Chapter 4 Cell Structure
... • Animal cells secrete glycoproteins, elastins, and collagen to form an extracellular matrix (ECM) around the cell. • This ECM is bound to integrins which help hold the cytoskeleton in place. • The ECM provides support and strength. ...
... • Animal cells secrete glycoproteins, elastins, and collagen to form an extracellular matrix (ECM) around the cell. • This ECM is bound to integrins which help hold the cytoskeleton in place. • The ECM provides support and strength. ...
Cells and Tissues
... As blood flows through the capillary, smaller molecules are filtered out through tiny openings and larger molecules stay inside ...
... As blood flows through the capillary, smaller molecules are filtered out through tiny openings and larger molecules stay inside ...
ON-Line Assignment - Biology
... News and updates subscription Our team constantly updates the portal with various new services Keep up with our news! ...
... News and updates subscription Our team constantly updates the portal with various new services Keep up with our news! ...
Cells and Tissues - Lone Star College
... As blood flows through the capillary, smaller molecules are filtered out through tiny openings and larger molecules stay inside ...
... As blood flows through the capillary, smaller molecules are filtered out through tiny openings and larger molecules stay inside ...
Different Types of Cells
... agents of fermentation play important roles in digestive systems involved in many nutrient cycles – ex: the nitrogen cycle, which restores nitrate into the soil for plants. ...
... agents of fermentation play important roles in digestive systems involved in many nutrient cycles – ex: the nitrogen cycle, which restores nitrate into the soil for plants. ...
Cell Structure and Function Matching KEY
... vesicles pinch off these structures; proteins modified and packaged here cellular "stomach" selectively permeable "doorman" the most important plastid, turns CO2, H2O, sunlight into glucose membrane-bound spheres that store water & dissolved materials. Membrane surrounding it is called a tonoplast. ...
... vesicles pinch off these structures; proteins modified and packaged here cellular "stomach" selectively permeable "doorman" the most important plastid, turns CO2, H2O, sunlight into glucose membrane-bound spheres that store water & dissolved materials. Membrane surrounding it is called a tonoplast. ...
1 Chapter 3-b2 Cell Structure and Function Applying the concepts
... b.Intermediate filaments -gives support to cell (varies with type of tissue) -eg. -eg. Support plasma membrane (skin/human hair) c. Microtubules -centrosome in animal cells controls microtubules -spindle apparatus during mitosis/meiosis. -eg. Increase in chameleon for movement of pigments quickly d. ...
... b.Intermediate filaments -gives support to cell (varies with type of tissue) -eg. -eg. Support plasma membrane (skin/human hair) c. Microtubules -centrosome in animal cells controls microtubules -spindle apparatus during mitosis/meiosis. -eg. Increase in chameleon for movement of pigments quickly d. ...
Chapter 3: Concepts and Tools for Studying Microorganisms
... • All organisms have similar genetic organization whereby heredity material is expressed • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have internal compartments • Metabolism occurs in the cytoplasm • Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: The Structural Distinctions • E ...
... • All organisms have similar genetic organization whereby heredity material is expressed • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have internal compartments • Metabolism occurs in the cytoplasm • Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: The Structural Distinctions • E ...
Cytoskeleton Handout
... repeats. Heptad repeats promote the association of parallel α-helices into a structure known as a coiled-coil. Intermediate filament proteins assemble into dimers via coiled-coil interactions. The basic unit of intermediate filaments are possibly tetramers formed from dimers in a head-to-tail orient ...
... repeats. Heptad repeats promote the association of parallel α-helices into a structure known as a coiled-coil. Intermediate filament proteins assemble into dimers via coiled-coil interactions. The basic unit of intermediate filaments are possibly tetramers formed from dimers in a head-to-tail orient ...
OLD BIO Cell ?`s
... Which of the following is TRUE of cell (plasma) membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membra ...
... Which of the following is TRUE of cell (plasma) membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membra ...
Skills Worksheet
... An analogy is a relationship between two pairs of terms or phrases written as a : b :: c : d. The symbol : is read as “is to,” and the symbol :: is read as “as.” In the space provided, write the letter of the pair of terms that best completes the analogy shown. ...
... An analogy is a relationship between two pairs of terms or phrases written as a : b :: c : d. The symbol : is read as “is to,” and the symbol :: is read as “as.” In the space provided, write the letter of the pair of terms that best completes the analogy shown. ...
Plasma Membrane and Cell Wall
... 1. How can you tell the difference between an onion cell and a Elodea cell? 1. Why was the Human cheek cell round and not square? -Turn in Wake-up and Animal/Plant Cell Lab ...
