
A T y
... that assigns to each pair of vectors x and y in V a real number satisfying the following conditions:
Ⅰ. ≥0 with equality if and only if x=0.
Ⅱ. = for all x and y in V.
...
... that assigns to each pair of vectors x and y in V a real number
Course notes APPM 5720 — PG Martinsson February 08, 2016 This
... the least squares sense making sure to enforce C∗ = C. Now consider replacing step (3) with the calculation of an ’econ’ SVD on Y. Let Q contain the first k left singular vectors of our factorization and proceed as normal. This will yield a substantially overdetermined system. The above procedure re ...
... the least squares sense making sure to enforce C∗ = C. Now consider replacing step (3) with the calculation of an ’econ’ SVD on Y. Let Q contain the first k left singular vectors of our factorization and proceed as normal. This will yield a substantially overdetermined system. The above procedure re ...
Math 200 Spring 2010 March 12 Definition. An n by n matrix E is
... k nonzero rows), what is the dimension of a) ker(A)? b) the image of A? c) the column space of A? 4. Suppose that M is an n by n matrix that is row-equivalent to In . a) Is M invertible? Explain. b) What is ker(M )? c) What is the image of M ? d) Does M~x = ~b have a solution for every ~b ∈ Rn ? e) ...
... k nonzero rows), what is the dimension of a) ker(A)? b) the image of A? c) the column space of A? 4. Suppose that M is an n by n matrix that is row-equivalent to In . a) Is M invertible? Explain. b) What is ker(M )? c) What is the image of M ? d) Does M~x = ~b have a solution for every ~b ∈ Rn ? e) ...
Solutions for Midterm I - Stony Brook Math Department
... counterclockwise rotation by 45◦ . Then T = R ◦ P . Let A and B be standard matrices of P and R respectively. Then the standard matrix of T is BA. Let us evaluate matrices A and B. Matrix A consists of two columns representing the coordinates of the images of the standard basis vectors e1 , e2 under ...
... counterclockwise rotation by 45◦ . Then T = R ◦ P . Let A and B be standard matrices of P and R respectively. Then the standard matrix of T is BA. Let us evaluate matrices A and B. Matrix A consists of two columns representing the coordinates of the images of the standard basis vectors e1 , e2 under ...
Matrices - what is a matrix
... Note that whereas all the non-diagonal elements are zero, the elements on the leading diagonal can be any number including zero. An identity matrix, sometimes called a unit matrix, is a diagonal matrix with all its diagonal elements equal to 1. The following are identity matrices. ...
... Note that whereas all the non-diagonal elements are zero, the elements on the leading diagonal can be any number including zero. An identity matrix, sometimes called a unit matrix, is a diagonal matrix with all its diagonal elements equal to 1. The following are identity matrices. ...
Worksheet, March 14th
... skew-symmetric). Show that for all x ∈ R3 and c ∈ R, kx + cAxk ≥ kxk, where k · k is the Euclidean norm on R3 . Solution: First we claim that for any 3 × 3 matrix A and any vector x ∈ R3 , hx, Axi = hAT x, xi. You should check this for yourself.3 Then since our A is skew-symmetric, we have hx, Axi = ...
... skew-symmetric). Show that for all x ∈ R3 and c ∈ R, kx + cAxk ≥ kxk, where k · k is the Euclidean norm on R3 . Solution: First we claim that for any 3 × 3 matrix A and any vector x ∈ R3 , hx, Axi = hAT x, xi. You should check this for yourself.3 Then since our A is skew-symmetric, we have hx, Axi = ...
Math 480 Notes on Orthogonality The word orthogonal is a synonym
... We now consider in detail the question of why every subspace of Rn has a basis. Theorem 3. If S is a subspace of Rn , then S has a basis containing at most n elements. Equivalently, dim(S) 6 n. Proof. First, recall that every set of n + 1 (or more) vectors in Rn is linearly dependent, since they for ...
... We now consider in detail the question of why every subspace of Rn has a basis. Theorem 3. If S is a subspace of Rn , then S has a basis containing at most n elements. Equivalently, dim(S) 6 n. Proof. First, recall that every set of n + 1 (or more) vectors in Rn is linearly dependent, since they for ...
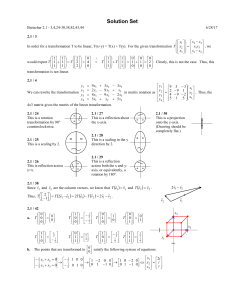
Solution Set - Harvard Math Department
... a. We can show that transformation T is linear by finding a matrix of T. Recalling the definition of matrix multiplication, the formula for T is similar to the matrix multiplication of a row vector by a column vector. In fact, the row vector is ...
... a. We can show that transformation T is linear by finding a matrix of T. Recalling the definition of matrix multiplication, the formula for T is similar to the matrix multiplication of a row vector by a column vector. In fact, the row vector is ...
M.E. 530.646 Problem Set 1 [REV 1] Rigid Body Transformations
... the multiplication of a polynomial by a scalar. For example, let x1 = s2 + 3s + 1, and x2 = s5 , then x1 + x2 = s5 + s2 + 3s + 1. b. Show that xi = si−1 , i = 1, . . . , n form a basis for the LVS. (Hint: show linear independence by making an argument about the expression p0 + p1 s1 + · · · pn−1 sn ...
... the multiplication of a polynomial by a scalar. For example, let x1 = s2 + 3s + 1, and x2 = s5 , then x1 + x2 = s5 + s2 + 3s + 1. b. Show that xi = si−1 , i = 1, . . . , n form a basis for the LVS. (Hint: show linear independence by making an argument about the expression p0 + p1 s1 + · · · pn−1 sn ...
MATLAB Tutorial
... • www.mathworks.com/help/techdoc/ref/funcalpha.html • If everything else fails, google it! ...
... • www.mathworks.com/help/techdoc/ref/funcalpha.html • If everything else fails, google it! ...
Elementary Linear Algebra
... solve systems of linear equations using Gaussian elimination, matrix, and determinant techniques; compute determinants of all orders; perform all algebraic operations on matrices and be able to construct their inverses, adjoints, transposes; determine the rank of a matrix and relate this to systems ...
... solve systems of linear equations using Gaussian elimination, matrix, and determinant techniques; compute determinants of all orders; perform all algebraic operations on matrices and be able to construct their inverses, adjoints, transposes; determine the rank of a matrix and relate this to systems ...
54 Quiz 3 Solutions GSI: Morgan Weiler Problem 0 (1 pt/ea). (a
... (a). True or false: if A and B are invertible, then AB is invertible. Solution: This problem is going to be taken off the quiz, because I did not specify the dimensions of A and B. (b). True or false: if A and B are n × n matrices and AB is invertible, A is invertible. Solution: True – this was a ho ...
... (a). True or false: if A and B are invertible, then AB is invertible. Solution: This problem is going to be taken off the quiz, because I did not specify the dimensions of A and B. (b). True or false: if A and B are n × n matrices and AB is invertible, A is invertible. Solution: True – this was a ho ...

















![M.E. 530.646 Problem Set 1 [REV 1] Rigid Body Transformations](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017245963_1-2f60978169e1255dbeaf6de62def96e1-300x300.png)
![1. Let A = 1 −1 1 1 0 −1 2 1 1 . a) [2 marks] Find the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005284378_1-9abef9398f6a7d24059a09f56fe1ac13-300x300.png)



