Ecology
... From sun to the producers to the consumers •Producers (plants)= organisms that make their own food to obtain energy •Consumers( animals)= organisms that consume other organism for energy •Heat Energy (sun) is converted to Chemical Energy (food) through energy flow. •Some energy is lost to heat at ea ...
... From sun to the producers to the consumers •Producers (plants)= organisms that make their own food to obtain energy •Consumers( animals)= organisms that consume other organism for energy •Heat Energy (sun) is converted to Chemical Energy (food) through energy flow. •Some energy is lost to heat at ea ...
Evolution Guided Notes
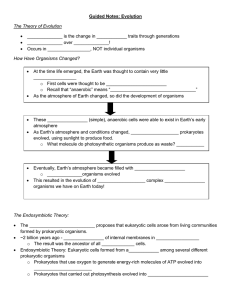
... Genetic Recombination: Dominant and Recessive alleles in genes, along with polygenetic traits and complex genetics, lead to individual organisms with different ________________ (and thus, adaptations) ...
... Genetic Recombination: Dominant and Recessive alleles in genes, along with polygenetic traits and complex genetics, lead to individual organisms with different ________________ (and thus, adaptations) ...
James A. Estes , 301 (2011); DOI: 10.1126/science.1205106
... emphasize the urgent need for interdisciplinary research to forecast the effects of trophic downgrading on process, function, and resilience in global ecosystems. he history of life on Earth is punctuated by several mass extinction events (2), during which global biological diversity was sharply red ...
... emphasize the urgent need for interdisciplinary research to forecast the effects of trophic downgrading on process, function, and resilience in global ecosystems. he history of life on Earth is punctuated by several mass extinction events (2), during which global biological diversity was sharply red ...
Population Ecology
... Environmental Resistance: • Factors that Decrease the birth rate, or increase death rate, related to environmental conditions, such as food & space. • Density Independent Factors: weather and other natural disasters • Density Dependent Factors: food, space, ...
... Environmental Resistance: • Factors that Decrease the birth rate, or increase death rate, related to environmental conditions, such as food & space. • Density Independent Factors: weather and other natural disasters • Density Dependent Factors: food, space, ...
MC Review Answers
... 17. A crab lives on a beach, which is where the crab finds food, shelter and a space to live. For the crab, the beach is an example of what division of the biosphere? A. niche B. habitat C. ecosystem D. community 18. Which of the following statements about water is not true? A. Water anchors plants ...
... 17. A crab lives on a beach, which is where the crab finds food, shelter and a space to live. For the crab, the beach is an example of what division of the biosphere? A. niche B. habitat C. ecosystem D. community 18. Which of the following statements about water is not true? A. Water anchors plants ...
CURRENT ZOOLOGY Vol. 60 (2014) Index
... Special Column The Role of Behavior in Conservation Editor: Ximena J. NELSON, University of Canterbury, Christchurch 8001, New Zealand Editorial Animal Behavior can inform conservation policy, we just need to get on with the job – or can it? ... ...................................................... ...
... Special Column The Role of Behavior in Conservation Editor: Ximena J. NELSON, University of Canterbury, Christchurch 8001, New Zealand Editorial Animal Behavior can inform conservation policy, we just need to get on with the job – or can it? ... ...................................................... ...
UNIT 1: Biology Review
... 19. A biologist wants to introduce a new species (species A) into an ecosystem. Species B already lives in the ecosystem and occupies the same niche as species A. What will be the likely outcome if species A is introduced into the ecosystem? A. mutualism between the two species B. parasitism of spec ...
... 19. A biologist wants to introduce a new species (species A) into an ecosystem. Species B already lives in the ecosystem and occupies the same niche as species A. What will be the likely outcome if species A is introduced into the ecosystem? A. mutualism between the two species B. parasitism of spec ...
File
... and is expected to continue to do so. • Population growth will naturally slow down as it nears its carrying capacity due to an increase in the death rate and a decrease in the birth rate as a result of: – Food and water shortages – Pollution of the environment – Spread of diseases • An increasing po ...
... and is expected to continue to do so. • Population growth will naturally slow down as it nears its carrying capacity due to an increase in the death rate and a decrease in the birth rate as a result of: – Food and water shortages – Pollution of the environment – Spread of diseases • An increasing po ...
Evolution Practice Questions
... beginning of life in the ocean change in organisms over a period of time migration of organisms similarity of organism ...