... 1. How can you tell the difference between an onion cell and a Elodea cell? 1. Why was the Human cheek cell round and not square? -Turn in Wake-up and Animal/Plant Cell Lab ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site Chapter 28 Figure 28.3 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: How could a microbiologist determine whether unknown filaments growing in diseased plant leaves were fungus-like protists or true fungi? ANSWER: In order to determine whether an unkn ...
... Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site Chapter 28 Figure 28.3 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: How could a microbiologist determine whether unknown filaments growing in diseased plant leaves were fungus-like protists or true fungi? ANSWER: In order to determine whether an unkn ...
Unit2 classification microorganismsnotes
... Taxis: movement toward or away from a certain stimulus. • Chemotaxis refers to movement ...
... Taxis: movement toward or away from a certain stimulus. • Chemotaxis refers to movement ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... YOGURT 100x Use no water, but use a coverslip. Focus with very low light Label where the cell is. ...
... YOGURT 100x Use no water, but use a coverslip. Focus with very low light Label where the cell is. ...
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
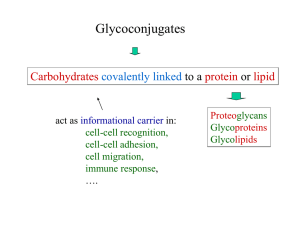
... • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination labels (secreted, membrane proteins, ly ...
... • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination labels (secreted, membrane proteins, ly ...
Document
... • Cilia- short hair-like projection of plasma membrane that have beating motion (found in lining of wind pipe) • Flagella- long, whip-like projections that lash back and forth ( found in sperm cells ) ...
... • Cilia- short hair-like projection of plasma membrane that have beating motion (found in lining of wind pipe) • Flagella- long, whip-like projections that lash back and forth ( found in sperm cells ) ...
Cell City Analogy
... Organelle – is the small specialized structures found inside a cell that perform a specific function. The cell is a fabulous piece of machinery. All tiny intricate parts or organelles work together to make the cell function properly. We can compare cells to real-life structures that enable us to bet ...
... Organelle – is the small specialized structures found inside a cell that perform a specific function. The cell is a fabulous piece of machinery. All tiny intricate parts or organelles work together to make the cell function properly. We can compare cells to real-life structures that enable us to bet ...
Nucleus - JeongAPbiology
... - no membrane-bound organelles (ribosomes are present, but are not membrane bound) - much smaller than Eukaryotes • 3 things about Eukaryotes - has membrane bound nucleus - many membrane-bound organelles in cytoplasm - average larger than Prokaryotes ...
... - no membrane-bound organelles (ribosomes are present, but are not membrane bound) - much smaller than Eukaryotes • 3 things about Eukaryotes - has membrane bound nucleus - many membrane-bound organelles in cytoplasm - average larger than Prokaryotes ...
Semester Study Guide
... What is an energy pyramid and what is each level of an energy pyramid called? ...
... What is an energy pyramid and what is each level of an energy pyramid called? ...
Matching Cell Parts Name: FI Bio Date: 2013
... continuation of the outer nuclear membrane (you will use this number twice) 4. Membrane bound sac with digestive enzymes 5. Membrane bound stacked structure that small vesicles pinch off from, these vesicles contain macromolecules 6. Phospholipid bilayer that creates a hydrophobic region on the insi ...
... continuation of the outer nuclear membrane (you will use this number twice) 4. Membrane bound sac with digestive enzymes 5. Membrane bound stacked structure that small vesicles pinch off from, these vesicles contain macromolecules 6. Phospholipid bilayer that creates a hydrophobic region on the insi ...
The Eukaryotic Cell (plant and animal cells) Eukaryotes: Organisms
... Function: assists with cell _________________ -‐ Cilia = __________ hair-‐like structures (usually more numerous) -‐ Flagella = ___________ hair-‐like structure (usually fewer) Function: used for _____________ (swim ...
... Function: assists with cell _________________ -‐ Cilia = __________ hair-‐like structures (usually more numerous) -‐ Flagella = ___________ hair-‐like structure (usually fewer) Function: used for _____________ (swim ...
CHAPTER 7 THE CELL
... 9. structures for movement flagella - long thin structure that uses a “whipping motion” to move the cell cilia – many short hair-like structures that use a “rowing motion” to move the cell ...
... 9. structures for movement flagella - long thin structure that uses a “whipping motion” to move the cell cilia – many short hair-like structures that use a “rowing motion” to move the cell ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.