STAAR Biology EOC Practice Test #1
... 6 Cells often need to take in materials from their environment, many of which are found in lower concentrations outside the cell compared to inside the cell. In order to do this, cells must use the energy from ATP to move these materials A against the concentration gradient through active transport ...
... 6 Cells often need to take in materials from their environment, many of which are found in lower concentrations outside the cell compared to inside the cell. In order to do this, cells must use the energy from ATP to move these materials A against the concentration gradient through active transport ...
B.4.A compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
... B.7.F analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Genetic drift – random changes in allele frequencies Gene flow – individuals can migrate into new populations and interbreed, which incorporates their genes into ...
... B.7.F analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Genetic drift – random changes in allele frequencies Gene flow – individuals can migrate into new populations and interbreed, which incorporates their genes into ...
HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM Cells
... Digestive- converts food into simple sugars. mechanical and chemical. Excretory- removes wastes through kidneys, skin, lungs. 2 wastes- urea and excess h2o. Reproductive- sperm and eggs. produces a zygote--->fetus (this ...
... Digestive- converts food into simple sugars. mechanical and chemical. Excretory- removes wastes through kidneys, skin, lungs. 2 wastes- urea and excess h2o. Reproductive- sperm and eggs. produces a zygote--->fetus (this ...
Jeoparday_Final
... For evolution to happen there MUST be change in specific genes of all member of the population. Change in genes is called mutation. Mutations are usually harmful but in RARE cases they can be helpful. If this happens, and the mutation eventually affects the entire species, the species has evolved. E ...
... For evolution to happen there MUST be change in specific genes of all member of the population. Change in genes is called mutation. Mutations are usually harmful but in RARE cases they can be helpful. If this happens, and the mutation eventually affects the entire species, the species has evolved. E ...
EOCT REVIEW
... New cells are genetically varied from parent cell (due to crossing over) This is why two offspring don’t look exactly alike (unless identical twins) Gametes are made by meiosis Types: • Conjugation – Exchange DNA (not sperm/egg) – Bacteria & protists • Sexual – Separate male and females of species – ...
... New cells are genetically varied from parent cell (due to crossing over) This is why two offspring don’t look exactly alike (unless identical twins) Gametes are made by meiosis Types: • Conjugation – Exchange DNA (not sperm/egg) – Bacteria & protists • Sexual – Separate male and females of species – ...
12C Analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels
... Mendelian Genetics Definitions Gene – section of DNA that codes for proteins Alleles - different forms of a gene; either dominant or recessive Chromosome - structure made up of DNA and proteins Genotype - genetic makeup of an organism (ex. AA, Aa, aa) Phenotype - visible expression of genetic makeup ...
... Mendelian Genetics Definitions Gene – section of DNA that codes for proteins Alleles - different forms of a gene; either dominant or recessive Chromosome - structure made up of DNA and proteins Genotype - genetic makeup of an organism (ex. AA, Aa, aa) Phenotype - visible expression of genetic makeup ...
Release Test items 11th Grade Obj 2
... Why are photosynthesis and cellular ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells respiration often considered opposites and bursts. Which of these causes water to F Photosynthesis produces twice as enter the egg? many ATP molecules as cellular F Coagulation ...
... Why are photosynthesis and cellular ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells respiration often considered opposites and bursts. Which of these causes water to F Photosynthesis produces twice as enter the egg? many ATP molecules as cellular F Coagulation ...
EOCT REVIEW
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
eoct review
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
BIOLOGY EOCT REVIEW
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
CRCT Review PPT
... back through the body. Before it can be reused, which organ must the blood pass through before it is returned to the rest of the body? A. the stomach, because it must receive nutrients B. the lungs, because it must be re-oxygenated ...
... back through the body. Before it can be reused, which organ must the blood pass through before it is returned to the rest of the body? A. the stomach, because it must receive nutrients B. the lungs, because it must be re-oxygenated ...
