Lecture 38 - Amino Acid Metabolism 1
... by plants and bacteria 4. What are examples of nitrogen fixation and assimilation in real life? Natural fertilizers can be used in organic farming to reduce the dependence on industrial sources of nitrogen. By plowing under the leguminous plants, the nitrogen contained in the plants is released into ...
... by plants and bacteria 4. What are examples of nitrogen fixation and assimilation in real life? Natural fertilizers can be used in organic farming to reduce the dependence on industrial sources of nitrogen. By plowing under the leguminous plants, the nitrogen contained in the plants is released into ...
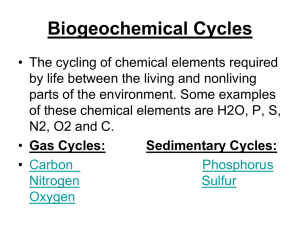
Biogeochemical Cycles
... • In most ecosystems nitrogen is primarily stored in living and dead organic matter. This organic nitrogen is converted into inorganic forms when it re-enters the biogeochemical cycle via decomposition. Decomposers, found in the upper soil layer, chemically modify the nitrogen found in organic matte ...
... • In most ecosystems nitrogen is primarily stored in living and dead organic matter. This organic nitrogen is converted into inorganic forms when it re-enters the biogeochemical cycle via decomposition. Decomposers, found in the upper soil layer, chemically modify the nitrogen found in organic matte ...
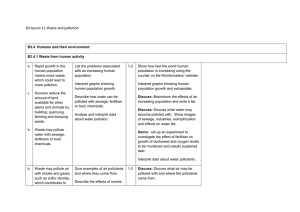
B3 lesson 11 Waste and pollution B3.4 Humans and their
... growth of duckweed and oxygen levels and make conclusions. Activity: Show images of how land is used or damaged by man and the effects of pollution – make a list. Discuss: Discuss the sources and effects of toxic chemicals; what pesticides and herbicides are used for. How might these affect life in ...
... growth of duckweed and oxygen levels and make conclusions. Activity: Show images of how land is used or damaged by man and the effects of pollution – make a list. Discuss: Discuss the sources and effects of toxic chemicals; what pesticides and herbicides are used for. How might these affect life in ...
Living organisms require between 30 to 40 elements for their normal
... The atmosphere contains 79% of nitrogen, however the majority of organisms can not use (or synthesise) this type of nitrogen. First there must be a change from nitrogen into nitrogen compounds, which are used by plants to build up proteins. Animals consume nitrogen by feeding on plant tissues where ...
... The atmosphere contains 79% of nitrogen, however the majority of organisms can not use (or synthesise) this type of nitrogen. First there must be a change from nitrogen into nitrogen compounds, which are used by plants to build up proteins. Animals consume nitrogen by feeding on plant tissues where ...
Intermediate 1 Chemistry
... Elements are present in the diet and in the body as chemical compounds and not as the free elements. Essential compounds include carbohydrates, fats and proteins. More than 60% of body weight is made up of water. Minerals supply the body with small quantities of calcium for bones and teeth, ...
... Elements are present in the diet and in the body as chemical compounds and not as the free elements. Essential compounds include carbohydrates, fats and proteins. More than 60% of body weight is made up of water. Minerals supply the body with small quantities of calcium for bones and teeth, ...
Pulmonary Intoxicants
... Phosgene dissolves slowly in water to form carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid (HCl). In contact with the moist mucosa the HCl causes a transient irritation of the eyes, nose, sinuses, and throat. It can also irritate the upper airway and bronchi, causing a dry cough. However, the primary damage fr ...
... Phosgene dissolves slowly in water to form carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid (HCl). In contact with the moist mucosa the HCl causes a transient irritation of the eyes, nose, sinuses, and throat. It can also irritate the upper airway and bronchi, causing a dry cough. However, the primary damage fr ...
Cycles of Matter
... • Summarize the steps of the water cycle in a diagram. • Explain how carbon and oxygen are cycled through an ecosystem in the carbon cycle. • Define the steps in the nitrogen cycle. • Summarize the 3 major conversions of nitrogen in the nitrogen cycle. • Be able to define the steps and know how one ...
... • Summarize the steps of the water cycle in a diagram. • Explain how carbon and oxygen are cycled through an ecosystem in the carbon cycle. • Define the steps in the nitrogen cycle. • Summarize the 3 major conversions of nitrogen in the nitrogen cycle. • Be able to define the steps and know how one ...
Exploring Nitrogen Fixing, Chemo heterotrophic Oligophiles from
... *Corresponding author: Leena Pathak, H.P.T.Arts and R.Y.K.Science College, Nashik, Maharashtra, India, E-mail: [email protected] ...
... *Corresponding author: Leena Pathak, H.P.T.Arts and R.Y.K.Science College, Nashik, Maharashtra, India, E-mail: [email protected] ...
37.3 Plants Nutrition Often Involves Other Relationship with Other
... • Legume-Rhizobium relationships make more usable nitrogen for plants than all industrial fertilizers. The mutualism provides the correct amount of nitrogen at the right time without the cost of the farmer. This is a form of nitrogen fixation which significantly reduces spending on fertilizers ...