... beginning of life in the ocean change in organisms over a period of time migration of organisms similarity of organism ...
Sandy, Standard Assessment-Ecosystems and
... A. are free-floating organisms B. are unicellular C. live only in saltwater environments D. are fed on by zooplankton 6. Ecologists group Earth’s diverse environments into: A. Niches B. Biomes C. Classes D. Lands 7. An organism’s _________________ is described as the ability to survive and reproduce ...
... A. are free-floating organisms B. are unicellular C. live only in saltwater environments D. are fed on by zooplankton 6. Ecologists group Earth’s diverse environments into: A. Niches B. Biomes C. Classes D. Lands 7. An organism’s _________________ is described as the ability to survive and reproduce ...
biodiversity in lake macquarie
... different plants, animals and microorganisms, the genes they contain, and the ecosystems they form. It is usually considered at three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. ...
... different plants, animals and microorganisms, the genes they contain, and the ecosystems they form. It is usually considered at three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. ...
Ecosystems Unit Review
... (h) False. The input energy required from the Sun for photosynthesis is not given off as light energy in respiration. Light energy is required for photosynthesis. (i) False. Phosphorus cycles only between the land and the biotic components. (j) False. Decomposers do not release energy that is cycled ...
... (h) False. The input energy required from the Sun for photosynthesis is not given off as light energy in respiration. Light energy is required for photosynthesis. (i) False. Phosphorus cycles only between the land and the biotic components. (j) False. Decomposers do not release energy that is cycled ...
es_123_exam_notes
... Extinction means that the last individual member of a species has died and the species is gone forever. The extinction rate has increase due to habitat destruction and pollution. Why does this matter to us? All livings things exist in an area surrounding the Earth called the biosphere. The biosphere ...
... Extinction means that the last individual member of a species has died and the species is gone forever. The extinction rate has increase due to habitat destruction and pollution. Why does this matter to us? All livings things exist in an area surrounding the Earth called the biosphere. The biosphere ...
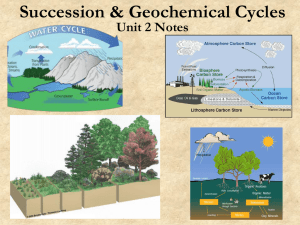
Ecological Succession College Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... • Ecosystems are constantly changing in response to natural and human disturbances • As older inhabitants die out new organism move in, changing the community • Ecological succession is a series predictable change that happens in a community over a period of time ...
... • Ecosystems are constantly changing in response to natural and human disturbances • As older inhabitants die out new organism move in, changing the community • Ecological succession is a series predictable change that happens in a community over a period of time ...
THE DELICATE BALANCE OF ECOSYSTEMS
... General rules for this simulation: I.- Every generation, the number of producer doubles. Assume that the plant population has enough sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce new organisms. II.- Every generation, each native herbivore eats one plant to survive. Two native herbivores produce on ...
... General rules for this simulation: I.- Every generation, the number of producer doubles. Assume that the plant population has enough sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce new organisms. II.- Every generation, each native herbivore eats one plant to survive. Two native herbivores produce on ...
Evolution PPT Notes
... that lived in the distant past. This process, by which diverse species evolved from common ancestors, unites all organisms on Earth into a single ____________________________. ...
... that lived in the distant past. This process, by which diverse species evolved from common ancestors, unites all organisms on Earth into a single ____________________________. ...
Energy Flow Notes
... - “Rule of 10”: only 10% of energy is passed on to each trophic level - # of organisms go ___ as you go up the pyramid ...
... - “Rule of 10”: only 10% of energy is passed on to each trophic level - # of organisms go ___ as you go up the pyramid ...
Main page ==> oil-refining http://www.ycysoft.com Copyright ycysoft
... other small organisms) • Every interaction it has with other species (It disperses nuts, limits other populations, its waste fertilizes the soil, & it is food for many predators) ...
... other small organisms) • Every interaction it has with other species (It disperses nuts, limits other populations, its waste fertilizes the soil, & it is food for many predators) ...
class fill in notes - Social Circle City Schools
... chromosomes move ____________________ (crossing over) producing ______________________ of combinations of genes Genetic drift - ________ in alleles due to __________________ Example: ...
... chromosomes move ____________________ (crossing over) producing ______________________ of combinations of genes Genetic drift - ________ in alleles due to __________________ Example: ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.