Nitrogen cycle
... Humans affect the carbon cycle • Burning fossil fuels moves carbon from the ground to the air • Cutting forests and burning fields moves carbon from organisms to the air • Today’s atmospheric carbon dioxide reservoir is the largest in the past 650,000 years - The driving force behind climate change ...
... Humans affect the carbon cycle • Burning fossil fuels moves carbon from the ground to the air • Cutting forests and burning fields moves carbon from organisms to the air • Today’s atmospheric carbon dioxide reservoir is the largest in the past 650,000 years - The driving force behind climate change ...
Introduction to toxicology
... Main types of combined effects Synergistic effects Combined effect is greater than the sum of the individual effects if each substance encountered alone e.g. (2 + 2 = 20): • Carbon tetrachloride and ethanol – both are hepatoxic – but total liver damage by combined exposure is much greater than expe ...
... Main types of combined effects Synergistic effects Combined effect is greater than the sum of the individual effects if each substance encountered alone e.g. (2 + 2 = 20): • Carbon tetrachloride and ethanol – both are hepatoxic – but total liver damage by combined exposure is much greater than expe ...
3 H 2 - KMIT
... soil. Rhizobia are bacteria which are single cells about one thousandth of a millimetre long. Rhizobia belong to a specific group of bacteria that form a close association with legume plants. This association is called a SYMBIOSIS. The symbiosis results in visible, balllike structures being formed o ...
... soil. Rhizobia are bacteria which are single cells about one thousandth of a millimetre long. Rhizobia belong to a specific group of bacteria that form a close association with legume plants. This association is called a SYMBIOSIS. The symbiosis results in visible, balllike structures being formed o ...
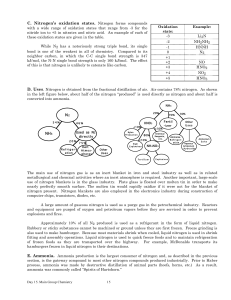
Nitrogen`s oxidation states
... Ammonia is a colorless gas with sharp irritating odor. Its density is about half that of air’s, thus it tends to rise in a still room. The odor is detectable to the human nose at 20 - 50 ppm and becomes irritating to the eyes at 100 -200 ppm. Ammonia is extremely soluble in water. Household ammonia ...
... Ammonia is a colorless gas with sharp irritating odor. Its density is about half that of air’s, thus it tends to rise in a still room. The odor is detectable to the human nose at 20 - 50 ppm and becomes irritating to the eyes at 100 -200 ppm. Ammonia is extremely soluble in water. Household ammonia ...
Diapositive 1
... • Overaddition of N could be detrimental in terms of N uptake, fermentation progress and flavors • N extra addition function of potential EtOH yield increase More functional proteins and more resistant cell wall necessary ...
... • Overaddition of N could be detrimental in terms of N uptake, fermentation progress and flavors • N extra addition function of potential EtOH yield increase More functional proteins and more resistant cell wall necessary ...
Formulae/ Equations homework - St Peter the Apostle High School
... solution of sodium hydroxide. (c) When iron is produced in the blast furnace from iron ore, the iron (III) oxide in the ore reacts with carbon monoxide gas. Carbon dioxide is also formed in the reaction. (d) Carbon dioxide gas and black copper oxide powder are formed when green copper carbonate powd ...
... solution of sodium hydroxide. (c) When iron is produced in the blast furnace from iron ore, the iron (III) oxide in the ore reacts with carbon monoxide gas. Carbon dioxide is also formed in the reaction. (d) Carbon dioxide gas and black copper oxide powder are formed when green copper carbonate powd ...
Cyanide Destruction with Chlorine Dioxide
... treatment of cyanides in wastewater. Oxidation should be considered when levels of oxidizable cyanide are too high to be processed by a biological treatment system. Chlorine dioxide Chlorine dioxide is unique in its ability to be used at moderately basic pH's. All other oxidants require pH's greater ...
... treatment of cyanides in wastewater. Oxidation should be considered when levels of oxidizable cyanide are too high to be processed by a biological treatment system. Chlorine dioxide Chlorine dioxide is unique in its ability to be used at moderately basic pH's. All other oxidants require pH's greater ...
Topic 16 Some non-metals and their compounds notes
... digestion of plant matter (cows and sheep) due to the presence of certain bacteria in their gut. Methane is also a greenhouse gas which contributes to global warming. There are millions of organic compounds such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, pharmaceutical drugs, fuels and plastics which are all ...
... digestion of plant matter (cows and sheep) due to the presence of certain bacteria in their gut. Methane is also a greenhouse gas which contributes to global warming. There are millions of organic compounds such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, pharmaceutical drugs, fuels and plastics which are all ...
NitrogenCycle
... to less harmful nitrate. Nitrification aids in the decomposition of nitrogenous material and thus in the recycling of nitrogen atoms since the decontamination of organic nitrogen produces ammonia that is subsequently oxidized to nitrate by nitrification. There two bacterial species involved. Nitroso ...
... to less harmful nitrate. Nitrification aids in the decomposition of nitrogenous material and thus in the recycling of nitrogen atoms since the decontamination of organic nitrogen produces ammonia that is subsequently oxidized to nitrate by nitrification. There two bacterial species involved. Nitroso ...
biochem 38 [4-20
... i. Arginine levels will be elevated when protein has been consumed for example Since arginine is an intermediary in the urea cycle, it also increases urea production by itself 14. What is the most common defect in the urea cycle? How is it inherited? Ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTC) deficiency ...
