cscope Specialized Cell Structures ppt notes
... Flattened sacs called cisternae Function: Modifies and packages materials created in the cell for transport (inside or outside of the cell) Analogy ...
... Flattened sacs called cisternae Function: Modifies and packages materials created in the cell for transport (inside or outside of the cell) Analogy ...
Chapter 4
... 2. Which organelles acts as a kind of recycling center for the cell and breaks down old molecules so they can be used again? ...
... 2. Which organelles acts as a kind of recycling center for the cell and breaks down old molecules so they can be used again? ...
The History of the Cell Theory
... • Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts • Chloroplasts contain green pigment called chlorophyll. ...
... • Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts • Chloroplasts contain green pigment called chlorophyll. ...
Cell Growth and Mitosis Notes:
... Cell Growth and Mitosis Notes: What problems does growth cause for cells? The larger a cell becomes… • the more __________ the cell places on its ____________ • more trouble moving enough ___________ and __________ across the ______________. The rate at which ________, ___________, _________, and___ ...
... Cell Growth and Mitosis Notes: What problems does growth cause for cells? The larger a cell becomes… • the more __________ the cell places on its ____________ • more trouble moving enough ___________ and __________ across the ______________. The rate at which ________, ___________, _________, and___ ...
Tour of Cell Organelles - Western Sierra Collegiate Academy
... bodies are made up of cells cells do all the work of life! ...
... bodies are made up of cells cells do all the work of life! ...
Review of the Cell and its Organelles
... oxygen. They are found close to mitochondria and chloroplasts in the cell, and are involved in the production of energy by these organelles. Peroxisomes look much like lysosomes, however peroxisomes are generally bigger than lysosomes and are found surrounding mitochondria and chloroplasts, while ly ...
... oxygen. They are found close to mitochondria and chloroplasts in the cell, and are involved in the production of energy by these organelles. Peroxisomes look much like lysosomes, however peroxisomes are generally bigger than lysosomes and are found surrounding mitochondria and chloroplasts, while ly ...
Title - Angelfire
... 1. Cell shape – without cell walls, the cytoskeleton, especially networks of intermediate filaments, determines the shape of the cell ...
... 1. Cell shape – without cell walls, the cytoskeleton, especially networks of intermediate filaments, determines the shape of the cell ...
CHAPTER 7 A TOUR OF THE CELL
... The smooth ER is rich in enzymes and plays a role in a variety of metabolic processes. Enzymes of smooth ER synthesize lipids, including oils, phospholipids, and steroids. These include the sex hormones of vertebrates and adrenal steroids. In the smooth ER of the liver, enzymes help detoxify p ...
... The smooth ER is rich in enzymes and plays a role in a variety of metabolic processes. Enzymes of smooth ER synthesize lipids, including oils, phospholipids, and steroids. These include the sex hormones of vertebrates and adrenal steroids. In the smooth ER of the liver, enzymes help detoxify p ...
The cell notes - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... inside) Their out membrane stretches (like blowing up a balloon). ...
... inside) Their out membrane stretches (like blowing up a balloon). ...
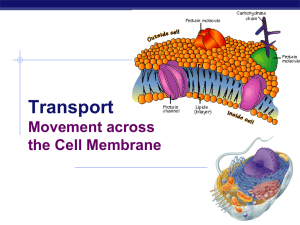
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... Diffusion (passive transport) movement from high low concentration ...
... Diffusion (passive transport) movement from high low concentration ...
Cell Structure & Function Review
... Idea that all living things are made of cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and new cells are produced from existing cells ...
... Idea that all living things are made of cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and new cells are produced from existing cells ...
Cell Membrane
... to make sure the cell stays intact in this environment. What would happen if a cell dissolved in water, like sugar does? Obviously, the cell could not survive in such an environment. So something must protect the cell and allow it to survive in its water-based environment. All cells have a barrier a ...
... to make sure the cell stays intact in this environment. What would happen if a cell dissolved in water, like sugar does? Obviously, the cell could not survive in such an environment. So something must protect the cell and allow it to survive in its water-based environment. All cells have a barrier a ...
Intro to Diffusion - Biology Fall Semester
... • When molecules are equal they are considered to be at equilibrium. 4 of each ...
