Chapter 16: Section 1 The World of Cells
... Why are cells important? They help us do what we do Breakdown food Move Grow Reproduce ...
... Why are cells important? They help us do what we do Breakdown food Move Grow Reproduce ...
Cells are the units of structure and function of an organism
... The diffusion of water through a membrane. ...
... The diffusion of water through a membrane. ...
Passive Vs. Active Transport
... What is osmosis? • Osmosis: The diffusion of water through a cell membrane. • Water will leave a cell when there is not the same amount of water inside and outside the cell. • When plant cells lose water the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall. ...
... What is osmosis? • Osmosis: The diffusion of water through a cell membrane. • Water will leave a cell when there is not the same amount of water inside and outside the cell. • When plant cells lose water the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall. ...
Label a Plant Cell (Up to 16yrs old / GCSE)
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired
... individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
... individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
Unit 3 (Cells and Transport) Review Guide
... the scope of the information presented in lecture and your text. These review items are meant to be indicative of the possible material one might expect to see on the exam. With a set time limit of one class period, however, it is not possible to test your knowledge regarding all of the subject mate ...
... the scope of the information presented in lecture and your text. These review items are meant to be indicative of the possible material one might expect to see on the exam. With a set time limit of one class period, however, it is not possible to test your knowledge regarding all of the subject mate ...
Cytology ch. 7 Study
... 2. 2. Make sure you know all of the cell part locations in the cell. THESE ARE THE DRAWINGS YOU MADE ...
... 2. 2. Make sure you know all of the cell part locations in the cell. THESE ARE THE DRAWINGS YOU MADE ...
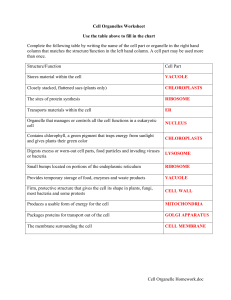
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more ...
... Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more ...
Homework 3.2 : Cell Organelles - BIOLOGY 2013-2014
... 16. Which cell part is a maze of folded membranes where proteins and lipids are produced? _______________________________________________________________ 17. Which cell part converts food into energy that is usable by a cell? _______________________________________________________________ ...
... 16. Which cell part is a maze of folded membranes where proteins and lipids are produced? _______________________________________________________________ 17. Which cell part converts food into energy that is usable by a cell? _______________________________________________________________ ...
Why Are Cells So Small?
... interior. The size and shape of a cell determines how well this process takes place and whether or not the cell will survive. ...
... interior. The size and shape of a cell determines how well this process takes place and whether or not the cell will survive. ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • These organelles receive materials from the ER and send them to other parts or outside of the cell. ...
... • These organelles receive materials from the ER and send them to other parts or outside of the cell. ...
Looking Inside Cells: Organelles
... • These organelles receive materials from the ER and send them to other parts or outside of the cell. ...
... • These organelles receive materials from the ER and send them to other parts or outside of the cell. ...
Cell - WordPress.com
... -(ER) is collectively a continuous network of outer membrane of the nuclear envelop -Granular/rough endoplasmic reticulum involves in packaging proteins -Agranular/smooth ER lacks ribosome, is the site of lipid, carbohydrate…..synthesis and also detoxifies ...
... -(ER) is collectively a continuous network of outer membrane of the nuclear envelop -Granular/rough endoplasmic reticulum involves in packaging proteins -Agranular/smooth ER lacks ribosome, is the site of lipid, carbohydrate…..synthesis and also detoxifies ...
Cell Wall (Plants Only) Chloroplasts (Plants Only)
... To learn more about plant cell structure, Go to Nelson Science ...
... To learn more about plant cell structure, Go to Nelson Science ...
Cell City - TeacherWeb
... Vacuole Cytoplasm Written portion completed _________(15) Each structure in your cell city is compared with a cell structure and a reason why it is a good representation of that structure. (Example: The water tower is like the vacuole because it stores water.) This is to be written on a separate she ...
... Vacuole Cytoplasm Written portion completed _________(15) Each structure in your cell city is compared with a cell structure and a reason why it is a good representation of that structure. (Example: The water tower is like the vacuole because it stores water.) This is to be written on a separate she ...
B-3 Notes
... • The ‘brain’ of the cell. It controls the cell’s activities. It also contains all of the genetic material of the cell. The nucleus is responsible for growth and reproduction of cells. (Cell splitting). It is a large circular object in a cell that is easily seen in a compound microscope. • Vacuoles ...
... • The ‘brain’ of the cell. It controls the cell’s activities. It also contains all of the genetic material of the cell. The nucleus is responsible for growth and reproduction of cells. (Cell splitting). It is a large circular object in a cell that is easily seen in a compound microscope. • Vacuoles ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