... i. Arginine levels will be elevated when protein has been consumed for example Since arginine is an intermediary in the urea cycle, it also increases urea production by itself 14. What is the most common defect in the urea cycle? How is it inherited? Ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTC) deficiency ...
Лекция 3
... of air pollution causes growth retardation and developmental processes, the growing disharmony due increase of fat deposition, and low concentrations of harmful substances activate the processes of acceleration. Comparison of anthropometric data in children showed that height, weight and chest circu ...
... of air pollution causes growth retardation and developmental processes, the growing disharmony due increase of fat deposition, and low concentrations of harmful substances activate the processes of acceleration. Comparison of anthropometric data in children showed that height, weight and chest circu ...
1A. Growing Plants - The Royal Society of Chemistry
... plant’s food requirements but while this is not strictly wrong it does not indicate what happens in reality. Potassium metal for example will react with air and moisture and has to be kept under oil. So potassium as the metal element is not the material to put on your indoor plants! Yellow phosphoru ...
... plant’s food requirements but while this is not strictly wrong it does not indicate what happens in reality. Potassium metal for example will react with air and moisture and has to be kept under oil. So potassium as the metal element is not the material to put on your indoor plants! Yellow phosphoru ...
Chlorine Dioxide Gas Sterilization
... Actually, chlorine dioxide is an environmentally preferred alternative to elemental chlorine. When chlorine reacts with organic matter, undesirable pollutants such as dioxins and bio-accumulative toxic substances are produced. Thus, the EPA supports the substitution of chlorine dioxide for chlorine ...
... Actually, chlorine dioxide is an environmentally preferred alternative to elemental chlorine. When chlorine reacts with organic matter, undesirable pollutants such as dioxins and bio-accumulative toxic substances are produced. Thus, the EPA supports the substitution of chlorine dioxide for chlorine ...
Poisoning with metals, metalloids and their derivates.
... Clinical features • Ingestion of metallic mercury is usually with severe systemic effects as metalic Mercury is poorly absorbed from the GI tract. • May cause- irritant gastroenteritis with corrosive ulceration bloody diarrhea, and abdominal cramps and may lead to circulatory collaps and shock. • M ...
... Clinical features • Ingestion of metallic mercury is usually with severe systemic effects as metalic Mercury is poorly absorbed from the GI tract. • May cause- irritant gastroenteritis with corrosive ulceration bloody diarrhea, and abdominal cramps and may lead to circulatory collaps and shock. • M ...
Document
... Environmental limitations to N fixation • Nutrient limitation (e.g., P, Mo, Fe, S) – These elements may be the ultimate controls over N supply and NPP ...
... Environmental limitations to N fixation • Nutrient limitation (e.g., P, Mo, Fe, S) – These elements may be the ultimate controls over N supply and NPP ...
File
... 2. When nitrogen dioxide is bubbled through water it produces nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide. What are the states of matter of nitrogen dioxide, nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide? ...
... 2. When nitrogen dioxide is bubbled through water it produces nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide. What are the states of matter of nitrogen dioxide, nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide? ...
Carbon moves from plants and animals to the ground.
... amount of warm, tropical, shallow oceans on the planet because this is where prolific limestone-producing organisms such as corals live. The carbon can be released back to the atmosphere if the limestone melts or is metamorphosed in a subduction zone. ...
... amount of warm, tropical, shallow oceans on the planet because this is where prolific limestone-producing organisms such as corals live. The carbon can be released back to the atmosphere if the limestone melts or is metamorphosed in a subduction zone. ...
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning is the illness resulting from the toxic effect of Nitrogen (II) oxide. It usually occurs after the inhalation of the gas beyond the threshold limit value.Nitrogen (II) oxide is reddish-brown with very a sharp, harsh smell at high concentrations. It is colourless and odourless at lower concentration but yet harmful. Nitrogen dioxide poisoning depends on the duration, frequency and intensity of exposure.Nitrogen (II) oxide is an irritant of the mucous membrane linked with other air pollutant that causes pulmonary diseases such as OLD, asthma, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sometimes Acute exacerbation of COPD and in fatal cases, deaths.Its poor solubility in water enhances its passage and its ability to pass through the moist oral mucosa of the respiratory tract.Like most toxic gases, the dose inhaled determines the toxicity on the respiratory tract. Occupational exposures constitute the highest risk of toxicity and domestic exposure is uncommon. Prolonged exposure to low concentration of the gas may have lethal effects, as can short-term exposure to high concentrations like Chlorine gas poisoning. It is one of the major air pollutant capable of causing severe heath hazards such as Coronary artery disease as well as Stroke.Nitrogen (II) oxide is often released into the environment as a byproduct of fuel combustion but rarely released by Spontaneous combustion. Known sources of Nitrogen gas poisoning includes automobile exhaust, Power stations, The toxicity may also results from non-combustible sources such as the one released from anaerobic fermentation of food grains and Anaerobic digestion of Biodegradable waste.The WHO developed a global recommendation limiting exposures less than 20 part per billion for chronic exposure and value less 100ppb for one hour for acute exposure, using Nitrogen (II)oxide as a marker for other pollutant from fuel combustions. The standardss also based on the concentration of Nitrogen (II) oxide that show a significant and profound effects on the function of the pulmonary of asthmatic patients.Historically, some states in the U.S including Chicago and L.A have high levels of Nitrogen (II) oxide but the EPA set a standard values less than 100 ppb for one hour exposure and less than 53 ppb for chronic exposure.