CELLS POWERPOINT
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are basic units of structure and function in living things • New cells come from existing cells ...
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are basic units of structure and function in living things • New cells come from existing cells ...
cell organelle WS 2014
... in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. Each organelle will be used only once. ...
... in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. Each organelle will be used only once. ...
BIO Cell Color Key
... Cells You need to COLOR and LABEL the organelles (parts) of EACH cell. Attach the diagrams in your notebook, each on their own page. You will be writing notes beside the diagrams so put the picture in the middle so you have room to write. These should take up THREE separate pages. Use the internet O ...
... Cells You need to COLOR and LABEL the organelles (parts) of EACH cell. Attach the diagrams in your notebook, each on their own page. You will be writing notes beside the diagrams so put the picture in the middle so you have room to write. These should take up THREE separate pages. Use the internet O ...
The Cell PPT File
... • Are not part of the cell structure (e.g. melanin in skin / haemoglobin in RBC) • If the inclusion is a liquid that is capable of mixing with the cytoplasm, then it is surrounded by a membrane and known as a vacuole. Vacuoles are like a storage compartment. Rare in animal cells, more common in plan ...
... • Are not part of the cell structure (e.g. melanin in skin / haemoglobin in RBC) • If the inclusion is a liquid that is capable of mixing with the cytoplasm, then it is surrounded by a membrane and known as a vacuole. Vacuoles are like a storage compartment. Rare in animal cells, more common in plan ...
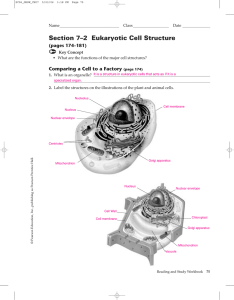
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... 25. Biologist Lynn Margulis has suggested that mitochondria and chloroplasts are descendants of what kind of organisms? They are descendants of ancient prokaryotes. ...
... 25. Biologist Lynn Margulis has suggested that mitochondria and chloroplasts are descendants of what kind of organisms? They are descendants of ancient prokaryotes. ...
The following is a glossary of plant cell anatomy terms.
... functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane photosynthesis - a process in which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugars and starches), oxygen and water. Chlorophyll o ...
... functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane photosynthesis - a process in which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugars and starches), oxygen and water. Chlorophyll o ...
4-2 Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell
... Both types of proteins form channels for nutrients to travel and also give cell its selectively permeable status. Both the lipids and the proteins help in structure and support of the cell. ...
... Both types of proteins form channels for nutrients to travel and also give cell its selectively permeable status. Both the lipids and the proteins help in structure and support of the cell. ...
Cell Organelle Powerpoint
... Function: site of photosynthesis Double membrane Thylakoid disks in stacks (grana); stroma (fluid) Contains chlorophylls (pigments) for capturing ...
... Function: site of photosynthesis Double membrane Thylakoid disks in stacks (grana); stroma (fluid) Contains chlorophylls (pigments) for capturing ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents
... Proteins are produced by ribosomes which normally attach to the ER. Ions, water, and food are stored in vacuoles in the ER. There are 5 major animal tissues including epithelial tissue which lines cavities. If a disaccharide is split, 2 monosaccharides and 1 water molecule are produced. Monosacchari ...
... Proteins are produced by ribosomes which normally attach to the ER. Ions, water, and food are stored in vacuoles in the ER. There are 5 major animal tissues including epithelial tissue which lines cavities. If a disaccharide is split, 2 monosaccharides and 1 water molecule are produced. Monosacchari ...
Assignment # 35 Cell Organelles - Mr. Le`s Living Environment
... These organelles are quite small, made up of 50 proteins and several long RNAs intricately bound together. Ribosomes have no membrane. Ribosomes disassemble into two subunits when not actively synthesizing protein. Mitochondria Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration, and generally are the ...
... These organelles are quite small, made up of 50 proteins and several long RNAs intricately bound together. Ribosomes have no membrane. Ribosomes disassemble into two subunits when not actively synthesizing protein. Mitochondria Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration, and generally are the ...
Science Lesson Plan
... 1. The students will read as and class or in pairs pages 26 and 27 in the text book. 2. Teacher will discuss. 3. We will, as a class, review the definition of cell unicellular and multi cellular and define the parts of the cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuoles. (Notes) 4. Students wi ...
... 1. The students will read as and class or in pairs pages 26 and 27 in the text book. 2. Teacher will discuss. 3. We will, as a class, review the definition of cell unicellular and multi cellular and define the parts of the cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuoles. (Notes) 4. Students wi ...
