemistry: ____________ with more similar sequences suggest species are ________________ closely _________________________. o EX: ______________________ and _______________________________ share more than _______________ of ________________________ DNA sequences. ...
Bioassessment of Water Quality
... More than 400 of the over 1,300 species currently protected under the Endangered Species Act, and more than 180 candidate species for listing are considered to be at risk at least partly due to displacement by, competition with, and predation by invasive species USFWS ...
... More than 400 of the over 1,300 species currently protected under the Endangered Species Act, and more than 180 candidate species for listing are considered to be at risk at least partly due to displacement by, competition with, and predation by invasive species USFWS ...
and non-living things (abiotic factors)
... biotic factors, which include plants, fish, invertebrates, and single-celled organisms. • The non-living components, or abiotic factors, include the physical and chemical components in the environment—temperature, wind, water, sunlight, and oxygen. ...
... biotic factors, which include plants, fish, invertebrates, and single-celled organisms. • The non-living components, or abiotic factors, include the physical and chemical components in the environment—temperature, wind, water, sunlight, and oxygen. ...
6-1 A Changing Landscape
... A. Habitat Alteration Habitat Alteration splitting of ecosystems into small fragments ...
... A. Habitat Alteration Habitat Alteration splitting of ecosystems into small fragments ...
Ecology Goals
... 1. Define Ecology. Discuss the approaches taken by biologists who focus at each of these levels: organism, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere. 2. Identify the abiotic and biotic factors that control ecological relationships, stressing the role of natural selection in shaping the adaptat ...
... 1. Define Ecology. Discuss the approaches taken by biologists who focus at each of these levels: organism, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere. 2. Identify the abiotic and biotic factors that control ecological relationships, stressing the role of natural selection in shaping the adaptat ...
PhD position - timing in ecological interaction networks Department
... - Research experience on species interactions, insect biodiversity or (any kind of) networks, knowledge of entomology and/or botany (species identification, etc.) - Experience with publishing in scientific journals University of Freiburg is an equal opportunities employer and explicitly encourages w ...
... - Research experience on species interactions, insect biodiversity or (any kind of) networks, knowledge of entomology and/or botany (species identification, etc.) - Experience with publishing in scientific journals University of Freiburg is an equal opportunities employer and explicitly encourages w ...
Ecology terms
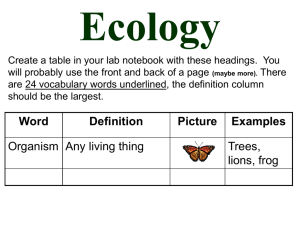
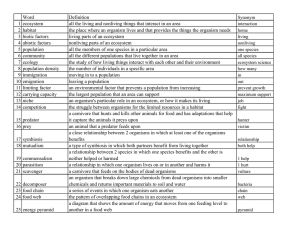
... will probably use the front and back of a page (maybe more). There are 24 vocabulary words underlined, the definition column should be the largest. ...
... will probably use the front and back of a page (maybe more). There are 24 vocabulary words underlined, the definition column should be the largest. ...
File
... Eventually the trees will dies, new species of plants and wildlife will arrive to take advantage of the new conditions. Eventually, this forest will become a meadow. The beaver’s NICHE is the role it plays in shaping the environment. But… it is also a main prey species for predators. ...
... Eventually the trees will dies, new species of plants and wildlife will arrive to take advantage of the new conditions. Eventually, this forest will become a meadow. The beaver’s NICHE is the role it plays in shaping the environment. But… it is also a main prey species for predators. ...
Ecology = scientific study of interactions among organisms and
... Roles and Relationships in an Ecosystem Ecological niche = role that each species plays in the ecosystem. Only one species at a time can occupy a particular niche. A niche includes the type of food the organism eats, how it obtains its food, and which other species use the organism for food. Co ...
... Roles and Relationships in an Ecosystem Ecological niche = role that each species plays in the ecosystem. Only one species at a time can occupy a particular niche. A niche includes the type of food the organism eats, how it obtains its food, and which other species use the organism for food. Co ...
Ecology Biomes - Peterson Science
... all the members of one species in a particular area all the different populations that live together in an area the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment the number of individuals in a specific area moving in to a population leaving a population an environmental f ...
... all the members of one species in a particular area all the different populations that live together in an area the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment the number of individuals in a specific area moving in to a population leaving a population an environmental f ...
Ecosystems
... Greek word oikos, for “house,” eco-is the combining form meaning “environment or habitat.” ...
... Greek word oikos, for “house,” eco-is the combining form meaning “environment or habitat.” ...
Chapter 3: Ecosystems - micsapes
... interacting with one another and with their nonliving environment (soil, water, other forms of matter, and energy) No clear boundaries Not isolated ...
... interacting with one another and with their nonliving environment (soil, water, other forms of matter, and energy) No clear boundaries Not isolated ...
Rocky_Mountain_Ecosystems_Course_Outline
... Unit 1: Intro to Ecology and Rocky Mountain Ecosystems a. What is ecology? b. Ecosystems i. Interactions, Habitat, Niche, Keystone species ii. Levels of organization iii. EcosystemCommunityPopulationSpeciesOrganism… c. Local ecosystems i. Characteristics of Local Ecosystems ii. MT Ecosystems Map ...
... Unit 1: Intro to Ecology and Rocky Mountain Ecosystems a. What is ecology? b. Ecosystems i. Interactions, Habitat, Niche, Keystone species ii. Levels of organization iii. EcosystemCommunityPopulationSpeciesOrganism… c. Local ecosystems i. Characteristics of Local Ecosystems ii. MT Ecosystems Map ...
Exam 6 Review - Iowa State University
... 1.) The amount of chemical energy that is produced/stored by autotrophs and is available for consumption is called A) Net Primary Production B) Cellular Respiration C) Gross Primary Production D) Photosynthesis Follow up? 2.) A secondary consumer (a fox) receives what percent of the energy fixed by ...
... 1.) The amount of chemical energy that is produced/stored by autotrophs and is available for consumption is called A) Net Primary Production B) Cellular Respiration C) Gross Primary Production D) Photosynthesis Follow up? 2.) A secondary consumer (a fox) receives what percent of the energy fixed by ...
Ecology Review Set
... 12. Sketch a picture of an energy pyramid with 5 trophic levels. a. What type of organism is found at the 1st trophic level? b. If the 1st trophic level contained 10,000 J of energy, how much energy would be passed to the 2nd trophic level? The 3rd trophic level? 13. What happens to the total amount ...
... 12. Sketch a picture of an energy pyramid with 5 trophic levels. a. What type of organism is found at the 1st trophic level? b. If the 1st trophic level contained 10,000 J of energy, how much energy would be passed to the 2nd trophic level? The 3rd trophic level? 13. What happens to the total amount ...
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY
... describe, explain and discuss aspects of ecology in novel and applied situations or examples. ...
... describe, explain and discuss aspects of ecology in novel and applied situations or examples. ...
Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... niche, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere 2. Be able to relate the ecological concept of niche to what you learned in evolution. (i.e., what happens when an organism tries to move into a niche that is already occupied by another organism?) 3. Be able to discuss and define differe ...
... niche, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere 2. Be able to relate the ecological concept of niche to what you learned in evolution. (i.e., what happens when an organism tries to move into a niche that is already occupied by another organism?) 3. Be able to discuss and define differe ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.