Biology
... 9) Define each of the properties of life and give an example. Property of Life Definition Example Cellular Organization All living things are made Cells are compartmentalized. They make up tissues, up of one or more cells & which make up organs, which make up organ are organized in such a systems, w ...
... 9) Define each of the properties of life and give an example. Property of Life Definition Example Cellular Organization All living things are made Cells are compartmentalized. They make up tissues, up of one or more cells & which make up organs, which make up organ are organized in such a systems, w ...
Cell Organelle Notes - Hamilton Local Schools
... It also keeps turgor ____________________ for the plant. o Turgor pressure is the force exerted ________________ by water on the cell _________ that helps a plant _________________ up. ...
... It also keeps turgor ____________________ for the plant. o Turgor pressure is the force exerted ________________ by water on the cell _________ that helps a plant _________________ up. ...
Cell Organelles
... forward by snakelike wriggling, or stick out in front and draw it along. Each sperm cell is propelled by a trailing flagellum that accelerates the little torpedo forward in its quest to ...
... forward by snakelike wriggling, or stick out in front and draw it along. Each sperm cell is propelled by a trailing flagellum that accelerates the little torpedo forward in its quest to ...
PROKARYOTE VS EUKARYOTE
... • Now that you identified structures in a prokaryotic cell, what are their functions. • Go to internet and search prokaryotic cell to describe the following structures: flagella cell wall pili plasma membrane nucleoid ribosomes capsule DNA ...
... • Now that you identified structures in a prokaryotic cell, what are their functions. • Go to internet and search prokaryotic cell to describe the following structures: flagella cell wall pili plasma membrane nucleoid ribosomes capsule DNA ...
Mader/Biology, 10/e – Chapter Outline
... 1. Centrioles are short cylinders with a ring pattern (9 + 0) of microtubule triplets. 2. In animal cells and most protists, centrosome contains two centrioles lying at right angles to each other. 3. Plant and fungal cells have the equivalent of a centrosome, but they do not contain centrioles. 4. C ...
... 1. Centrioles are short cylinders with a ring pattern (9 + 0) of microtubule triplets. 2. In animal cells and most protists, centrosome contains two centrioles lying at right angles to each other. 3. Plant and fungal cells have the equivalent of a centrosome, but they do not contain centrioles. 4. C ...
Microbe Vocabulary
... Bacteria: unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures; a common term used to describe prokaryotes. Capsid: the protein shell that surrounds a virus. Capsule: a surface layer on some bacteria that helps them stick to each other and surfaces. Cilia: a short hair-like appendage used by mi ...
... Bacteria: unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures; a common term used to describe prokaryotes. Capsid: the protein shell that surrounds a virus. Capsule: a surface layer on some bacteria that helps them stick to each other and surfaces. Cilia: a short hair-like appendage used by mi ...
Structure and Function of the Cell
... Structure and Function of the Cell Study Guide 1. Explain prokaryotic v. eukaryotic. Prokaryotic – single cell organism with no nucleus or membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic – multi cell organism where cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles 2. Describe the cell membrane. A phospholipid ...
... Structure and Function of the Cell Study Guide 1. Explain prokaryotic v. eukaryotic. Prokaryotic – single cell organism with no nucleus or membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic – multi cell organism where cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles 2. Describe the cell membrane. A phospholipid ...
Cellular Structure
... animal or protist (unicellular organisms –fungi) cells Centriole: Found in animal cells and some protists. Protein fibers that aid in cell ...
... animal or protist (unicellular organisms –fungi) cells Centriole: Found in animal cells and some protists. Protein fibers that aid in cell ...
Microbe Vocbaulary
... Bacteria: unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures; a common term used to describe prokaryotes. Capsid: the protein shell that surrounds a virus. Capsule: a surface layer on some bacteria that helps them stick to each other and surfaces. Cilia: a short hair-like appendage used by mi ...
... Bacteria: unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures; a common term used to describe prokaryotes. Capsid: the protein shell that surrounds a virus. Capsule: a surface layer on some bacteria that helps them stick to each other and surfaces. Cilia: a short hair-like appendage used by mi ...
Cell surface dynamics, and the role of endocytic machineries All
... of GPI-linked receptors, galectins, membranes, fluid, virus and bacterial toxins. This novel pathway is very dynamic and accounts for a major part of the endocytosed material in fibroblasts. Uptake is orchestrated by the small G-protein cdc42, which cooperates with GRAF1, Arf1 and ARHGAP10 to contro ...
