2 - UCSD Math Department
... Note that a · n = b · n = 0 as it should be. Parametric equations of a plane If (x0 , y0 , z0 ) is a point in the plane and a = (a1 , a2 , a3 ) and b = (b1 , b2 , b3 ) are two vectors in the plane then any point in the plane is given by (x, y, z) = (x0 , y0 , z0 )+(a1 , a2 , a3 ) t+(b1 , b2 , b3 ) s ...
... Note that a · n = b · n = 0 as it should be. Parametric equations of a plane If (x0 , y0 , z0 ) is a point in the plane and a = (a1 , a2 , a3 ) and b = (b1 , b2 , b3 ) are two vectors in the plane then any point in the plane is given by (x, y, z) = (x0 , y0 , z0 )+(a1 , a2 , a3 ) t+(b1 , b2 , b3 ) s ...
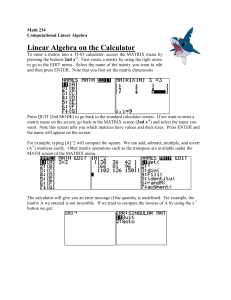
Matrix Algebra Tutorial
... V1 ×V2 = (V1yV2 z −V1zV2 y ,V1zV2 x −V1xV2 z ,V1xV2 y −V1yV2 x ) direction perpendicular to the two original vectors (u) and with a magnitude equal to the area of ...
... V1 ×V2 = (V1yV2 z −V1zV2 y ,V1zV2 x −V1xV2 z ,V1xV2 y −V1yV2 x ) direction perpendicular to the two original vectors (u) and with a magnitude equal to the area of ...
6301 (Discrete Mathematics for Computer Scientists)
... arguments, modular arithmetic and linear algebra. Recommended Texts A relevant book is Kenneth H Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and its Applications, Third Edition, McGraw-Hill, 1995. Detailed Syllabus Foundations. Sets theoretic notation. Relations, in particular equivalence relations. Injections, sur ...
... arguments, modular arithmetic and linear algebra. Recommended Texts A relevant book is Kenneth H Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and its Applications, Third Edition, McGraw-Hill, 1995. Detailed Syllabus Foundations. Sets theoretic notation. Relations, in particular equivalence relations. Injections, sur ...
Slides - DidaWiki - Università di Pisa
... Relative distances are (approximately) preserved Of all m n matrices of rank k, Ak is the best approximation to A wrt the following measures: ...
... Relative distances are (approximately) preserved Of all m n matrices of rank k, Ak is the best approximation to A wrt the following measures: ...
Isometries of the plane
... a matrix AF it will be an orthogonal matrix, and as such it possesses a lot of nice properties, as is well known from linear algebra. For instance we have that T A−1 F = AF from which it follows that (det AF )2 = det(AF ) det(ATF ) = det(AF ATF ) = det(I) = 1 and so, any orthogonal matrix has determ ...
... a matrix AF it will be an orthogonal matrix, and as such it possesses a lot of nice properties, as is well known from linear algebra. For instance we have that T A−1 F = AF from which it follows that (det AF )2 = det(AF ) det(ATF ) = det(AF ATF ) = det(I) = 1 and so, any orthogonal matrix has determ ...
Solution - Math-UMN
... Solution: The cross product of the vectors is orthogonal to both of them. h0, 1, 2i × h1, −1, 2i = h0, 2, −1i ...
... Solution: The cross product of the vectors is orthogonal to both of them. h0, 1, 2i × h1, −1, 2i = h0, 2, −1i ...
2.5 Multiplication of Matrices Outline Multiplication of
... However, multiplication of matrices is not done entrywise. It turns out that when we are dealing with data matrices, entrywise multiplication often does not give us the information we are looking for. Given two matrices A and B, we write AB for the matrix A × B. To multiply two matrices, the number ...
... However, multiplication of matrices is not done entrywise. It turns out that when we are dealing with data matrices, entrywise multiplication often does not give us the information we are looking for. Given two matrices A and B, we write AB for the matrix A × B. To multiply two matrices, the number ...
12 How to Compute the SVD
... We saw earlier that the nonzero singular values of A are given by the square roots of the nonzero eigenvalues of either A∗ A or AA∗ . However, computing the singular values in this way is usually not stable (cf. solution of the normal equations). Recall the strategy for finding the eigenvalues of a ...
... We saw earlier that the nonzero singular values of A are given by the square roots of the nonzero eigenvalues of either A∗ A or AA∗ . However, computing the singular values in this way is usually not stable (cf. solution of the normal equations). Recall the strategy for finding the eigenvalues of a ...
matrices - ginawalker2525
... BIG BOOK OF MATRICES • What is a Matrix? • Adding & Subtracting • Multiply by a Scalar • Multiplication ...
... BIG BOOK OF MATRICES • What is a Matrix? • Adding & Subtracting • Multiply by a Scalar • Multiplication ...