... • Legume-Rhizobium relationships make more usable nitrogen for plants than all industrial fertilizers. The mutualism provides the correct amount of nitrogen at the right time without the cost of the farmer. This is a form of nitrogen fixation which significantly reduces spending on fertilizers ...
Calibrating Standard Conductivity
... However, we make no warranty of merchantability, or fitness for any particular use, or any other warranty, express or implied, with respect to this information, and we assume no liability resulting from the use of this information. Users should make their own investigations to determine the suitabil ...
... However, we make no warranty of merchantability, or fitness for any particular use, or any other warranty, express or implied, with respect to this information, and we assume no liability resulting from the use of this information. Users should make their own investigations to determine the suitabil ...
2.2 PPT – Nutrient Cycles
... wind, water and freezing release the phosphates. Uptake: plants suck up PO43-, then are eaten by animals. Decomposition: Bacteria break down organic matter & phosphorous is returned to soil. Geologic Uplift: when rocks under the ground are ...
... wind, water and freezing release the phosphates. Uptake: plants suck up PO43-, then are eaten by animals. Decomposition: Bacteria break down organic matter & phosphorous is returned to soil. Geologic Uplift: when rocks under the ground are ...
Nitrogen in Lakes
... If the C:N ration is > 8:1 N may be limiting and heterocyst formation is induced [conversely a negative feedback system exists in that high concentrations of NO3- or NH4+ inhibit nitrogenase synthesis bringing about a reduction in heterocysts in the population. Nutrition and nitrogenase flow through ...
... If the C:N ration is > 8:1 N may be limiting and heterocyst formation is induced [conversely a negative feedback system exists in that high concentrations of NO3- or NH4+ inhibit nitrogenase synthesis bringing about a reduction in heterocysts in the population. Nutrition and nitrogenase flow through ...
Document
... been used in the past 50 years than were used in the entire previous history of the ...
... been used in the past 50 years than were used in the entire previous history of the ...
MSDS Mascou-Oil
... HAZARDS OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS : Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide can be found in the combustion products of this product and other forms of hydrocarbon combustion. Carbon monoxide in moderate concentrations can cause symptoms of headache, nausea, vomiting, increased cardiac output and confusion. ...
... HAZARDS OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS : Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide can be found in the combustion products of this product and other forms of hydrocarbon combustion. Carbon monoxide in moderate concentrations can cause symptoms of headache, nausea, vomiting, increased cardiac output and confusion. ...
Nitrogen Cycle Power Point
... A “cycled” aquarium is one that has an established population of the bacteria that convert ammonium to nitrite and nitrite to nitrate. ...
... A “cycled” aquarium is one that has an established population of the bacteria that convert ammonium to nitrite and nitrite to nitrate. ...
Biocrusts role on nitrogen cycle and microbial communities from
... Biocrusts are distributed in arid areas widely covering most of the soil surface and playing an essential role in the functioning of nitrogen cycle. The absence of biocrust coverage might affect the soil nitrogen content and the quantity and diversity of microbial communities in underlying biocrust ...
... Biocrusts are distributed in arid areas widely covering most of the soil surface and playing an essential role in the functioning of nitrogen cycle. The absence of biocrust coverage might affect the soil nitrogen content and the quantity and diversity of microbial communities in underlying biocrust ...
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning is the illness resulting from the toxic effect of Nitrogen (II) oxide. It usually occurs after the inhalation of the gas beyond the threshold limit value.Nitrogen (II) oxide is reddish-brown with very a sharp, harsh smell at high concentrations. It is colourless and odourless at lower concentration but yet harmful. Nitrogen dioxide poisoning depends on the duration, frequency and intensity of exposure.Nitrogen (II) oxide is an irritant of the mucous membrane linked with other air pollutant that causes pulmonary diseases such as OLD, asthma, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sometimes Acute exacerbation of COPD and in fatal cases, deaths.Its poor solubility in water enhances its passage and its ability to pass through the moist oral mucosa of the respiratory tract.Like most toxic gases, the dose inhaled determines the toxicity on the respiratory tract. Occupational exposures constitute the highest risk of toxicity and domestic exposure is uncommon. Prolonged exposure to low concentration of the gas may have lethal effects, as can short-term exposure to high concentrations like Chlorine gas poisoning. It is one of the major air pollutant capable of causing severe heath hazards such as Coronary artery disease as well as Stroke.Nitrogen (II) oxide is often released into the environment as a byproduct of fuel combustion but rarely released by Spontaneous combustion. Known sources of Nitrogen gas poisoning includes automobile exhaust, Power stations, The toxicity may also results from non-combustible sources such as the one released from anaerobic fermentation of food grains and Anaerobic digestion of Biodegradable waste.The WHO developed a global recommendation limiting exposures less than 20 part per billion for chronic exposure and value less 100ppb for one hour for acute exposure, using Nitrogen (II)oxide as a marker for other pollutant from fuel combustions. The standardss also based on the concentration of Nitrogen (II) oxide that show a significant and profound effects on the function of the pulmonary of asthmatic patients.Historically, some states in the U.S including Chicago and L.A have high levels of Nitrogen (II) oxide but the EPA set a standard values less than 100 ppb for one hour exposure and less than 53 ppb for chronic exposure.