Chp 4 Questions
... Explain why microbes (microorganisms) are so important. Distinguish among a species, population, genetic diversity, habitat, community, ecosystem, and biosphere. Distinguish among the atmosphere, troposphere, stratosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. How does the sun help sustain life o ...
... Explain why microbes (microorganisms) are so important. Distinguish among a species, population, genetic diversity, habitat, community, ecosystem, and biosphere. Distinguish among the atmosphere, troposphere, stratosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. How does the sun help sustain life o ...
Community interactions
... Think about all of the relationships you have. Some might be helpful to you, some might not affect you, and others might be hard for you to maintain. Take 4 minutes to name 3 different ...
... Think about all of the relationships you have. Some might be helpful to you, some might not affect you, and others might be hard for you to maintain. Take 4 minutes to name 3 different ...
Niche
... ecosystem. – Niche is “what the organism does” – Niche includes “where an organism lives” ...
... ecosystem. – Niche is “what the organism does” – Niche includes “where an organism lives” ...
Niche - BellevilleBiology.com
... ecosystem. – Niche is “what the organism does” – Niche includes “where an organism lives” ...
... ecosystem. – Niche is “what the organism does” – Niche includes “where an organism lives” ...
Chapter 4
... that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. Every population is part of a community. The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what other organisms ca ...
... that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. Every population is part of a community. The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what other organisms ca ...
S R : COASTAL
... can be recolonised within 10 to 15 years. • Inorganic nutrients and organic matter (derived from agricultural and industrial discharges, sewage and aquaculture) lead to eutrophication and deoxygenation, and cause changes to many habitats, particularly muddy sands, seagrass and sheltered rocky reefs. ...
... can be recolonised within 10 to 15 years. • Inorganic nutrients and organic matter (derived from agricultural and industrial discharges, sewage and aquaculture) lead to eutrophication and deoxygenation, and cause changes to many habitats, particularly muddy sands, seagrass and sheltered rocky reefs. ...
Evolution
... • Jean-Baptiste Lamarck - French naturalist – Published hypothesis of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics same year Darwin was born – Proposed that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits during their lifetime. • Traits could then be passed on to offsprin ...
... • Jean-Baptiste Lamarck - French naturalist – Published hypothesis of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics same year Darwin was born – Proposed that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits during their lifetime. • Traits could then be passed on to offsprin ...
Intro to Ecology
... • Different species living in the same environment, or habitat, may require the same resources. When the resources are limited, competition occurs among the species. • Competition- is the struggle between different species for the same limited resources. The more similar the needs of the species, th ...
... • Different species living in the same environment, or habitat, may require the same resources. When the resources are limited, competition occurs among the species. • Competition- is the struggle between different species for the same limited resources. The more similar the needs of the species, th ...
Conservation in the Anthropocene
... and species (Table 1), and it is vital to identify and protect them now. We define intact ecosystems as those in which the majority of native species are still present in abundances at which they play the same functional roles as they did before extensive human settlement or use, where pollution has ...
... and species (Table 1), and it is vital to identify and protect them now. We define intact ecosystems as those in which the majority of native species are still present in abundances at which they play the same functional roles as they did before extensive human settlement or use, where pollution has ...
NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY Life on Earth
... This type of competition takes place between plants or animals that belong to the same species. An example of this is the competition that exists between two or more robins. Since members of the same species will compete for exactly the same resources in an ecosystem, intraspecific competition is mu ...
... This type of competition takes place between plants or animals that belong to the same species. An example of this is the competition that exists between two or more robins. Since members of the same species will compete for exactly the same resources in an ecosystem, intraspecific competition is mu ...
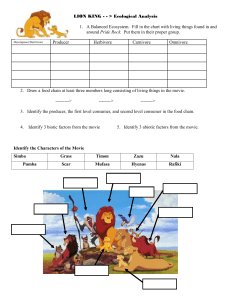
Name
... 16. When Simba falls from exhaustion what animals begin to encircle him? _________ 17. What is the ecological role of the animal in #16. _________________________ 19. When Scar replaces Mufasa the pride's stable ecosystem is replaced by an unstable ecosystem. Describe three ways the movie indicates ...
