Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is
... 3) Long whip-like structure found attached to cell membrane of motile (able to move) cells (like sperm cells or some protists) 4) Organelle that controls and manages cell functions in eukaryotic cells 5) Fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are found 6) Produces a usable form of energy (ATP ...
... 3) Long whip-like structure found attached to cell membrane of motile (able to move) cells (like sperm cells or some protists) 4) Organelle that controls and manages cell functions in eukaryotic cells 5) Fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are found 6) Produces a usable form of energy (ATP ...
Cell Motility - Cochran`s Half Acre
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
Chapter Outline
... F. Mitochondria: Energy Generators of the Cell 1. Structure- outer membrane, inner membrane (cristae) and matrix 2. DNA, ribosomes 3. Aerobic respiration G. Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis 1. Structure- triple membrane, thylakoid membrane, stacks of grana 2. Photosynthesis-light and carbon dioxide to f ...
... F. Mitochondria: Energy Generators of the Cell 1. Structure- outer membrane, inner membrane (cristae) and matrix 2. DNA, ribosomes 3. Aerobic respiration G. Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis 1. Structure- triple membrane, thylakoid membrane, stacks of grana 2. Photosynthesis-light and carbon dioxide to f ...
A Tour of the Cell - Ludlow Independent Schools
... gentlemen can see, but microscopes are prudent in an emergency.” Emily Dickinson ...
... gentlemen can see, but microscopes are prudent in an emergency.” Emily Dickinson ...
File
... Cell Structure and Functions UNDERSTANDING CELLS: What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? List them in to order from least to most complex. What is cell specialization (differentiation)? How is ...
... Cell Structure and Functions UNDERSTANDING CELLS: What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? List them in to order from least to most complex. What is cell specialization (differentiation)? How is ...
MICROTUBULES Tracks guide motor proteins to destination
... Cilia and Flagella – Are locomotor appendages – Extensions of cytoskeleton Examples: Many unicellular protists move with flagella Some plant reproductive cells have flagella Cilia in oviducts move egg toward uterus Cilia lining windpipe sweep mucous out of lungs Flagellum in sperm cells (Prokaryoti ...
... Cilia and Flagella – Are locomotor appendages – Extensions of cytoskeleton Examples: Many unicellular protists move with flagella Some plant reproductive cells have flagella Cilia in oviducts move egg toward uterus Cilia lining windpipe sweep mucous out of lungs Flagellum in sperm cells (Prokaryoti ...
5 kingdoms
... * some make their own food (autotrophic); others can't make their own food (heterotrophic) ...
... * some make their own food (autotrophic); others can't make their own food (heterotrophic) ...
Bacterial Morphology
... • Flagella: Helical filaments, which produce motility by rotation. – Monotrichous is a single polar flagellum; lophotrichous has two or more polar flagella at one end of the cell; amphitrichous has a single flagellum at each end of the cell; and peritrichous with flagella distributed over the cell. ...
... • Flagella: Helical filaments, which produce motility by rotation. – Monotrichous is a single polar flagellum; lophotrichous has two or more polar flagella at one end of the cell; amphitrichous has a single flagellum at each end of the cell; and peritrichous with flagella distributed over the cell. ...
Prokaryotic Cells
... Very early, prokaryotes split into two lines – Archaea and bacteria are as different in structure and metabolism from each other as either is from eukarya. Comparing archaebacteria and bacteria – plasma membranes composed of different lipids ...
... Very early, prokaryotes split into two lines – Archaea and bacteria are as different in structure and metabolism from each other as either is from eukarya. Comparing archaebacteria and bacteria – plasma membranes composed of different lipids ...
General Biology lab
... • Some bacteria cause disease, but most are actually helpful. • Because of their small size, it is impossible to see details inside bacterial cell with the light microscope. ...
... • Some bacteria cause disease, but most are actually helpful. • Because of their small size, it is impossible to see details inside bacterial cell with the light microscope. ...
Deflagellation and Flagellar Regeneration in Chlamydomonas
... The microtubules are always observed in a characteristic array of 9 outer doublet microtubules surrounding a central pair of two single microtubules. This 9+2 arrangement is highly conserved. You will be able to identify the axonemal microtubules as well as their associated accessory structures, suc ...
... The microtubules are always observed in a characteristic array of 9 outer doublet microtubules surrounding a central pair of two single microtubules. This 9+2 arrangement is highly conserved. You will be able to identify the axonemal microtubules as well as their associated accessory structures, suc ...
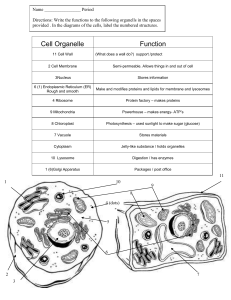
Cell Organelle
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Cell Membrane Animal Cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell
... Cell Membrane Animal Cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
... Cell Membrane Animal Cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
form follows function in organelles
... cilia & flagella on outside can move cell cytoplasm Thick fluid, fills cell, chemical reactions take place here, organelles “float” in it Cell wall Provides rigid structure to cell and plant, m ...
... cilia & flagella on outside can move cell cytoplasm Thick fluid, fills cell, chemical reactions take place here, organelles “float” in it Cell wall Provides rigid structure to cell and plant, m ...
IGCSE Biology Chapter 2 ANSWERS 1. a) i Fungi, ii Protoctists, iii
... b) Euglena is difficult to classify as a plant or animal because it has features of both types of organism. It has a cell wall and chloroplasts and is therefore photosynthetic like a plant, but it is motile like an animal because of its flagellum. It is included in the Protoctists because this group ...
... b) Euglena is difficult to classify as a plant or animal because it has features of both types of organism. It has a cell wall and chloroplasts and is therefore photosynthetic like a plant, but it is motile like an animal because of its flagellum. It is included in the Protoctists because this group ...
Golgi apparatus
... Ribosomes attached to rough ER synthesize proteins that leave cells via the Golgi complex; smooth ER synthesizes lipids incorporated in cell membranes, steroid hormones, and certain carbohydrates used to form glycoproteins. ...
... Ribosomes attached to rough ER synthesize proteins that leave cells via the Golgi complex; smooth ER synthesizes lipids incorporated in cell membranes, steroid hormones, and certain carbohydrates used to form glycoproteins. ...
Chapter 4 Eukaryotic Cell
... ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
... ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
Homeostasis Nucleus Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic
... Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic Biotic Asexual Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Chloroplasts Vacuole Echinoderm Bivalve Protozoa Flagella Pseudopod Mycelium Arthropod Turn over for more → ...
... Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic Biotic Asexual Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Chloroplasts Vacuole Echinoderm Bivalve Protozoa Flagella Pseudopod Mycelium Arthropod Turn over for more → ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Breaks down high-energy organic molecules (cellular respiration) to store in chemical bonds as chemical potential energy. • In addition to glucose, it can also use lipids and proteins • The released energy is stored in the form of ATP ...
... • Breaks down high-energy organic molecules (cellular respiration) to store in chemical bonds as chemical potential energy. • In addition to glucose, it can also use lipids and proteins • The released energy is stored in the form of ATP ...
Review Sheet: A Tour of the Cell
... Explain why there are upper and lower limits to cell size Distinguish between the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain why compartmentalization is important in eukaryotic cells. Compare the structures of plant and animal cells. Note the function of each cell organelle. ...
... Explain why there are upper and lower limits to cell size Distinguish between the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain why compartmentalization is important in eukaryotic cells. Compare the structures of plant and animal cells. Note the function of each cell organelle. ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.