Looking Inside Cells
... between the cell membrane and the nucleus gel-like fluid B. Made up of a clear, thick, _____________________________________________ C. The fluid in the cytoplasm is __________________________________________ constantly moving D. Mitochondria “powerhouses” of the cell 1. Mitochondria are known as th ...
... between the cell membrane and the nucleus gel-like fluid B. Made up of a clear, thick, _____________________________________________ C. The fluid in the cytoplasm is __________________________________________ constantly moving D. Mitochondria “powerhouses” of the cell 1. Mitochondria are known as th ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
... microscope to really see it. If you look at a plant cell under a microscope you can see that it has tiny green granules in sacs. These granules are green because they contain the pigment chlorophyll. This These are baby squirrel monkeys in a tree. pigment absorbs energy from sunlight. This energy Ca ...
... microscope to really see it. If you look at a plant cell under a microscope you can see that it has tiny green granules in sacs. These granules are green because they contain the pigment chlorophyll. This These are baby squirrel monkeys in a tree. pigment absorbs energy from sunlight. This energy Ca ...
worksheet 7-2
... c. They produce proteins that are modified by the ER. d. They contain enzymes that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Vacuoles (page 179) 17. What are vacuoles? ...
... c. They produce proteins that are modified by the ER. d. They contain enzymes that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Vacuoles (page 179) 17. What are vacuoles? ...
CELL MEMBRANE: Structure and Function
... Osmosis- the movement of water from an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. ...
... Osmosis- the movement of water from an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. ...
GCPS_05_SC_LS_T4 (_GCPS_05_SC_LS_T4)
... D. snails, whales, sunfish 8. Which object would best demonstrate how roots function in the soil? A. rock B. sponge C. mirror D. jar of water 9. Which is a characteristic of reptiles? A. They have slimy skin. B. They use lungs to breathe. C. They are invertebrates. D. They maintain a constant body t ...
... D. snails, whales, sunfish 8. Which object would best demonstrate how roots function in the soil? A. rock B. sponge C. mirror D. jar of water 9. Which is a characteristic of reptiles? A. They have slimy skin. B. They use lungs to breathe. C. They are invertebrates. D. They maintain a constant body t ...
Cell Organelle Functions · Nucleus (both) = the “control center” for
... Cell wall (only plants) = found only in plants, the cell wall is a rigid (tough) layer of protection for the cell due to the harsh environment that plants have to endure o ...
... Cell wall (only plants) = found only in plants, the cell wall is a rigid (tough) layer of protection for the cell due to the harsh environment that plants have to endure o ...
Observing Plasmolysis in Elodea
... All forms of life are composed of only two fundamentally different types of cells. The first type, which include the bacteria and archaeans, is called prokaryotic, Greek for "before the nucleus". The second type of cell, which almost certainly evolved from the prokaryotic cell and makes up the bodie ...
... All forms of life are composed of only two fundamentally different types of cells. The first type, which include the bacteria and archaeans, is called prokaryotic, Greek for "before the nucleus". The second type of cell, which almost certainly evolved from the prokaryotic cell and makes up the bodie ...
Cell Organelles
... Cell Organelles Organelle= “little organ” Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the gel like fluid between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
... Cell Organelles Organelle= “little organ” Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the gel like fluid between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
File
... 1. What is the energy molecule of the cell called? ATP 2. What macromolecule made by plants is "burned" in the mitochondria? GLUCOSE 3. Where is chlorophyll found in the chloroplast? THYLAKOIDS 4. In which part of a plant would you expect to find the most chloroplasts and why? LEAVES – HAVE THE GREA ...
... 1. What is the energy molecule of the cell called? ATP 2. What macromolecule made by plants is "burned" in the mitochondria? GLUCOSE 3. Where is chlorophyll found in the chloroplast? THYLAKOIDS 4. In which part of a plant would you expect to find the most chloroplasts and why? LEAVES – HAVE THE GREA ...
cell organelles and membranes powerpoint
... twisted actin chains (smallest) Function Bears tension ...
... twisted actin chains (smallest) Function Bears tension ...
A Head - School
... Write notes beside each cell to explain how it is adapted for its function. (6 marks) ...
... Write notes beside each cell to explain how it is adapted for its function. (6 marks) ...
Cells Compared to Manhattan Beach, CA
... and even Manhattan Beach, CA. These cells are busy building and breaking down macromolecules. They are at work releasing energy from foods, and then using that energy to make needed cell parts. Together your cells function to make your body operate like Manhattan Beach, CA. Procedure: 1. Use your fl ...
... and even Manhattan Beach, CA. These cells are busy building and breaking down macromolecules. They are at work releasing energy from foods, and then using that energy to make needed cell parts. Together your cells function to make your body operate like Manhattan Beach, CA. Procedure: 1. Use your fl ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