File - Hawk Nation Biology
... What process creates molecule 2? __Transcription______ Describe what is happening at molecule 5. (Use the names of all numbered molecules involved) ______Ribosomes are the site of translation where tRNA brings the amino acids and amino acids are assembled building polypeptide (protein) chains. _____ ...
... What process creates molecule 2? __Transcription______ Describe what is happening at molecule 5. (Use the names of all numbered molecules involved) ______Ribosomes are the site of translation where tRNA brings the amino acids and amino acids are assembled building polypeptide (protein) chains. _____ ...
Biology EOC Voc Review
... Method of cutting DNA from one organism and inserting the DNA fragment into a host Genetic engineering organism of the same or different species Genetics Branch of biology that studies heredity Mitochondria ...
... Method of cutting DNA from one organism and inserting the DNA fragment into a host Genetic engineering organism of the same or different species Genetics Branch of biology that studies heredity Mitochondria ...
HERE
... We can make any type of cell, therefore we can repair cells, organs, and repairing limbs. Discuss the steps in Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection: 1) Beneficial traits help organisms survive are passes from parents to offspring. 2) Resources limit carrying capacity with limits the num ...
... We can make any type of cell, therefore we can repair cells, organs, and repairing limbs. Discuss the steps in Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection: 1) Beneficial traits help organisms survive are passes from parents to offspring. 2) Resources limit carrying capacity with limits the num ...
1.8_Evolution
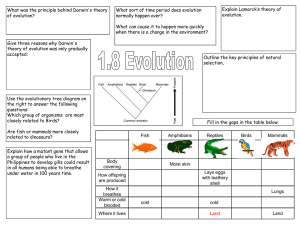
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
EOC Review power point (1)
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
... you don’t use a part you will lose it. – Inheritance of Acquired Traits- an organism obtains a trait during life (large muscles) so offspring are born with that trait – No longer accepted theory ...
File
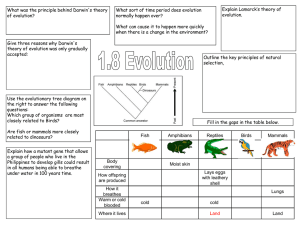
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
Biological Context
... Note qualifiers: likely, on average, possibly, decreased odds ... Outcomes may not be black-andwhite since one trait can be affected by many genes or variants (polygenic or quantitative trait) ...
... Note qualifiers: likely, on average, possibly, decreased odds ... Outcomes may not be black-andwhite since one trait can be affected by many genes or variants (polygenic or quantitative trait) ...
File
... Proteins are crucial to life. They carry out the functions of our genes. Proteins are synthesized during G1 phase of interphase. They are synthesized in two steps: transcription and translation. Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis. This step occurs in nucleus of the cell. A specific ...
... Proteins are crucial to life. They carry out the functions of our genes. Proteins are synthesized during G1 phase of interphase. They are synthesized in two steps: transcription and translation. Transcription is the first step in protein synthesis. This step occurs in nucleus of the cell. A specific ...
biocomp-exam-2009 - National Biology Competition
... c. The cell’s ability to repair mistakes made during DNA replication decreases, allowing the number of base substitutions in the genome to increase. d. DNA replication in the 3' to 5' direction is unaffected, but replication in the 5' to 3' direction slows down, decreasing the rate at which dying ce ...
... c. The cell’s ability to repair mistakes made during DNA replication decreases, allowing the number of base substitutions in the genome to increase. d. DNA replication in the 3' to 5' direction is unaffected, but replication in the 5' to 3' direction slows down, decreasing the rate at which dying ce ...
Life Science Final Key Terms
... o ex: T means Tall and t means short o a Capital letter represents a Dominant allele and the offspring only needs 1 allele for that trait to show o a lower case letter represents a recessive allele and the offspring needs 2 alleles for that trait to show heterozygous – means 2 different alleles ex ...
... o ex: T means Tall and t means short o a Capital letter represents a Dominant allele and the offspring only needs 1 allele for that trait to show o a lower case letter represents a recessive allele and the offspring needs 2 alleles for that trait to show heterozygous – means 2 different alleles ex ...