... • When molecules are equal they are considered to be at equilibrium. 4 of each ...
Under what conditions do cells gain or lose water
... hypotonic to the cell. Water will move into the cell by osmosis. The pressure against the inside of the cell membrane will steadily increase. If the pressure becomes great enough, the cell membrane will burst. A solution is isotonic to the inside of the cell when there is the same concentration of w ...
... hypotonic to the cell. Water will move into the cell by osmosis. The pressure against the inside of the cell membrane will steadily increase. If the pressure becomes great enough, the cell membrane will burst. A solution is isotonic to the inside of the cell when there is the same concentration of w ...
membrane structure and function
... • Tonicity: the ability of a solution to move water – Hypertonic: Greater ability to move H2O; gains water – Hypotonic: Lesser ability to move H2O; loses water – Isotonic: equal ability to move H2O; no net water movement ...
... • Tonicity: the ability of a solution to move water – Hypertonic: Greater ability to move H2O; gains water – Hypotonic: Lesser ability to move H2O; loses water – Isotonic: equal ability to move H2O; no net water movement ...
CELLS
... A sack surrounded by a membrane Temporary storage of materials Often store food, enzymes, wastes, and other materials ...
... A sack surrounded by a membrane Temporary storage of materials Often store food, enzymes, wastes, and other materials ...
cell analog project
... 1. Your group must come up with an analogy that compares the parts of a cell to something you are more familiar with. You must include all the items with a star next to it on the next page that apply to your type of cell and choose enough other cell parts to total eight. Animal cells have 4 starred ...
... 1. Your group must come up with an analogy that compares the parts of a cell to something you are more familiar with. You must include all the items with a star next to it on the next page that apply to your type of cell and choose enough other cell parts to total eight. Animal cells have 4 starred ...
Passive Transport
... If there is a concentration gradient in the solution, the substance will move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Diffusion – movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to low concentration caused by the random motion of particles ...
... If there is a concentration gradient in the solution, the substance will move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Diffusion – movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to low concentration caused by the random motion of particles ...
Cell Transport Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... (concentration gradient) Equilibrium occurs when the concentration of solute (particles) is the same throughout (the particles still move!) ...
... (concentration gradient) Equilibrium occurs when the concentration of solute (particles) is the same throughout (the particles still move!) ...
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
... In pinocytosis (literally "cell drinking"), the plasma membrane forms a kind of harbor that pinches off and moves into the cytoplasm as a vesicle. The vesicle carries primarily water and some solutes. ...
... In pinocytosis (literally "cell drinking"), the plasma membrane forms a kind of harbor that pinches off and moves into the cytoplasm as a vesicle. The vesicle carries primarily water and some solutes. ...
paramecium tetraurelia.
... performed according to the methods reviewed by SONNEBORN(1970). In these experiments, all matjng-type tests were made on “caryonides”, i.e., on clones derived from one product of the first post-conjugal cell division. A caryonide is classified as 0 or E on the basis of its reaction with solely E or ...
... performed according to the methods reviewed by SONNEBORN(1970). In these experiments, all matjng-type tests were made on “caryonides”, i.e., on clones derived from one product of the first post-conjugal cell division. A caryonide is classified as 0 or E on the basis of its reaction with solely E or ...
Cell Analogy Project Exemplar Mini-Essay Your Task from Part V. of
... In the same way that a Cell has parts that make up the cell, a City has parts that make up what it is; but this doesn’t mean each part is as important as the “larger structure.” A cell has parts such as the __________________, __________________, __________________, ________________________, and____ ...
... In the same way that a Cell has parts that make up the cell, a City has parts that make up what it is; but this doesn’t mean each part is as important as the “larger structure.” A cell has parts such as the __________________, __________________, __________________, ________________________, and____ ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... Nerve cell are charged where no other cell in the body is. The reason why nerve cell are different is because they have a rich supply of ions (+/-) both inside and outside the cell’s membrane. The electrochemical impulse is caused by an unequal concentration of positive ions across the membrane. A p ...
... Nerve cell are charged where no other cell in the body is. The reason why nerve cell are different is because they have a rich supply of ions (+/-) both inside and outside the cell’s membrane. The electrochemical impulse is caused by an unequal concentration of positive ions across the membrane. A p ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