... 16. When Simba falls from exhaustion what animals begin to encircle him? _________ 17. What is the ecological role of the animal in #16. _________________________ 19. When Scar replaces Mufasa the pride's stable ecosystem is replaced by an unstable ecosystem. Describe three ways the movie indicates ...
Natural Selection
... This theory states that the following conditions must exist for evolution to occur... 1. There must be VARIATION in a population. 2. There is a change in the environment. (The video calls this… Struggle for existence) ...
... This theory states that the following conditions must exist for evolution to occur... 1. There must be VARIATION in a population. 2. There is a change in the environment. (The video calls this… Struggle for existence) ...
Ecology `16 Notes
... When producers convert the sun’s energy into food energy, they use some of it for daily functions, store some, and use some to build new plant tissue. When a herbivore, such as a cow, eats the plant, does the cow get 100% of the plant’s energy? Will one plant, such as alfalfa, support one cow? Of co ...
... When producers convert the sun’s energy into food energy, they use some of it for daily functions, store some, and use some to build new plant tissue. When a herbivore, such as a cow, eats the plant, does the cow get 100% of the plant’s energy? Will one plant, such as alfalfa, support one cow? Of co ...
Introduction - Coastal Climate Wiki
... Ecological buffers are land use practices that can lessen the impact of development on natural areas. In coastal settings they can be used to create a transition zone between a coastal ecosystem and human activity in which no disturbance is allowed. They promote good habitat and connectivity, ...
... Ecological buffers are land use practices that can lessen the impact of development on natural areas. In coastal settings they can be used to create a transition zone between a coastal ecosystem and human activity in which no disturbance is allowed. They promote good habitat and connectivity, ...
(1) natural selection
... (2) Two organisms on the same branch of an evolutionary pathway are more closely related to each other than to those on distant branches. (3) All the organisms shown at the ends of evolutionary pathway branch tips are alive today. (4) Evolutionary pathways show that evolution is a short-term process ...
... (2) Two organisms on the same branch of an evolutionary pathway are more closely related to each other than to those on distant branches. (3) All the organisms shown at the ends of evolutionary pathway branch tips are alive today. (4) Evolutionary pathways show that evolution is a short-term process ...
Unit 4: Landscape and Ecosystem Ecology Unit 4
... Food Webs more complex than linear chains: -complexity increases with increase community diversity ...
... Food Webs more complex than linear chains: -complexity increases with increase community diversity ...
Document
... 7. Draw an exponential growth curve with a sudden crash, and list factors that might cause the crash. Distinguish between those that are density-dependent, and those that are density-independent. 8. Distinguish between an r-selected species and a K-selected species with respect to body size, lifespa ...
... 7. Draw an exponential growth curve with a sudden crash, and list factors that might cause the crash. Distinguish between those that are density-dependent, and those that are density-independent. 8. Distinguish between an r-selected species and a K-selected species with respect to body size, lifespa ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... of a nest • Camo coloration • Less vocal, short calls • Stay secluded • From an evolutionary standpoint, the males have developed traits that make them an easier target for predators but they result in better reproductive success. ...
... of a nest • Camo coloration • Less vocal, short calls • Stay secluded • From an evolutionary standpoint, the males have developed traits that make them an easier target for predators but they result in better reproductive success. ...
Choose the correct answer:
... Darwin's opinion about evolution depends on the following: 1-Great productivity: (struggle for survival) *Most of live in organisms produce great numbers of offspring. * the number of individuals of any species remains constant for long periods due to the competition between them for food and shelte ...
... Darwin's opinion about evolution depends on the following: 1-Great productivity: (struggle for survival) *Most of live in organisms produce great numbers of offspring. * the number of individuals of any species remains constant for long periods due to the competition between them for food and shelte ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.