... of GPI-linked receptors, galectins, membranes, fluid, virus and bacterial toxins. This novel pathway is very dynamic and accounts for a major part of the endocytosed material in fibroblasts. Uptake is orchestrated by the small G-protein cdc42, which cooperates with GRAF1, Arf1 and ARHGAP10 to contro ...
Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
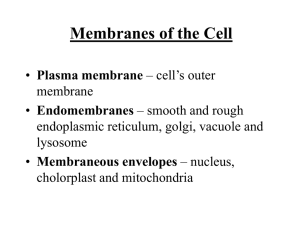
... • Plasma membrane – cell’s outer membrane • Endomembranes – smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria ...
... • Plasma membrane – cell’s outer membrane • Endomembranes – smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, vacuole and lysosome • Membraneous envelopes – nucleus, cholorplast and mitochondria ...
Study Guide for the LS
... Bacteria- includes most types of bacteria (except those that live in extreme conditions) Archaea- bacteria that live in extreme conditions Eukarya- eukaryotic organisms ● Know the six kingdoms: Eubacteria- includes most types of bacteria (except those that live in extreme conditions) Archaebacteria- ...
... Bacteria- includes most types of bacteria (except those that live in extreme conditions) Archaea- bacteria that live in extreme conditions Eukarya- eukaryotic organisms ● Know the six kingdoms: Eubacteria- includes most types of bacteria (except those that live in extreme conditions) Archaebacteria- ...
Venn Diagram Organelles sgi_cell_ss_4
... On the second screen of the simulation you will see a column with 12 cell organelles and structures. Roll your mouse over each cell organelle or structure to read some information about it. Your task is to build a typical animal cell and a typical plant cell. To build each type of cell, drag the app ...
... On the second screen of the simulation you will see a column with 12 cell organelles and structures. Roll your mouse over each cell organelle or structure to read some information about it. Your task is to build a typical animal cell and a typical plant cell. To build each type of cell, drag the app ...
7 3-2DR - Groupfusion.net
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
Directed Reading A
... ___19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___21.Chloroplasts ar ...
... ___19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___21.Chloroplasts ar ...
Prokaryotic cell
... – Small nonpolar molecules such as – Other larger or polar molecules do not easily diffuse across the bilayer and transport proteins provide passage across membranes through a process called facilitated diffusion Solute molecule Figure 5.15 ...
... – Small nonpolar molecules such as – Other larger or polar molecules do not easily diffuse across the bilayer and transport proteins provide passage across membranes through a process called facilitated diffusion Solute molecule Figure 5.15 ...
Concept Covered: Cell Internal Organiza8on
... 1. Basic eukaryotic cell structure consists of an outer membrane, cytoplasm filled with organelles and a nucleus. Describe and give the function of each of the following: ...
... 1. Basic eukaryotic cell structure consists of an outer membrane, cytoplasm filled with organelles and a nucleus. Describe and give the function of each of the following: ...
Organelles 2010_1
... which allows for chemical reactions to be separated and for specific reactions to be isolated which increases efficiency in a cell • Different types of cells have different organelles • Definitions found on IB External exam questions for the term “organelle”: ...
... which allows for chemical reactions to be separated and for specific reactions to be isolated which increases efficiency in a cell • Different types of cells have different organelles • Definitions found on IB External exam questions for the term “organelle”: ...
Name:
... 20. What is the composition of a phospholipid? a. Which part is polar and which part is non-polar? 21. What are the functions of proteins in the cell membrane? 22. What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane? 23. Why is the plasma membrane referred to as the “fluid mosaic model?” 24. W ...
... 20. What is the composition of a phospholipid? a. Which part is polar and which part is non-polar? 21. What are the functions of proteins in the cell membrane? 22. What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane? 23. Why is the plasma membrane referred to as the “fluid mosaic model?” 24. W ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... 1. Cilia are short, usually numerous hairlike projections that can move in an undulating fashion (e.g., Paramecium). 2. Flagella are longer, usually fewer, projections that move in whip-like fashion (e.g., sperm cells). 3. Both have similar construction, but differ from prokaryotic flagella. a. Memb ...
... 1. Cilia are short, usually numerous hairlike projections that can move in an undulating fashion (e.g., Paramecium). 2. Flagella are longer, usually fewer, projections that move in whip-like fashion (e.g., sperm cells). 3. Both have similar construction, but differ from prokaryotic flagella. a. Memb ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.