Sickle Cell Anemia - Woodcliff Lake School
... consequences. In this mutation, one base that is part of a gene on chromosomes 11 is changed. People with 2 copies of this mutation (ss) have a disease called sickle cell anemia. Their bodies, because of the wrong DNA sequence make an abnormal protein, causing there red blood cells to become sickle ...
... consequences. In this mutation, one base that is part of a gene on chromosomes 11 is changed. People with 2 copies of this mutation (ss) have a disease called sickle cell anemia. Their bodies, because of the wrong DNA sequence make an abnormal protein, causing there red blood cells to become sickle ...
Introduction to genetics

Genetics is the study of genes — what they are, what they do, and how they work. Genes are made up of molecules inside the nucleus of a cell that are strung together in such a way that the sequence carries information: that information determines how living organisms inherit phenotypic traits, (features) determined by the genes they received from their parents and thereby going back through the generations. For example, offspring produced by sexual reproduction usually look similar to each of their parents because they have inherited some of each of their parents' genes. Genetics identifies which features are inherited, and explains how these features pass from generation to generation. In addition to inheritance, genetics studies how genes are turned on and off to control what substances are made in a cell - gene expression; and how a cell divides - mitosis or meiosis.Some phenotypic traits can be seen, such as eye color while others can only be detected, such as blood type or intelligence. Traits determined by genes can be modified by the animal's surroundings (environment): for example, the general design of a tiger's stripes is inherited, but the specific stripe pattern is determined by the tiger's surroundings. Another example is a person's height: it is determined by both genetics and nutrition.Genes are made of DNA, which is divided into separate pieces called chromosomes. Humans have 46: 23 pairs, though this number varies between species, for example many primates have 24 pairs. Meiosis creates special cells, sperm in males and eggs in females, which only have 23 chromosomes. These two cells merge into one during the fertilization stage of sexual reproduction, creating a zygote in which a nucleic acid double helix divides, with each single helix occupying one of the daughter cells, resulting in half the normal number of genes. The zygote then divides into four daughter cells by which time genetic recombination has created a new embryo with 23 pairs of chromosomes, half from each parent. Mating and resultant mate choice result in sexual selection. In normal cell division (mitosis) is possible when the double helix separates, and a complement of each separated half is made, resulting in two identical double helices in one cell, with each occupying one of the two new daughter cells created when the cell divides.Chromosomes all contain four nucleotides, abbreviated C (cytosine), G (guanine), A (adenine), or T (thymine), which line up in a particular sequence and make a long string. There are two strings of nucleotides coiled around one another in each chromosome: a double helix. C on one string is always opposite from G on the other string; A is always opposite T. There are about 3.2 billion nucleotide pairs on all the human chromosomes: this is the human genome. The order of the nucleotides carries genetic information, whose rules are defined by the genetic code, similar to how the order of letters on a page of text carries information. Three nucleotides in a row - a triplet - carry one unit of information: a codon. The genetic code not only controls inheritance: it also controls gene expression, which occurs when a portion of the double helix is uncoiled, exposing a series of the nucleotides, which are within the interior of the DNA. This series of exposed triplets (codons) carries the information to allow machinery in the cell to ""read"" the codons on the exposed DNA, which results in the making of RNA molecules. RNA in turn makes either amino acids or microRNA, which are responsible for all of the structure and function of a living organism; i.e. they determine all the features of the cell and thus the entire individual. Closing the uncoiled segment turns off the gene. Heritability means the information in a given gene is not always exactly the same in every individual in that species, so the same gene in different individuals does not give exactly the same instructions. Each unique form of a single gene is called an allele; different forms are collectively called polymorphisms. As an example, one allele for the gene for hair color and skin cell pigmentation could instruct the body to produce black pigment, producing black hair and pigmented skin; while a different allele of the same gene in a different individual could give garbled instructions that would result in a failure to produce any pigment, giving white hair and no pigmented skin: albinism. Mutations are random changes in genes creating new alleles, which in turn produce new traits, which could help, harm, or have no new effect on the individual's likelihood of survival; thus, mutations are the basis for evolution.